Abstract
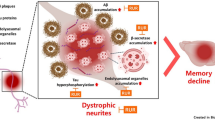
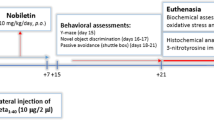
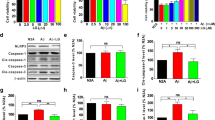
Lately, interest surrounding the utilization of plant-derived compounds as a viable beneficial approach for treating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has significantly increased. This study aimed to assess the defensive properties of rosavin against Alzheimer’s disease induced by amyloid-β, utilizing experimental models. We found that rosavin exhibited anti-aggregation and disaggregation properties, suggesting its potential to prevent the gathering of Aβ-aggregates. In vitro experiments revealed that rosavin effectively mitigated the neurotoxicity induced by Aβ in Neuro-2a cells, showcasing its protective potential. Rosavin significantly improved the Aβ-induced cognitive deficits in Wistar rats, particularly in spatial memory. Which the pathophysiology of AD includes oxidative damage, which negatively impacts biological macromolecules. Triggers the apoptotic process, causing macromolecular destruction. Interestingly, rosavin attenuated Aβ-induced macromolecular damages, thereby preserving neuronal integrity. Furthermore, the activation of antioxidative defense enzymes by rosavin inhibited oxidative damage. The positive outcomes associated with rosavin were primarily attributed to its capacity to enhance acetylcholine-mediated effects. Finally, rosavin has the potential to alleviate Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and macromolecular damages, ultimately resulting in enhanced memorial and reasoning function in Wistar rats, offering promising prospects for the treatment of AD.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material.
References
Afshar S, Shahidi S, Rohani AH, Asl SS, Komaki A (2019) Protective effects of 5-HT1A receptor antagonist and 5-HT2A receptor agonist on the biochemical and histological features in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 96:140–147
Ahmed MF, Rao AS, Ahemad SR, Ibrahim M (2012) Phytochemical studies and antioxidant activity of Melia azedarach Linn leaves by DPPH scavenging assay. Int J Pharm Appl 3(1):271–276
Ahmed S, Khan ST, Zargaham MK, Khan AU, Khan S, Hussain A, Uddin J, Khan A, Al-Harrasi A (2021) Potential therapeutic natural products against Alzheimer’s disease with reference of acetylcholinesterase. Biomed Pharmacother 139:111609
Albadawy R, Hasanin AH, Agwa SH, Hamady S, Aboul-Ela YM, Raafat MH, Kamar SS, Othman M, Yahia YA, Matboli M (2022) Rosavin ameliorates hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in the NASH rat model via targeting hepatic cell death. Int J Mol Sci 23(17):10148
Alghazwi M, Smid S, Musgrave I, Zhang W (2019) In vitro studies of the neuroprotective activities of astaxanthin and fucoxanthin against amyloid beta (Aβ1–42) toxicity and aggregation. Neurochem Int 124:215–224
Areti A, Komirishetty P, Kumar A (2017) Carvedilol prevents functional deficits in peripheral nerve mitochondria of rats with oxaliplatin-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 322:97–103
Asanad S, Ross-Cisneros FN, Barron E, Nassisi M, Sultan W, Karanjia R, Sadun AA (2019) The retinal choroid as an oculovascular biomarker for Alzheimer’s dementia: a histopathological study in severe disease. Alzheimer’s Dement Diagn Assess Dis Monit 11:775–783
Asghar A, Yousuf M, Fareed G, Nazir R, Hassan A, Maalik A, Noor T, Iqbal N, Rasheed L (2020) Synthesis, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) activities, and molecular docking studies of a novel compound based on combination of flurbiprofen and isoniazide. RSC Adv 10(33):19346–19352
Ashrafian H, Zadeh EH, Khan RH (2021) Review on Alzheimer’s disease: inhibition of amyloid beta and tau tangle formation. Int J Biol Macromol 167:382–394
Bai R, Guo J, Ye XY, **e Y, **e T (2022) Oxidative stress: the core pathogenesis and mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 77:101619
Bao WD, Pang P, Zhou XT, Hu F, **ong W, Chen K, Wang J, Wang F, **e D, Hu YZ, Han ZT (2021) Loss of ferroportin induces memory impairment by promoting ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ 28(5):1548–1562
Bektaşoğlu B, Celik SE, Özyürek M, Güçlü K, Apak R (2006) Novel hydroxyl radical scavenging antioxidant activity assay for water-soluble antioxidants using a modified CUPRAC method. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345(3):1194–1200
Benussi A, Cantoni V, Grassi M, Brechet L, Michel CM, Datta A, Thomas C, Gazzina S, Cotelli MS, Bianchi M, Premi E (2022) Increasing brain gamma activity improves episodic memory and restores cholinergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 92(2):322–334
