Abstract
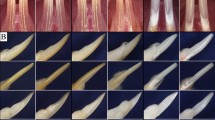
Mutations in the gene encoding family with sequence similarity 20, member A (FAM20A) caused amelogenesis imperfecta (AI), in humans. However, the roles of FAM20A in amelogenesis and dentinogenesis are poorly understood. In this study, we generated a Fam20a knockout (Sox2-Cre;Fam20afl/fl) mouse model by crossing Fam20afl/fl mice with Sox2-Cre transgenic mice, in which Fam20a was ablated in both dental epithelium and dental mesenchyme. We found that these mice developed an enamel phenotype that resembles human AI associated with FAM20A mutations, but did not have apparent dentin defects. The secretory stage ameloblasts in the mandibular incisors from the Sox2-Cre;Fam20afl/fl mice were shorter and detached from the enamel matrix, and subsequently lost their polarity, became disorganized and formed numerous spherical extracellular matrices in place of normal enamel. At the molecular level, the Sox2-Cre;Fam20afl/fl mice displayed dramatically reduced expression levels of the genes encoding the enamel matrix proteins, but unaltered levels of the genes encoding the dentin matrix proteins. Moreover, Fam20a ablation resulted in a great decrease in FAM20C protein level, but it did not alter the intracellular localization of FAM20C protein in ameloblasts and odontoblasts. These results indicate that FAM20A is essential for amelogenesis, but is dispensable for dentinogenesis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ababneh FK, AlSwaid A, Youssef T, Al Azzawi M, Crosby A, AlBalwi MA (2013) Hereditary deletion of the entire fam20c gene in a patient with Raine syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 161A(12):3155–3160
Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA, Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ, Muller R (2010) Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res 25(7):1468–1486
Butler WT, Bhown M, DiMuzio MT, Cothran WC, Linde A (1983) Multiple forms of rat dentin phosphoproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys 225(1):178–186
Cui J, **ao J, Tagliabracci VS, Wen J, Rahdar M, Dixon JE (2015) A secretory kinase complex regulates extracellular protein phosphorylation. eLife 4:e06120
Faundes V, Castillo-Taucher S, Gonzalez-Hormazabal P, Chandler K, Crosby A, Chioza B (2014) Raine syndrome: an overview. Eur J Med Genet 57(9):536–542
Fukumoto S, Kiba T, Hall B, Iehara N, Nakamura T, Longenecker G, Krebsbach PH, Nanci A, Kulkarni AB, Yamada Y (2004) Ameloblastin is a cell adhesion molecule required for maintaining the differentiation state of ameloblasts. J Cell Biol 167(5):973–983
Gibson MP, Zhu Q, Wang S, Liu Q, Liu Y, Wang X, Yuan B, Ruest LB, Feng JQ, D’Souza RN et al (2013) The rescue of dentin matrix protein 1 (dmp1)-deficient tooth defects by the transgenic expression of dentin sialophosphoprotein (dspp) indicates that dspp is a downstream effector molecule of dmp1 in dentinogenesis. J Biol Chem 288(10):7204–7214
Hayashi S, Lewis P, Pevny L, McMahon AP (2002) Efficient gene modulation in mouse epiblast using a sox2cre transgenic mouse strain. Mech Dev 119(Suppl 1):S97–S101
Hu JC, Lertlam R, Richardson AS, Smith CE, McKee MD, Simmer JP (2011) Cell proliferation and apoptosis in enamelin null mice. Eur J Oral Sci 119(Suppl 1):329–337
Ishikawa HO, Xu A, Ogura E, Manning G, Irvine KD (2012) The Raine syndrome protein fam20c is a Golgi kinase that phosphorylates bio-mineralization proteins. PLoS ONE 7(8):e42988
Jaureguiberry G, De la Dure-Molla M, Parry D, Quentric M, Himmerkus N, Koike T, Poulter J, Klootwijk E, Robinette SL, Howie AJ et al (2012) Nephrocalcinosis (enamel renal syndrome) caused by autosomal recessive fam20a mutations. Nephron Physiol 122(1–2):1–6
Kantaputra PN, Kaewgahya M, Khemaleelakul U, Dejkhamron P, Sutthimethakorn S, Thongboonkerd V, Iamaroon A (2014) Enamel-renal–gingival syndrome and fam20a mutations. Am J Med Genet A 164A(1):1–9
Koike T, Izumikawa T, Tamura J, Kitagawa H (2009) Fam20b is a kinase that phosphorylates xylose in the glycosaminoglycan-protein linkage region. Biochem J 421(2):157–162
Li LL, Liu PH, **e XH, Ma S, Liu C, Chen L, Qin CL (2016) Loss of epithelial fam20a in mice causes amelogenesis imperfecta, tooth eruption delay and gingival overgrowth. Int J Oral Sci 8(2):98–109
Liang T, Meng T, Wang S, Qin C, Lu Y (2016) The lpv motif is essential for the efficient export of secretory dmp1 from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Physiol 231(7):1468–1475
Liang T, Zhang H, Xu Q, Wang S, Qin C, Lu Y (2019) Mutant dentin sialophosphoprotein causes dentinogenesis imperfecta. J Dent Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034519854029
Meng T, Huang Y, Wang S, Zhang H, Dechow PC, Wang X, Qin C, Shi B, D’Souza RN, Lu Y (2015) Twist1 is essential for tooth morphogenesis and odontoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem 290(49):29593–29602
