Abstract
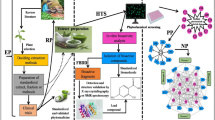
Medulla Tetrapanacis (MT) is a commonly used herb to promote lactation and manage mastitis in lactating mothers. However, its anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial effects are currently unknown. We hypothesized that MT water extract possesses anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial effects by modulating macrophage polarization to reduce the release of inflammatory mediators and phagocytosis via inactivation of MAPKs pathways. The chemical composition of the MT water extract was analyzed by UPLC-Orbitrap-mass spectrometry. The anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial properties of the MT water extract were examined using LPS-stimulated inflammation and Staphylococcus aureus infection model in RAW 264.7 cells, respectively. The underlying mechanism of action of the MT water extract was also investigated. We identified eight compounds by UPLC-Orbitrap-mass spectrometry that are abundant within the MT water extract. MT water extract significantly suppressed LPS-induced nitric oxide, TNF-α and IL-6 secretion in RAW 264.7 cells which was accompanied by the promotion of macrophage polarization from pro-inflammatory towards anti-inflammatory phenotypes. MT water extract significantly suppressed the LPS-induced MAPK activation. Finally, MT water extract decreased the phagocytic capacity of the RAW 264.7 cells against S. aureus infection. MT water extract could suppress LPS-induced inflammation by promoting macrophages towards an anti-inflammatory phenotype. In addition, MT also inhibited the growth of S. aureus.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available on request.
References
Angelopoulou A, Field D, Ryan CA, Stanton C, Hill C, Ross RP (2018) The microbiology and treatment of human mastitis. Med Microbiol Immunol 207:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-017-0532-z
Bousmaha-marroki L, Boutillier D, Marroki A, Grangette C (2021) In vitro anti-staphylococcal and anti-inflammatory abilities of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus from infant gut microbiota as potential probiotic against infectious women mastitis. Probiotics Antimicrobial Proteins 13:970–981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09755-x
Cai M, Shi Y, Zheng T, Hu S, Du K, Ren A, Jia X, Chen S, Wang J, Lai S (2020) Mammary epithelial cell derived exosomal MiR-221 mediates M1 macrophage polarization via SOCS1/STATs to promote inflammatory response. Int Immunopharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106493
Chaves RG, Lamounier JA, Cesar CC (2009) Self-medication in nursing mothers and its influence on the duration of breastfeeding. J Pediatr (rio j) 85:129–134. https://doi.org/10.2223/JPED.1874
De Oliveira JR, Viegas DD, Martins APR, Carvalho CAT, Soares CP, Camargo SEA, Jorge AOC, De Oliveira LD (2017) Thymus vulgaris L. extract has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects in the absence of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. Arch Oral Biol 82:271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.06.031
Dei Cas M, Paroni R, Signorelli P, Mirarchi A, Cerquiglini L, Troiani S, Cataldi S, Codini M, Beccari T, Ghidoni R, Albi E (2020) Human breast milk as source of sphingolipids for newborns: Comparison with infant formulas and commercial cow’s milk. J Trans Med. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-020-02641-0
Draelos ZD (2016) A pilot study investigating the efficacy of botanical anti-inflammatory agents in an OTC eczema therapy. J Cosmet Dermatol 15:117–119. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12199
Ge Z, Tong H, Qin J, Li Q, Gao X (2009) Effect of different Chinese herbs extracts on expression of β-casein of mouse mammary gland cells. J Northeast Agric Univ 40:6
Grzeskowiak LE, Saha MR, Ingman WV, Nordeng H, Ystrom E, Amir LH (2022) Incidence, antibiotic treatment and outcomes of lactational mastitis: Findings from the Norwegian mother, father and child cohort study (moba). Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 36:254–263. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppe.12824
Hassel C, Gausseres B, Guzylack-piriou L, Foucras G (2021) Ductal macrophages predominate in the immune landscape of the lactating mammary gland. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.754661
He X, Wei Z, Zhou E, Chen L, Kou J, Wang J, Yang Z (2015) Baicalein attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4 mediated NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced mastitis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 28:470–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.07.012
Ito S (2016) Mother and child: medication use in pregnancy and lactation. Clin Pharmacol Ther 100:8–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.383
Kinlay JR, O’connell DL, Kinlay S (2001) Risk factors for mastitis in breastfeeding women: results of a prospective cohort study. Aust N Z J Public Health 25:115–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-6405.2001.tb01831.x
Kwon OJ (1997) The role of nitric oxide in the immune response of tuberculosis. J Korean Med Sci 12:481–487. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.1997.12.6.481
Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, Sica A, Locati M (2013) Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J Pathol 229:176–185. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4133