Bruszt N, Bali ZK, Tadepalli SA, Nagy LV, Hernádi I (2021) Potentiation of cognitive enhancer effects of Alzheimer’s disease medication memantine by alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist PHA-543613 in the Morris water maze task. Psychopharmacology 238(11):3273–3281
Chauhan NB, Siegel GJ, Lichtor T (2001) Distribution of intraventricularly administered antiamyloid-beta peptide (Aβ) antibody in the mouse brain. J Neurosci Res 66(2):231–235
Cho JS, Lee J, Jeong DU, Kim HW, Chang WS, Moon J, Chang JW (2018) Effect of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a dementia rat model via microglial mediation: a comparison between stem cell transplant methods. Yonsei Med J 59(3):406–415
Eckert GP, Eckert SH, Eckmann J, Hagl S, Muller WE, Friedland K (2020) Olesoxime improves cerebral mitochondrial dysfunction and enhances Aβ levels in preclinical models of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 329:113286
Esselun C, Theyssen E, Eckert GP (2021) Effects of urolithin A on mitochondrial parameters in a cellular model of early Alzheimer disease. Int J Mol Sci 22(15):8333
Frozza RL, Bernardi A, Hoppe JB, Meneghetti AB, Matté A, Battastini AM, Pohlmann AR, Guterres SS, Salbego C (2013) Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol against Aβ administration in rats are improved by lipid-core nanocapsules. Mol Neurobiol 47:1066–1080
Ge Y, Song X, Chen L, Hu D, Hua L, Cui Y, Liu J, An Z, Yin Z, Ning H (2019) Cadmium induces actin cytoskeleton alterations and dysfunction in Neuro-2a cells. Environ Toxicol 34(4):469–475
Guo LL, Guan ZZ, Huang Y, Wang YL, Shi JS (2013) The neurotoxicity of β-amyloid peptide toward rat brain is associated with enhanced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis, all of which can be attenuated by scutellarin. Exp Toxicol Pathol 65(5):579–584
Horsley JR, Jovcevski B, Wegener KL, Yu J, Pukala TL, Abell AD (2020) Rationally designed peptide-based inhibitor of Aβ42 fibril formation and toxicity: a potential therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem J 477(11):2039–2054
Ionescu-Tucker A, Cotman CW (2021) Emerging roles of oxidative stress in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 107:86–95
Karunakaran S (2020) Unraveling early signs of navigational impairment in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice using Morris water maze. Front Neurosci 14:568200
Kasza Á, Penke B, Frank Z, Bozsó Z, Szegedi V, Hunya Á, Németh K, Kozma G, Fülöp L (2017) Studies for improving a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease: icv administration of well-characterized β-amyloid 1–42 oligomers induce dysfunction in spatial memory. Molecules 22(11):2007
Kim D, Jo YS, Jo HS, Bae S, Kwon YW, Oh YS, Yoon JH (2022) Comparative phosphoproteomics of neuro-2a cells under insulin resistance reveals new molecular signatures of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 23(2):1006
Kumar V, Saha A, Roy K (2020) In silico modeling for dual inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) enzymes in Alzheimer’s disease. Comput Biol Chem 88:107355
Lane CA, Hardy J, Schott JM (2018) Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol 25(1):59–70
Lee JH, Ahn NH, Choi SB, Kwon Y, Yang SH (2021) Natural products targeting amyloid beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 22(5):2341
Leyane TS, Jere SW, Houreld NN (2022) Oxidative stress in ageing and chronic degenerative pathologies: molecular mechanisms involved in counteracting oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. Int J Mol Sci 23(13):7273
Li C, Wang N, Zheng G, Yang L (2021) Oral administration of resveratrol-selenium-peptide nanocomposites alleviates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathogenesis by inhibiting Aβ aggregation and regulating gut microbiota. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(39):46406–46420
Lombardo S, Maskos U (2015) Role of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in Alzheimer’s disease pathology and treatment. Neuropharmacology 96:255–262
Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr AL, Randall R (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Ma C, Tao G, Lou Z, Wang H, Gu X, Hu L, Yin M (2009) Preparative separation and purification of rosavin in Rhodiola rosea by macroporous adsorption resins. Sep Purif Technol 69(1):22–28
Martins WC, dos Santos VV, Dos Santos AA, Vandresen-Filho S, Dal-Cim TA, De Oliveira KA, Mendes-de-Aguiar CB, Farina M, Prediger RD, Viola GG, Tasca CI (2015) Atorvastatin prevents cognitive deficits induced by intracerebroventricular amyloid-β 1–40 administration in mice: involvement of glutamatergic and antioxidant systems. Neurotox Res 28:32–42
Masters CL, Bateman R, Blennow K, Rowe CC, Sperling RA, Cummings JL (2015) Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Dis Prim 1(1):1–18
