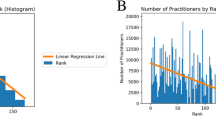
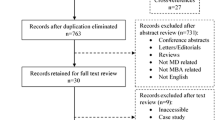
Abstract
The match rate of medical schools in the U.S. has been extensively studied from the perspective of applicants and influential factors. A method to objectively estimate the efficiency of a medical school’s match rate has not been described in the literature. Such a method constitutes a significant improvement opportunity for medical schools via benchmarking best practices. This research fills the gap and proposes a bootstrap data envelopment analysis (DEA) framework to assess the residency match rate efficiency of medical schools. The efficacy of the proposed method is confirmed when benchmarking the Texas allopathic medical schools to representative samples of allopathic medical schools in the United States. The model allows to determine the statistical significance of differences in the residency match rate efficiency between groups of medical schools. The proposed bootstrap DEA approach is used to estimate the real efficiency's density function of 40 medical schools in the U.S. over the 2018–2020 period. The aggregate efficiency estimation showed that the medical schools are performing at a high competitive level; they have experienced a slight decline in scale efficiencies and have preserved high managerial performance. The study measured four groups: Texas medical schools, top ten ranked, middle ten ranked, and bottom ten ranked U.S. medical schools. The overall major improvement opportunity for medical schools is the scale of operations. Results confirm that medical schools are shown to be efficient in training future physicians.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACOMAS Matriculants by Race and Ethnicity 2019: American Association of Colleges of Osteopathic Medicine (2020). Retrieved from: https://www.aacom.org/reports-programs-initiatives/aacom-reports/applicants
Abbott, M., Doucouliagos, C.: The efficiency of Australian universities: a data envelopment analysis. Econ. Educ. Rev. 22(1), 89–97 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7757(01)00068-1
Asandului, L., Roman, M., Fatulescu, P.: The efficiency of healthcare systems in Europe: a data envelopment analysis approach. Procedia Econ. Finance 10, 261–268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S2212-5671(14)00301-3
Banker, R.D., Charnes, A., Cooper, W.W.: Some models for estimating technical and scale inefficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Manag. Sci. 30(9), 1078–1092 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.30.9.1078
Barra, C., Zotti, R.: Measuring efficiency in higher education: an empirical study using a bootstrapped data envelopment analysis. Int. Adv. Econ. Res. 22(1), 11–33 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11294-015-9558-4
Benicio, J., Mello, J.C.S.D.: Different types of return to scale in DEA. Pesquisa Operacional 39(2), 245–260 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1590/0101-7438.2019.039.02.0245
Bolli, T., Olivares, M., Bonaccorsi, A., Daraio, C., Aracil, A.G., Lepori, B.: The differential effects of competitive funding on the production frontier and the efficiency of universities. Econ. Educ. Rev. 52, 91–104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econedurev.2016.01.007
Chakraborti, C., Crowther, J.E., Koretz, Z.A., Kahn, M.J.: How well did our students match? A peer-validated quantitative assessment of medical school match success: the match quality score. Med. Educ. Online 24(1), 1681068 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/10872981.2019.1681068
Charnes, A., Cooper, W.W., Rhodes, E.: Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2(6), 429–444 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(78)90138-8
Chen, Y., Chen, Y., Oztekin, A.: A hybrid data envelopment analysis approach to analyse college graduation rate at higher education institutions. INFOR Inf. Syst. Oper. Res. 55(3), 188–210 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/03155986.2016.1262584
Chilingerian, J.A.: Evaluating physician efficiency in hospitals: a multivariate analysis of best practices. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 80(3), 548–574 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(94)00137-2
De Witte, K., Lopez-Torres, L.: Efficiency in education: a review of literature and a way forward. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 68(4), 339–363 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1057/jors.2015.92
Dogbey, G.Y., Collins, K., Russ, R., Brannan, G.D., Mivsek, M., Sewell, S.: Factors associated with osteopathic primary care residency choice decisions. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 118(4), 225–233 (2018). https://doi.org/10.7556/jaoa.2018.046
Eff, E.A., Klein, C.C., Kyle, R.: Identifying the best buys in US higher education. Res. High. Educ. 53(8), 860–887 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11162-012-9259-2
