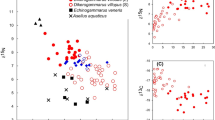
Abstract
The trophic niche of invasive species can vary overtime because of different processes related to ecological opportunity and invader activity that condition biological interactions with the native biodiversity. We conducted an annual-based survey of the trophic niche of the mysid Hemimysis anomala in the largest European peri-alpine lake by combining molecular and isotope analyses. We hypothesized that the population trophic niche width would vary seasonally, expanding in warm periods due to greater ecological opportunities and higher mysid metabolic activity. Molecular analyses identified a diversified set of prey throughout the year ranging from autotrophic protists to zooplankton and converged with isotope analyses to support the diet seasonality hypothesis of H. anomala with wider trophic niches and, in a lower extent, richer diets in spring and summer when compared to autumn and winter. Isotope analyses also highlighted a seasonal pattern in resources used with a dominance of pelagic reliance in summer and autumn. These results underlined the significant seasonal variability in the trophic niche of this invasive mysid suggesting that future assessments of its ecological impacts should account for the temporal variations of its trophic interactions with the native biodiversity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and R codes are available upon request to the corresponding author.
References
Andvik, R. T., J. A. VanDeHey, M. J. Fincel, W. E. French, K. N. Bertrand, S. R. Chipps, R. A. Klumb & B. D. S. Graeb, 2010. Technical contribution: Application of non-lethal stable isotope analysis to assess feeding patterns of juvenile pallid sturgeon Scaphirhynchus albus: a comparison of tissue types and sample preservation methods. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 26: 1–5.
Araújo, M. S. & R. Costa-Pereira, 2013. Latitudinal gradients in intraspecific ecological diversity. Biology Letters 9: 20130778.
Araújo, M. S., D. I. Bolnick & C. A. Layman, 2011. The ecological causes of individual specialisation. Ecology Letters 14: 948–958.
Beck, M., 2017. ggord: ordination plots with ggplot2. R package version 100.
Bolnick, D. I., L. H. Yang, J. A. Fordyce, J. M. Davis & R. Svanbäck, 2002. Measuring individual-level resource specialization. Ecology 83: 2936–2941.
Bolnick, D., R. Svanbäck, J. Fordyce, L. Yang, J. Davis, D. Hulsey & M. Forister, 2003. The ecology of individuals: incidence and implications of individual specialization. The American Naturalist 161: 1–28.
Bolnick, D. I., L. K. Snowberg, C. Patenia, W. E. Stutz, T. Ingram & O. L. Lau, 2009. Phenotype-dependent native habitat preference facilitates divergence between parapatric lake and stream stickleback. Evolution 63: 2004–2016.
Borcherding, J., S. Murawski & H. Arndt, 2006. Population ecology, vertical migration and feeding of the Ponto-Caspian invader Hemimysis anomala in a gravel-pit lake connected to the River Rhine. Freshwater Biology 51: 2376–2387.
Boscarino, B. T., S. Oyagi, E. K. Stapylton, K. E. McKeon, N. O. Michels, S. F. Cushman & M. E. Brown, 2020. The influence of light, substrate, and fish on the habitat preferences of the invasive bloody red shrimp, Hemimysis anomala. Journal of Great Lakes Research 46: 311–322.
Boyer, F., C. Mercier, A. Bonin, et al., 2016. OBITools: a unix-inspired software package for DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology Resources 16: 176–182.
Brown, J., J. Gillooly, A. Allen, V. Savage & G. West, 2004. Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology 85: 1771–1789.
Brown, M. E., K. L. Buffington, L. B. Cleckner & N. R. Razavi, 2022. Elevated methylmercury concentration and trophic position of the non-native bloody red shrimp (Hemimysis anomala) increase biomagnification risk in nearshore food webs. Journal of Great Lakes Research 48: 252–259.
Calderón-Sanou, I., T. Münkemüller, F. Boyer, L. Zinger & W. Thuiller, 2020. From environmental DNA sequences to ecological conclusions: how strong is the influence of methodological choices? Journal of Biogeography 47: 193–206.
CIPEL, 2022. Rapports sur les études et recherches entreprises dans le bassin lémanique: campagne, p 250.
Cucherousset, J. & S. Villeger, 2015. Quantifying the multiple facets of isotopic diversity: new metrics for stable isotope ecology. Ecological Indicators 56: 152–160.