Maurice T, Lockhart BP, Privat A (1996) Amnesia induced in mice by centrally administered β-amyloid peptides involves cholinergic dysfunction. Brain Res 706(2):181–193
Miao S, He Q, Li C, Wu Y, Liu M, Chen Y, Qi S, Gong K (2022) Aaptamine—a dual acetyl—and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor as potential anti-Alzheimer’s disease agent. Pharm Biol 60(1):1502–1510
Michno W, Wehrli P, Meier SR, Sehlin D, Syvänen S, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Hanrieder J (2020) Chemical imaging of evolving amyloid plaque pathology and associated Aβ peptide aggregation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 152(5):602–616
Moreira PI, Nunomura A, Nakamura M, Takeda A, Shenk JC, Aliev G, Smith MA, Perry G (2008) Nucleic acid oxidation in Alzheimer disease. Free Radical Biol Med 44(8):1493–1505
Padmakumar S, D’Souza A, Parayath NN, Bleier BS, Amiji MM (2022) Nucleic acid therapies for CNS diseases: pathophysiology, targets, barriers, and delivery strategies. J Control Release 352:121–145
Pappolla MA, Chyan YJ, Poeggeler B, Frangione B, Wilson G, Ghiso J, Reiter RJ (2000) An assessment of the antioxidant and the antiamyloidogenic properties of melatonin: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 107:203–231
Parri HR, Hernandez CM, Dineley KT (2011) Research update: alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Pharmacol 82(8):931–942
Perry G, Taddeo MA, Petersen RB, Castellani RJ, Harris PL, Siedlak SL, Cash AD, Liu Q, Nunomura A, Atwood CS, Smith MA (2003) Adventiously-bound redox active iron and copper are at the center of oxidative damage in Alzheimer disease. Biometals 16:77–81
Preetham HD, Muddegowda U, Sharath Kumar KS, Rangappa S, Rangappa KS (2022) Identification of β-aminopyrrolidine containing peptides as β-amyloid aggregation inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. J Pept Sci 28(6):e3386
Prieur EA, Jadavji NM (2019) Assessing spatial working memory using the spontaneous alternation Y-maze test in aged male mice. Bio-Protoc 9(3):e3162–e3162
Roda AR, Serra-Mir G, Montoliu-Gaya L, Tiessler L, Villegas S (2022) Amyloid-beta peptide and tau protein crosstalk in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res 17(8):1666
Scheltens P, Blennow K, Breteler MM, De Strooper B, Frisoni GB, Salloway S, Van der Flier WM (2016) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 388(10043):505–517
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M, Holstege H, Chételat G, Teunissen CE, Cummings J, van der Flier WM (2021) Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet 397(10284):1577–1590
Sereia AL, de Oliveira MT, Baranoski A, Marques LLM, Ribeiro FM, Isolani RG, de Medeiros DC, Chierrito D, Lazarin-Bidoia D, Zielinski AAF, Novello CR (2019) In vitro evaluation of the protective effects of plant extracts against amyloid-beta peptide-induced toxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. PLoS ONE 14(2):e0212089
Shaw K, Bell L, Boyd K, Grijseels DM, Clarke D, Bonnar O, Crombag HS, Hall CN (2021) Neurovascular coupling and oxygenation are decreased in hippocampus compared to neocortex because of microvascular differences. Nat Commun 12(1):3190
Shekarian M, Komaki A, Shahidi S, Sarihi A, Salehi I, Raoufi S (2020) The protective and therapeutic effects of vinpocetine, a PDE1 inhibitor, on oxidative stress and learning and memory impairment induced by an intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of amyloid beta (aβ) peptide. Behav Brain Res 383:112512
Skopińska-Różewska E, Hartwich M, Siwicki AK, Wasiutyński A, Sommer E, Mazurkiewicz M, Bany J, Skurzak H (2008) Experimental immunology The influence of Rhodiola rosea extracts and rosavin on cutaneous angiogenesis induced in mice after grafting of syngeneic tumor cells. Central Eur J Immunol 33(3):102–107
Stefanescu R, Stanciu GD, Luca A, Paduraru L, Tamba BI (2020) Secondary metabolites from plants possessing inhibitory properties against beta-amyloid aggregation as revealed by thioflavin-T assay and correlations with investigations on transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomolecules 10(6):870
Stepanichev MY, Moiseeva YV, Lazareva NA, Onufriev MV, Gulyaeva NV (2003) Single intracerebroventricular administration of amyloid-beta (25–35) peptide induces impairment in short-term rather than long-term memory in rats. Brain Res Bull 61(2):197–205
Sun L, Liu D, Fu D, Yue T, Scharre D, Zhang L (2021) Fluorescent peptide nanoparticles to detect amyloid-beta aggregation in cerebrospinal fluid and serum for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and progression monitoring. Chem Eng J 405:126733
Svorc P, Bacova I, Svorc P Jr, Nováková M, Gresova S (2016) Zoletil anaesthesia in chronobiological studies. Biol Rhythm Res 47(1):103–110