Gordon, A.M., Malik, A.T.: Costs of US allopathic medical students applying to neurosurgery residency: geographic considerations and implications for the 2020–2021 application cycle. World Neurosurg. 150, e783–e789 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2021.03.149
Hadi-Vencheh, A., Foroughi, A.A.: A generalized DEA model for inputs/outputs estimation. Math. Comput. Model. 43(5–6), 447–457 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2005.08.005
Hayek, S., Lane, S., Fluck, M., Hunsinger, M., Blansfield, J., Shabahang, M.: Ten year projections for US residency positions: will there be enough positions to accommodate the growing number of US medical school graduates? J. Surg. Educ. 75(3), 546–551 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsurg.2017.08.021
Jajosky, R.P., Jajosky, A.N., Kleven, D.T., Singh, G.: Fewer seniors from United States allopathic medical schools are filling pathology residency positions in the main residency match, 2008–2017. Hum. Pathol. 73, 26–32 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2017.11.014
Johnes, J.: Data envelopment analysis and its application to the measurement of efficiency in higher education. Econ. Educ. Rev. 25(3), 273–288 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econedurev.2005.02.005
Johnes, J., Virmani, S.: Chief executive pay in UK higher education: the role of university performance. Ann. Oper. Res. 288(2), 547–576 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-019-03275-2
Johnes, J., Yu, L.: Measuring the research performance of Chinese higher education institutions using data envelopment analysis. China Econ. Rev. 19(4), 679–696 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2008.08.004
Kirjavainen, T.: Efficiency of Finnish general upper secondary schools: an application of stochastic frontier analysis with panel data. Educ. Econ. 20(4), 343–364 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/09645292.2010.510862
Kortz, M., Vegas, A., Moore, S.P., McCray, E., Mureb, M., Bernstein, J.E., May, J., Bishop, B., Frydenlund, M., Dobson, J.R.: National resident matching program performance among US MD and DO seniors in the early single accreditation graduate medical education era. Cureus J. Med. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.17319
Li, Q.: Nonparametric testing of closeness between two unknown distribution functions. Economet. Rev. 15(3), 261–274 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1080/07474939608800355
M.D. admissions. University of Michigan Medical School (2022). https://medicine.umich.edu/medschool/education/md-program/md-admissions. Accessed 12 Feb 2022
M.D. vs. D.O.: The Definitive Guide to Help You Decide: The SGU Pulse (2021). Retrieved from: https://www.sgu.edu/blog/medical/md-versus-do/
Mallon, W.T., Jones, R.F.: How do medical schools use measurement systems to track faculty activity and productivity in teaching? Acad. Med. 77(2), 115–123 (2002)
Matthews, C.N., Estrada, D.C., George-Weinstein, M., Claeson, K.M., Roberts, M.B.: Evaluating the influence of research on match success for osteopathic and allopathic applicants to residency programs. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 119(9), 588–596 (2019). https://doi.org/10.7556/jaoa.2019.102
McMillan, M.L., Datta, D.: The relative efficiencies of Canadian universities: a DEA perspective. Can. Public Policy/analyse De Politiques 24(4), 485–511 (1998)
Mitsouras, K., Dong, F., Safaoui, M.N., Helf, S.C.: Student academic performance factors affecting matching into first-choice residency and competitive specialties. BMC Med. Educ. 19(241), 1–13 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1669-9
Mosadeghrad, A.M., Esfahani, P., Nikafshar, M.: Hospitals’ efficiency in Iran: a systematic review and meta-analysis of two decades of research. J. Payavard Salamat 11(3), 318–331 (2017)
Nakata, Y., Watanabe, Y., Otake, H.: Association between surgeons’ technical efficiency and hospital revenue. INQUIRY J. Health Care Organ. Provision Financ. 56, 1–6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/0046958019889443
Nuthalapaty, F.S., Jackson, J.R., Owen, J.: The influence of quality-of-life, academic, and workplace factors on residency program selection. Acad. Med. 79(5), 417–425 (2004)
Oladeji, L.O., Raley, J.A., Smith, S., Perez, J.L., Mcgwin, G., Ponce, B.A.: Behind the match process: is there any financial difference lurking below the specialty of choice? Am. Surg. 82(12), 1163–1168 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1177/000313481608201221
Remnick, J.: The ultimate guide to the medical residency match process. Thalamus (2019). Retrieved from https://thalamusgme.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-the-medical-residency-match-process/
Ruggiero, J.: Measurement error, education production and data envelopment analysis. Econ. Educ. Rev. 25(3), 327–333 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econedurev.2005.03.003