David, P., E. Thébault, O. Anneville, P. F. Duyck, E. Chapuis & N. Loeuille, 2017. Chapter One: impacts of invasive species on food webs: a review of empirical data. In Bohan, D. A., A. J. Dumbrell & F. Massol (eds), Advances in Ecological Research, Vol. 56. Academic Press: 1–60.
Deagle, B. E., A. C. Thomas, J. C. McInnes, L. J. Clarke, E. J. Vesterinen, E. L. Clare, T. R. Kartzinel & J. P. Eveson, 2019. Counting with DNA in metabarcoding studies: how should we convert sequence reads to dietary data? Molecular Ecology 28: 391–406.
Dumont, S. & C. Muller, 2010. Distribution, ecology and impact of a small invasive shellfish, Hemimysis anomala in Alsatian water. Biological Invasions 12: 495–500.
Eby, L. A., W. J. Roach, L. B. Crowder & J. A. Stanford, 2006. Effects of stocking-up freshwater food webs. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 21: 576–584.
Englund, G., G. Öhlund, C. L. Hein & S. Diehl, 2011. Temperature dependence of the functional response. Ecology Letters 14: 914–921.
Evans, T. M., R. Naddafi, B. C. Weidel, B. F. Lantry, M. G. Walsh, B. T. Boscarino, O. E. Johannsson & L. G. Rudstam, 2018. Stomach contents and stable isotopes analysis indicate Hemimysis anomala in Lake Ontario are broadly omnivorous. Journal of Great Lakes Research 44: 467–475.
Ficetola, G. F., E. Coissac, S. Zundel, et al., 2010. An in silico approach for the evaluation of DNA barcodes. BMC Genomics 11: 434.
Finger, D., A. Wüest & P. Bossard, 2013. Effects of oligotrophication on primary production in peri-alpine lakes. Water Resources Research 49: 4700–4710.
Frossard, V. & D. Fontvieille, 2018. What is the invasiveness of Hemimysis anomala (Crustacea, Mysidae) in the large deep Lake Bourget, France? Hydrobiologia 814: 219–232.
Geisthardt, E. J., B. C. Suedel & J. A. Janssen, 2022. A Hemimysis-driven novel ecosystem at a modified rubble-mound breakwater: an engineering with nature® demonstration project. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management 18: 49–62.
Giraudoux, P., 2022. pgirmess: Spatial Analysis and Data Mining for Field Ecologists. R package version 2.0.0. Available on interenet at https://CRANR-project.org/package=pgirmess
Golaz, F. & R. Vainola, 2013. Répartition, dynamique saisonnière et analyse de l’ADN mitochondrial du crustacé mysidé invasif Hemimysis anomala G.O. Sars 1907 dans le Léman. Bulletin De La Société Vaudoise Des Sciences Naturelles 93: 101–117.
Grosbois, G. & M. Rautio, 2018. Active and colorful life under lake ice. Ecology 99: 752–754.
Guillerault, N., S. Bouletreau, A. Iribar, A. Valentini & F. Santoul, 2017. Application of DNA metabarcoding on faeces to identify European catfish Silurus glanis diet. Journal of Fish Biology 90: 2214–2219.
Guillerault, N., S. Boulêtreau & F. Santoul, 2019. Predation of European catfish on anadromous fish species in an anthropised area. Marine and Freshwater Research 70: 682–686.
Halpin, K. E., B. T. Boscarino, L. G. Rudstam, M. G. Walsh & B. F. Lantry, 2013. Effect of light, prey density, and prey type on the feeding rates of Hemimysis anomala. Hydrobiologia 720: 101–110.
Huryn, A., 1996. An appraisal of the Allen paradox in a New Zealand trout stream. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 243–252.
Ives, J., M. Marty, Y. de Lafontaine, T. Johnson, M. Koops & M. Power, 2013. Spatial variability in trophic offset and food sources of Hemimysis anomala in lentic and lotic ecosystems within the Great Lakes basin. Journal of Plankton Research 35: 772–784.
Jackson, A., R. Inger, A. Parnell & S. Bearhop, 2011. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER – Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. Journal of Animal Ecology 80: 595–602.
Jardine, T., S. McGeachy, C. Paton, M. Savoie & R. A. Cunjak, 2003. Stable isotopes in aquatic systems: sample preparation, analysis, and interpretation. Canadian Manuscript Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences No. 2656: 39
Ketelaars, H. M., F. Lambregts-van de Clundert, C. Carpentier, A. Wagenvoort & W. Hoogenboezem, 1999. Ecological effects of the mass occurrence of the Ponto-Caspian invader, Hemimysis anomala G.O. Sars, 1907 (Crustacea: Mysidacea), in a freshwater storage reservoir in the Netherlands, with notes on its autecology and new records. Hydrobiologia 394: 233–248.