Taha MA, Badawy ME, Abdel-Razik RK, Younis HM, Abo-El-Saad MM (2021) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in liver of male albino rats after exposing to sub-chronic intoxication of chlorpyrifos, cypermethrin, and imidacloprid. Pestic Biochem Physiol 178:104938
Takahashi J, Ueta Y, Yamada D, Sasaki-Hamada S, Iwai T, Akita T, Yamashita C, Saitoh A, Oka JI (2022) Intracerebroventricular administration of oxytocin and intranasal administration of the oxytocin derivative improve β-amyloid peptide (25–35)-induced memory impairment in mice. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep 42(4):492–501
Taqui R, Debnath M, Ahmed S, Ghosh A (2022) Advances on plant extracts and phytocompounds with acetylcholinesterase inhibition activity for possible treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Phytomed plus 2(1):100184
Teipel SJ, Meindl T, Grinberg L, Grothe M, Cantero JL, Reiser MF, Möller HJ, Heinsen H, Hampel H (2011) The cholinergic system in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: an in vivo MRI and DTI study. Hum Brain Mapp 32(9):1349–1362
Teleanu DM, Niculescu AG, Lungu II, Radu CI, Vladâcenco O, Roza E, Costăchescu B, Grumezescu AM, Teleanu RI (2022) An overview of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci 23(11):5938
Thakker DR, Weatherspoon MR, Harrison J, Keene TE, Lane DS, Kaemmerer WF, Stewart GR, Shafer LL (2009) Intracerebroventricular amyloid-β antibodies reduce cerebral amyloid angiopathy and associated micro-hemorrhages in aged Tg2576 mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(11):4501–4506
Tian H, Ding N, Guo M, Wang S, Wang Z, Liu H, Yang J, Li Y, Ren J, Jiang J, Li Z (2019) Analysis of learning and memory ability in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model using the Morris water maze. JoVE J Visual Exp 152:e60055
Van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, Bateman RJ, Chen C, Gee M, Kanekiyo M, Li D, Reyderman L, Cohen S, Froelich L (2023) Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 388(1):9–21
Wang CF, Song CY, Wang X, Huang LY, Ding M, Yang H, Wang P, Xu LL, **e ZH, Bi JZ (2019) Protective effects of melatonin on mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial structure and function in the HEK293-APPswe cell model of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23(8):3542–3550
Wang Z, Gao C, Zhang L, Sui R (2023) Hesperidin methylchalcone (HMC) hinders amyloid-β induced Alzheimer’s disease by attenuating cholinesterase activity, macromolecular damages, oxidative stress and apoptosis via regulating NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Int J Biol Macromol 233:123169
Wei Y, Jia S, Ding Y, **a S, Giunta S (2022) Balanced basal-levels of ROS (redox-biology), and very-low-levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (cold-inflammaging), as signaling molecules can prevent or slow-down overt-inflammaging, acting as early basic pillars of adaptive-homeostasis in aging. Exp Gerontol 172:112067
Wightman EL (2017) Potential benefits of phytochemicals against Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Nutr Soc 76(2):106–112
Wu Y, Su X, Lu J, Wu M, Yang SY, Mai Y, Deng W, Xue Y (2022) In Vitro and in silico analysis of phytochemicals from fallopia dentatoalata as dual functional cholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Pharmacol 13:905708
**n X, Yao D, Zhang K, Han S, Liu D, Wang H, Liu X, Li G, Huang J, Wang J (2019) Protective effects of Rosavin on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via suppressing fibrotic and inflammatory signaling pathways in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 115:108870
Zhang B, Zhao Y, Guo K, Tian H, Wang C, Wang R, Chen Y, Chen X, Zheng H, Gao B, Shen J (2023) Macromolecular nanoparticles to attenuate both reactive oxygen species and inflammatory damage for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Bioeng Transl Med 8(3):e10459
Zhao XC, Zhang L, Yu HX, Sun Z, Lin XF, Tan C, Lu RR (2011) Curcumin protects mouse neuroblastoma Neuro-2A cells against hydrogen-peroxide-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem 129(2):387–394
Zhou W, Chen K, Lu Q, Luo Y, Zhang C, Zheng Y, Zhuo Z, Guo K, Wang J, Chen H, Sha W (2020) The protective effect of rosavin from Rhodiola rosea on radiation-induced intestinal injury. Chem Biodivers 17(12):e2000652
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors affirm that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could potentially create a conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, M., Sui, R., Zhang, L. et al. Rosavin thwarts amyloid-β-induced macromolecular damages and neurotoxicity, exhibiting anti-Alzheimer’s disease activity in Wister rat model. Inflammopharmacol 32, 1461–1474 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01320-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01320-y