Montenegro-Burke JR, Kok BP, Guijas C, Domingo-Almenara X, Moon C, Galmozzi A, Kitamura S, Eckmann L, Saez E, Siuzdak GE, Wolan DW (2021) Metabolomics activity screening of T cell-induced colitis reveals anti-inflammatory metabolites. Sci Signal. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.abf6584
Norris GH, Milard M, Michalski MC, Blesso CN (2019) Protective properties of milk sphingomyelin against dysfunctional lipid metabolism, gut dysbiosis, and inflammation. J Nutr Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108224
Okafor AE (2022) Uche OA & Uche IB (2022) Sociocultural factors as predictor to exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among nursing mothers in some communities in Eastern. Nigeria Soc Work Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1080/19371918.2022.2135663
Pan T, Chang Y, He M, He Z, Jiang J, Ren X, Zhang F (2022) Beta-Hydroxyisovalerylshikonin regulates macrophage polarization via the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway and ameliorates sepsis in mice. Pharm Biol 60:729–742. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2022.2046111
Pevzner M, Dahan A (2020) Mastitis while breastfeeding: Prevention, the importance of proper treatment, and potential complications. J Clin Med 9(8):2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082328
Qiu R, Zhong Y, Hu M, Wu B (2022) Breastfeeding and reduced risk of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Comput Math Methods Med 2022:8500910. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8500910
Shu Y, Liu X, Ma X, Gao J, He W, Cao X, Chen J (2017) Immune response mechanism of mouse monocytes/macrophages treated with kappa-carrageenan polysaccharide. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 53:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.06.010
Song X, Guo M, Wang T, Wang W, Cao Y, Zhang N (2014) Geniposide inhibited lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis by modulating TLR4 and apoptosis-related factors in mouse mammary glands. Life Sci 119:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2014.10.006
Sun K, Chen M, Yin Y, Wu L, Gao L (2017) Why Chinese mothers stop breastfeeding: Mothers’ self-reported reasons for stop** during the first six months. J Child Health Care 21:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1177/1367493517719160
Vesper H, Schmelz EM, Nikolova-Karakashian MN, Dillehay DL, Lynch DV, Merrill AH (1999) Sphingolipids in food and the emerging importance of sphingolipids to nutrition. J Nutr 129:1239–1250. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/129.7.1239
Wang S, Zhang C, Li C, Li D, He P, Su Z, Li Y, Ding Y, Lu A (2018) Efficacy of Chinese herbal medicine Zengru Gao to promote breastfeeding: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 18:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-018-2121-0
Wilson GJ, Fukuoka A, Vidler F, Graham GJ (2022) Diverse myeloid cells are recruited to the develo** and inflamed mammary gland. Immunology 165:206–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.13430
Wu MY, Lu JH (2019) Autophagy and macrophage functions: Inflammatory response and phagocytosis. Cells 9:70. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010070
Yang C, Liu P, Wang S, Zhao G, Zhang T, Guo S, Jiang K, Wu H, Deng G (2018) Shikonin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-induced mastitis by inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 505:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.198
Zhang D, ** G, Liu W, Dou M, Wang X, Shi W, Bao Y (2022a) Salvia miltiorrhiza polysaccharides ameliorates Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in rats by inhibiting activation of the NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. BMC Vet Res 18:201. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-022-03312-6
Zhang Y, Xu Y, Chen B, Zhao B, Gao XJ (2022b) Selenium deficiency promotes oxidative stress-induced mastitis via activating the NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways in dairy cow. Biol Trace Elem Res 200:2716–2726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02882-0
Zhou B, Yang Z, Feng Q, Liang X, LI J, Zanin M, Jiang Z & Zhong N, (2017) Aurantiamide acetate from baphicacanthus cusia root exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-viral effects via inhibition of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in Influenza A virus-infected cells. J Ethnopharmacol 199:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.038
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Chui-Ying Yuen and Dr. Chi-On Chan for their technical support in this study.
Funding
SWS is supported by The Hong Kong Polytechnic University – General Research Fund (Project No.: P0036597) and Research Centre for Chinese Medicine Innovation, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (Project No.: P0041138). This work is partly supported by the College of Professional and Continuing Education Research Fund (Ref. No. SEHS-2021–233(E)), The Hong Kong Polytechnic University. FWNC is supported by PolyU Start-up Fund for RAPs under the Strategic Hiring Scheme (P0038407).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kwok, C.TK., Chow, F.WN., Cheung, K.YC. et al. Medulla Tetrapanacis water extract alleviates inflammation and infection by regulating macrophage polarization through MAPK signaling pathway. Inflammopharmacol 32, 393–404 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01266-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01266-1