Layman, C., A. Arrington, C. Montana & D. Post, 2007. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 88: 42–48.
Leggett, M. F., M. R. Servos, R. Hesslein, O. Johannsson, E. S. Millard & D. G. Dixon, 1999. Biogeochemical influences on the carbon isotope signatures of Lake Ontario biota. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 56: 2211–2218.
Leggett, M. F., O. Johannsson, R. Hesslein, D. G. Dixon, W. D. Taylor & M. R. Servos, 2000. Influence of inorganic nitrogen cycling on the δ15N of Lake Ontario biota. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 57: 1489–1496.
Marty, J., K. Bowen, M. Koops & M. Power, 2010. Distribution and ecology of Hemimysis anomala, the latest invader of the Great Lakes basin. Hydrobiologia 647: 71–80.
Marty, J., J. Ives, Y. de Lafontaine, S.-P. Despatie, M. Koops & M. Power, 2012. Evaluation of carbon pathways supporting the diet of invasive Hemimysis anomala in a large river. Journal of Great Lakes Research 38: 45–51.
McGaw, I. J. & D. L. Curtis, 2013. A review of gastric processing in decapod crustaceans. Journal of Comparative Physiology B, Biochemical, Systemic, and Environmental Physiology 183: 443–465.
Mercier, C., F. Boyer, E. Kopylova, P. Taberlet, A. Bonin & E. Coissac, 2013. SUMATRA and SUMACLUST: fast and exact comparison and clustering of sequences. Programs and Abstracts of the SeqBio 2013 Workshop, 27–29.
Minagawa, M. & E. Wada, 1984. Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between δ15N and animal age. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta 48: 1135–1140.
Moller Pillot, H. K. M., 2014. Chironomidae Larvae, Vol. 3: Orthocladiinae, Biology and Ecology of the Aquatic Orthocladiinae. BRILL. ISBN: 978-90-5011-459-2
Newman, R. M., 1991. Herbivory and detritivory on freshwater macrophytes by invertebrates: a review. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 10: 89–114.
Oksanen, J., G. Simpson, F. Blanchet, R. Kindt, P. Legendre, P. Minchin, R. O’Hara, P. Solymos, M. Stevens, E. Szoecs, H. Wagner, M. Barbour, M. Bedward, B. Bolker, D. Borcard, G. Carvalho, M. Chirico, M. De Caceres, S. Durand, H. Evangelista, R. FitzJohn, M. Friendly, B. Furneaux, G. Hannigan, M. Hill, L. Lahti, D. McGlinn, M. Ouellette, C. Ribeiro, E., T. Smith, A. Stier, C. Ter Braak & J. Weedon, 2022. vegan: Community Ecology Package_. R package version 2.6–2. Available on internet at https://CRANR-project.org/package=vegan
Olsson, K., P. Stenroth, P. Nyström & W. Granéli, 2009. Invasions and niche width: does niche width of an introduced crayfish differ from a native crayfish? Freshwater Biology 54: 1731–1740.
Parnell, A., D. Phillips, S. Bearhop, B. Semmens, E. Ward, J. Moore, A. Jackson & R. Inger, 2012. Bayesian Stable Isotope Mixing Models. Evironmetrics:eprint ar**v:1209.6457
Parnell, A., 2021. simmr: A Stable Isotope Mixing Model. R package version 045. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=simmr
Pérez-Fuentetaja, A. & J. Wuerstle, 2014. Prey size selection and feeding ecology of an omnivorous invader: Hemimysis anomala. Journal of Great Lakes Research 40: 257–264.
Pothoven, S. A., I. A. Grigorovich, G. L. Fahnenstiel & M. D. Balcer, 2007. Introduction of the Ponto-Caspian Bloody-red Mysid Hemimysis anomala into the Lake Michigan Basin. Journal of Great Lakes Research 33: 285–292.
R Core Team, 2022. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. Available on internet at http://www.R-project.org/
Rall, B. C., U. Brose, M. Hartvig, G. Kalinkat, F. Schwarzmüller, O. Vucic-Pestic & O. L. Petchey, 2012. Universal temperature and body-mass scaling of feeding rates. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 367: 2923–2934.
Ricciardi, A., S. Avlijas & J. Marty, 2012. Forecasting the ecological impacts of the Hemimysis anomala invasion in North America: lessons from other freshwater mysid introductions. Journal of Great Lakes Research 38: 7–13.