O’Sullivan J, Bitu CC, Daly SB, Urquhart JE, Barron MJ, Bhaskar SS, Martelli-Junior H, dos Santos Neto PE, Mansilla MA, Murray JC et al (2011) Whole-exome sequencing identifies fam20a mutations as a cause of amelogenesis imperfecta and gingival hyperplasia syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 88(5):616–620
Ohyama Y, Lin JH, Govitvattana N, Lin IP, Venkitapathi S, Alamoudi A, Husein D, An C, Hotta H, Kaku M et al (2016) Fam20a binds to and regulates fam20c localization. Sci Rep 6:27784
Qin C, Cook RG, Orkiszewski RS, Butler WT (2001) Identification and characterization of the carboxyl-terminal region of rat dentin sialoprotein. J Biol Chem 276(2):904–909
Qin C, Brunn JC, Cook RG, Orkiszewski RS, Malone JP, Veis A, Butler WT (2003) Evidence for the proteolytic processing of dentin matrix protein 1. Identification and characterization of processed fragments and cleavage sites. J Biol Chem 278(36):34700–34708
Simpson MA, Hsu R, Keir LS, Hao J, Sivapalan G, Ernst LM, Zackai EH, Al-Gazali LI, Hulskamp G, Kingston HM et al (2007) Mutations in fam20c are associated with lethal osteosclerotic bone dysplasia (Raine syndrome), highlighting a crucial molecule in bone development. Am J Hum Genet 81(5):906–912
Simpson MA, Scheuerle A, Hurst J, Patton MA, Stewart H, Crosby AH (2009) Mutations in fam20c also identified in non-lethal osteosclerotic bone dysplasia. Clin Genet 75(3):271–276
Sun Y, Lu Y, Chen S, Prasad M, Wang X, Zhu Q, Zhang J, Ball H, Feng J, Butler WT et al (2010) Key proteolytic cleavage site and full-length form of dspp. J Dent Res 89(5):498–503
Tagliabracci VS, Engel JL, Wen J, Wiley SE, Worby CA, Kinch LN, **ao J, Grishin NV, Dixon JE (2012) Secreted kinase phosphorylates extracellular proteins that regulate biomineralization. Science 336(6085):1150–1153
Tagliabracci VS, Wiley SE, Guo X, Kinch LN, Durrant E, Wen J, **ao J, Cui J, Nguyen KB, Engel JL et al (2015) A single kinase generates the majority of the secreted phosphoproteome. Cell 161(7):1619–1632
Vogel P, Hansen GM, Read RW, Vance RB, Thiel M, Liu J, Wronski TJ, Smith DD, Jeter-Jones S, Brommage R (2012) Amelogenesis imperfecta and other biomineralization defects in fam20a and fam20c null mice. Vet Pathol 49(6):998–1017
Wang X, Hao J, **e Y, Sun Y, Hernandez B, Yamoah AK, Prasad M, Zhu Q, Feng JQ, Qin C (2010) Expression of fam20c in the osteogenesis and odontogenesis of mouse. J Histochem Cytochem 58(11):957–967
Wang X, Wang S, Li C, Gao T, Liu Y, Rangiani A, Sun Y, Hao J, George A, Lu Y et al (2012a) Inactivation of a novel fgf23 regulator, fam20c, leads to hypophosphatemic rickets in mice. PLoS Genet 8(5):e1002708
Wang X, Wang S, Lu Y, Gibson MP, Liu Y, Yuan B, Feng JQ, Qin C (2012b) Fam20c plays an essential role in the formation of murine teeth. J Biol Chem 287(43):35934–35942
Wang SK, Aref P, Hu Y, Milkovich RN, Simmer JP, El-Khateeb M, Daggag H, Baqain ZH, Hu JC (2013a) Fam20a mutations can cause enamel-renal syndrome (ERS). PLoS Genet 9(2):e1003302
Wang SK, Samann AC, Hu JC, Simmer JP (2013b) Fam20c functions intracellularly within both ameloblasts and odontoblasts in vivo. J Bone Miner Res 28(12):2508–2511
Wang X, Jung J, Liu Y, Yuan B, Lu Y, Feng JQ, Qin C (2013c) The specific role of fam20c in amelogenesis. J Dent Res 92(11):995–999
Wang SK, Reid BM, Dugan SL, Roggenbuck JA, Read L, Aref P, Taheri AP, Yeganeh MZ, Simmer JP, Hu JC (2014) Fam20a mutations associated with enamel renal syndrome. J Dent Res 93(1):42–48
Zhang H, **e X, Liu P, Liang T, Lu Y, Qin C (2018) Transgenic expression of dentin phosphoprotein (dpp) partially rescued the dentin defects of dspp-null mice. PLoS ONE 13(4):e0195854
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research [Grant Numbers DE022549 (to CQ), DE027345 (to YL and CQ)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL and SF contributed to design, data acquisition, analysis and interpretation, drafted and critically revised the manuscript. HZ and SW contributed to data acquisition, analysis, drafted and critically revised the manuscript; QX contributed to data acquisition, analysis and critically revised the manuscript; CQ contributed to conception, interpretation, drafted and critically revised the manuscript; YL contributed to conception, design, interpretation, drafted and critically revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the submitted manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with respect to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Saiyin, W., Zhang, H. et al. FAM20A is essential for amelogenesis, but is dispensable for dentinogenesis. J Mol Hist 50, 581–591 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-019-09851-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-019-09851-x