Abstract
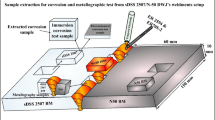
The EV31A magnesium alloy has the potential for use in aerospace and automotive applications. To ensure the longevity of magnesium and its alloys in final applications, it is essential to know how quickly they corrode. An electrochemical approach (Tafel extrapolation and EIS) was used to evaluate the corrosion behaviour of EV31A alloy in various electrolytic mediums, including 0.6 M NaCl, 0.05 M H2SO4, 0.1 M HNO3, and 0.1 M HF. In each electrolytic solution, the stir-cast, T4, and T6 heat-treated samples corroded electrochemically. The as-cast EV31A alloy has superior corrosion resistance than T4 (solutionising) and T6 (solutionising cum age hardened). Because intermetallic precipitates have a large volume percentage in as-cast, it offers excellent corrosion resistance due to micro-galvanic or localised corrosion. In EV31A, chloride and fluoride ions have the same impact as compared with sulphate and nitrate ions. The as-cast EV31A shows a corrosion rate of 0.03 mm/year in solution containing 0.6 M NaCl and 0.1 M HF.
Graphical abstract
The EV31A is analysed in electrolytes such as 0.6 N NaCl, 0.1 N H2SO4, HNO3, and HF. The electrochemical techniques such as Tafel method and EIS used to analysis the rate of corrosion. Stir-cast EV31A Mg alloy shows better corrosion resistance in all test conditions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prasad SVS, Prasad SB, Verma K, Kumar R, Kumar V, Singh S (2022) The role and significance of magnesium in modern day research—a review. J Magnes Alloy 10(1):1–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2021.05.012
Ding Z, Zhao X, Shaw LL (2015) Reaction between LiBH4 and MgH2 induced by high-energy ball milling. J Power Sources 293:236–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.05.079
Yartys VA, Lototskyy MV, Akiba E, Albert R, Antonov VE, Ares JR, Baricco M, Bourgeois N, Buckley CE, Von Colbe JB, Crivello JC (2019) Magnesium based materials for hydrogen-based energy storage: past, present and future Int. J Hydrog Energy 44:7809–7859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.212
Na Z, Zhang Z, Jie D, Li J, Wenjiang D (2013) Selective oxidation behavior of an ignition-proof Mg-Y-Ca-Ce alloy. J Rare Earths 31:1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0721(13)60021-6
Aydin DS, Bayindir Z, Hoseini M, Pekguleryuz MO (2013) The high temperature oxidation and ignition behavior of Mg–Nd alloys part I: the oxidation of dilute alloys. J Alloys Compd 569:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.03.130
Thandalam SK, Ramanathan S, Sundarrajan S (2015) Synthesis, microstructural and mechanical properties of ex situ zircon particles (ZrSiO4) reinforced metal matrix composites (MMCs): a review. J Mater Res Technol 4:333–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2008.12.013
Ouyang L, Chen K, Jiang J, Yang X-S, Zhu M (2020) Hydrogen storage in light-metal based systems: a review. J Alloys Compd 829:154597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154597
**a X, Chen Q, Li J, Shu D, Hu C, Huang S, Zhao Z (2014) Characterization of hot deformation behavior of as-extruded Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy. J Alloys Compd 610:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.04.210
Yu H, Hyuk Park S, Sun You B, Min Kim Y, Shun Yu H, Soo Park S (2013) Effects of extrusion speed on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ZK60 alloys with and without 1wt% cerium addition. Mater Sci Eng A 583:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.06.073
Park SH, You BS, Mishra RK, Sachdev AK (2014) Effects of extrusion parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-(Mn)-Ce/Gd alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 598:396–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.01.051
Song J, She J, Chen D, Pan F (2020) Latest research advances on magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide. J Magnes Alloys 8:1–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-8388(96)02239-6
Rokhlin LL, Nikitina NI, Dobatkina TV (1996) Solid-state phase equilibria in the Mg corner of the Mg-Gd-Sm phase diagram. J Alloys Compd 239:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-8388(96)02239-6
Kielbus A, Rzychon T, Przeliorz R (2010) DSC and microstructural investigations of the Elektron 21 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Forum 642:1447–1452. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.638-642.1447
Song GL (2011) Corrosion of magnesium alloys. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857091413
Somasundaram M, Narendrakumar U, Raja Annamalai A (2022) Effect of heat treatment on fatigue behaviour of stir-cast EV31A magnesium alloy. Mater Lett 313:131721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.131721
Somasundaram M, NarendraKumar U (2022) Microstructural and mechanical properties of a heat-treated EV31A magnesium alloy fabricated using the stir-casting process. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des 12(8):1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12081163
Astm G (1994) 102, Standard practice for from electrochemical measurements. Astm 89:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1520/G0102-89R15E01.2
**e Q, Ma A, Jiang J, Liu H, Cheng Z, Gu Y (2021) Tailoring the corrosion behavior and mechanism of AZ31 magnesium alloys by different Ca contents for marine application. Corros Sci 192:109842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109842
Cui Z, Zhang Y, Cheng Y, Gong D, Wang W (2019) Microstructure, mechanical, corrosion properties and cytotoxicity of beta-calcium polyphosphate reinforced ZK61 magnesium alloy composite by spark plasma sintering. Mater Sci Eng C 99:1035–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.02.050
Cao CN (2008) Principles of electrochemistry of corrosion. Chem. Ind. Press, Peking
Song D, Ma A, Jiang J, Lin P, Yang D, Fan J (2010) Corrosion behavior of equal-channel-angular-pressed pure magnesium in NaCl aqueous solution. Corros Sci 52:481–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2009.10.004
Shrestha N, Raja KS, Utgikar V (2019) Mg-RE alloy anode materials for Mg-Air battery application. J Electrochem Soc 166:A3139–A3153. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0131914jes
Silva Campos MDR, Blawert C, Mendis CL, Mohedano M, Zimmermann T, Proefrock D, Zheludkevich ML, Kainer KU (2020) Effect of heat treatment on the corrosion behavior of Mg-10Gd alloy in 0.5% NaCl solution. Front Mater 7:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2020.00084
Bao J, Li Q, Chen X, Zhang Q, Chen Z (2021) Effect of Nd on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of Mg-Gd-Nd-Zr alloys. Mater Res Express 8:046526. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abf52f
Li CQ, Xu DK, Chen XB, Wang BJ, Wu RZ, Han EH, Birbilis N (2018) Composition and microstructure dependent corrosion behaviour of Mg-Li alloys. Electrochim Acta 260:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.11.091
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. A. Raja Annamalai, Professor & Director, Centre for Innovation Manufacturing Research, Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore for introducing to the field of corrosion, giving his valuable inputs, and for providing the research facility to perform electrochemical corrosion analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Somasundaram, M., NarendraKumar, U. Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of stir cast and heat-treated EV31A magnesium alloy in different electrolytic mediums. J Appl Electrochem 53, 585–595 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01778-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01778-8