Rimet, F., A. Bouchez & K. Tapolczai, 2016. Spatial heterogeneity of littoral benthic diatoms in a large lake: monitoring implications. Hydrobiologia 771(1): 179–193.
Roughgarden, J., 1979. Theory of Population Genetics and Evolutionary Ecology: An Introduction, Macmillan, New York:
Sánchez-Hernández, J., A. G. Finstad, J. V. Arnekleiv, G. Kjærstad & P.-A. Amundsen, 2021. Beyond ecological opportunity: prey diversity rather than abundance shapes predator niche variation. Freshwater Biology 66: 44–61.
Schnell, I. B., K. Bohmann & M. T. P. Gilbert, 2015. Tag jumps illuminated – reducing sequence-to-samplemisidentifications in metabarcoding studies. Molecular Ecology Resources 15: 1289–1303.
Sentis, A., J. L. Hemptinne & J. Brodeur, 2012. Using functional response modeling to investigate the effect of temperature on predator feeding rate and energetic efficiency. Oecologia 169: 1117–1125.
Sinclair, J. S., S. E. Arnott & A. Cox, 2016. The quick and the dead: copepods dominate as cladocerans decline following invasion by Hemimysis anomala. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 73: 793–803.
Stroud, J. T. & J. B. Losos, 2016. Ecological opportunity and adaptive radiation. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 47: 507–532.
Svanbäck, R. & D. I. Bolnick, 2007. Intraspecific competition drives increased resource use diversity within a natural population. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 274: 839–844.
Taberlet, P., A. Bonin, L. Zinger & E. Coissac, 2018. Environmental DNA: For Biodiversity Research and Monitoring, Oxford University Press, Oxford:, 272.
Vander Zanden, M. J. & J. B. Rasmussen, 1999. Primary consumer δ13C and δ15N and the trophic position of aquatic consumers. Ecology 80: 1395–1404.
Walsh, J. R., S. R. Carpenter & M. J. Vander Zanden, 2016. Invasive species triggers a massive loss of ecosystem services through a trophic cascade. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 113: 4081–4085.
Weisse, T., H. Müller, R. Pinto-Coelho, A. Schweizer, D. Springmann & G. Baldringer, 1990. Response of the microbial loop to the phytoplankton spring bloom in a large prealpine lake. Limnology and Oceanography 35: 781–794.
Wellborn, G. A. & R. B. Langerhans, 2015. Ecological opportunity and the adaptive diversification of lineages. Ecology and Evolution 5: 176–195.
Wickham, H. & M. Girlich, 2022. tidyr: Tidy Messy Data_. R package version 1.2.1. https://CRANR-project.org/package=tidyr
Wickham, H., R. François, L. Henry & K. Müller, 2022. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R package version 1010. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr
Wickham, H., 2016. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Springer-Verlag: New York. ISBN :978-3-319-24277-4.
Wittmann, K. & A. Ariani, 2009. Reappraisal and range extension of non-indigenous Mysidae (Crustacea, Mysida) in continental and coastal waters of eastern France. Biological Invasions 11: 401–407.
Zinger, L., C. Lionnet, A. S. Benoiston, J. Donald, C. Mercier & F. Boyer, 2021. metabaR: an R package for the evaluation and improvement of DNA metabarcoding data quality. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 12: 586–592.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Pôle R&D Ecosystèmes Lacustres (ECLA) for funding the MYSILAC project. SJ was assisted by Jonathan Grimond from the SUBBEAR company during diving sessions. We are indebted to three anonymous reviewers for providing valuable suggestions that improved the early versions of the manuscript. We also would like to thank SILVATECH (Silvatech, INRAE, 2018. Structural and functional analysis of tree and wood Facility, https://doi.org/10.15454/1.5572400113627854E12) for stable isotope analyses.
Funding
Pôle R&D Ecosystèmes Lacustres (ECLA) for funding the MYSILAC project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived project: VF and SJ. Analyzed data: VF and CV. Original draft preparation: VF, SJ, and CV. All authors gave final approval for publication and agreed to be held accountable for the work performed therein.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
There was no requirement for ethical approval for the sampling of H. anomala.
Additional information
Handling editor: Ülkü Nihan Tavşanoğlu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Frossard, V., Vagnon, C. & Jacquet, S. Seasonal variations of the trophic niche width of Hemimysis anomala in Lake Geneva. Hydrobiologia 851, 487–501 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05334-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05334-z