Salas-Velasco, M.: Can educational laws improve efficiency in education production? Assessing students’ academic performance at Spanish public universities, 2008–2014. High. Educ. 77(6), 1103–1123 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-018-0322-6
Selva, M.L.M., Medina, R.P., Marzal, C.C.: Calidad y eficiencia de las Universidades Públicas Españolas. Revista De Estudios Regionales 99, 135–154 (2014)
Shulruf, B., Booth, R., Baker, H., Bagg, W., Barrow, M.: Using the objective borderline method (OBM) to support Board of Examiners’ decisions in a medical programme. J. Furth. High. Educ. 41(3), 425–434 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/0309877X.2015.1117603
Sikka, V., Luke, R.D., Ozcan, Y.A.: The efficiency of hospital-based clusters: Evaluating system performance using data envelopment analysis. Health Care Manag. Rev. 34(3), 251–261 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1097/HMR.0b013e3181a16ba7
Silverman, B.W.: Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis, vol. 26. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1986)
Simar, L., Wilson, P.W.: Sensitivity analysis of efficiency scores: how to bootstrap in nonparametric frontier models. Manag. Sci. 44(1), 49–61 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.44.1.49
Simar, L., Wilson, P.W.: A general methodology for bootstrap** in non-parametric frontier models. J. Appl. Stat. 27(6), 779–802 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1080/02664760050081951
Simar, L., Zelenyuk, V.: On testing equality of distributions of technical efficiency scores. Economet. Rev. 25(4), 497–522 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1080/07474930600972582
Stillman, M.D., Miller, K.H., Ziegler, C.H., Upadhyay, A., Mitchell, C.K.: Program characteristics influencing allopathic students’ residency selection. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 116(4), 214–226 (2016). https://doi.org/10.7556/jaoa.2016.046
Thanassoulis, E.: A data envelopment analysis approach to clustering operating units for resource allocation purposes. Omega 24(4), 463–476 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0483(96)00013-8
The Parts of Your Medical School Application: Association of American Medical Colleges (2020). Retrieved from: https://students-residents.aamc.org/applying-medical-school/faq/what-parts-your-application-tell-medical-schools-2/
Titus, M.A., Vamosiu, A., Buenaflor, S.H., Lukszo, C.M.: Persistent cost efficiency at public community colleges in the US: a stochastic frontier analysis. Res. High. Educ. 62(8), 1168–1197 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11162-021-09634-y
Toci, G.R., Elsner, J.A., Bigelow, B.F., Bryant, B.R., LaPorte, D.M.: Medical student research productivity: which variables are associated with matching to a highly ranked orthopaedic residency program? J. Surg. Educ. 78(2), 512–518 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsurg.2020.08.024
Tran, C.-D.T.T., Villano, R.A.: An empirical analysis of the performance of Vietnamese higher education institutions. J. Furth. High. Educ. 41(4), 530–544 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/0309877X.2015.1135886
U.S. Medical School Applications and Matriculants by School: Association of American Medical Colleges (2019). Retrieved from: https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/students-residents/interactive-data/2019-facts-applicants-and-matriculants-data
Waheed, A., Rana, M.S., Rauf, M.A., Green, L., Green, S., Azhar, E.: Applicants’ interview experience of family medicine residency match: reflections from a quality improvement initiative at a community hospital. Cureus (2020). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.11054
Weissbart, S.J., Kim, S.J., Feinn, R.S., Stock, J.A.: Relationship between the number of residency applications and the yearly match rate: time to start thinking about an application limit? J. Grad. Med. Educ. 7(1), 81–85 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4300/JGME-D-14-00270.1
What to expect in Medical School. AAMC. (n.d.). https://students-residents.aamc.org/choosing-medical-career/what-expect-medical-school. Accessed 12 Feb 2022
Wu, T.C., McCloskey, S.A., Wallner, P.E., Steinberg, M.L., Raldow, A.C.: The declining residency applicant pool: a multi-institutional medical student survey to identify precipitating factors. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 6(1), 100597 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adro.2020.10.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.H.A.R, C.E.G and L.S. wrote the main manuscript text. J.H.A.R. and A.J.R.T. designed and reviewed the method. Q.L. prepared all tables and figures. All the authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ablanedo-Rosas, J.H., Gonzalez, C.E., Smith, L.R. et al. A bootstrap DEA approach to estimate residency match rate efficiency: the case of allopathic medical schools in Texas. Health Serv Outcomes Res Method 24, 170–199 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10742-023-00308-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10742-023-00308-z