Abstract
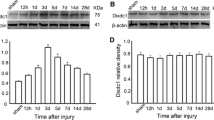
p21-activated Kinase 6 (PAK6) is a serine/threonine kinase belonging to the p21-activated kinase (PAK) family. PAK kinases are well-known regulators of a wide variety of cellular functions, including regulation of cytoskeleton rearrangement, cell survival, apoptosis and the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. To elucidate the expressions and possible functions of PAK6 in central nervous system (CNS) lesion and repair, we performed a traumatic brain injury (TBI) model in adult rats. Western blot analysis revealed that PAK6 level significantly increased at day 3 after damage, and then declined during the following days. Besides, double immunofluorescence staining showed PAK6 was primarily expressed in the neurons and a few of glial cells in the normal group. While after injury, the expression of PAK6 was increased significantly in the astrocytes and neurons, and the astrocytes had largely proliferated. We also examined the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) whose change was correlated with the expression of PAK6. Importantly, double immunofluorescence staining revealed that cell proliferation evaluated by PCNA appeared in many PAK6-expressing cells at day 3 after injury. In addition, injury-induced expression of PAK6 was co-labeled by active caspase-3 during neuronal apoptosis after injury. Collectively, we hypothesized PAK6 may play important roles in CNS pathophysiology after TBI and further research is needed to have a good understanding of its function and mechanism.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAK6:
-
p21-activated Kinase 6
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence system
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- NeuN:
-
Neuronal nuclei
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- PCNA:
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase
References
Arias-Romero LE, Chernoff J (2008) A tale of two Paks. Biol Cell 100:97–108
Bagrodia S, Taylor SJ, Jordon KA, Van Aelst L, Cerione RA (1998) A novel regulator of p21-activated kinases. J Biol Chem 273:23633–23636
Bokoch GM (2003) Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 72:743–781
Bredesen DE (1995) Neural apoptosis. Ann Neurol 38:839–851
Chen XH, Iwata A, Nonaka M, Browne KD, Smith DH (2003) Neurogenesis and glial proliferation persist for at least one year in the subventricular zone following brain trauma in rats. J Neurotrauma 20:623–631
Chen SH, Chang CY, Chang HK, Chen WC, Lin MT, Wang JJ, Chen JC, Chang FM (2009) Premarin stimulates estrogen receptor-alpha to protect against traumatic brain injury in male rats. Crit Care Med 37:3097–3106
Chirumamilla S, Sun D, Bullock MR, Colello RJ (2002) Traumatic brain injury induced cell proliferation in the adult mammalian central nervous system. J Neurotrauma 19:693–703
Clark RS, Chen J, Watkins SC, Kochanek PM, Chen M, Stetler RA, Loeffert JE, Graham SH (1997) Apoptosis-suppressor gene bcl-2 expression after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurosci 17:9172–9182
Clark RS, Kochanek PM, Watkins SC et al (2000) Caspase-3 mediated neuronal death after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurochem 74:740–753
Dan C, Nath N, Liberto M, Minden A (2002) PAK5, a new brain-specific kinase, promotes neurite outgrowth in N1E–115 cells. Mol Cell Biol 22:567–577
Di Giovanni S, Movsesyan V, Ahmed F, Cernak I, Schinelli S, Stoica B, Faden AI (2005) Cell cycle inhibition provides neuroprotection and reduces glial proliferation and scar formation after traumatic brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8333–8338
Elzer JG, Muhammad S, Wintermantel TM, Regnier-Vigouroux A, Ludwig J, Schutz G, Schwaninger M (2010) Neuronal estrogen receptor-alpha mediates neuroprotection by 17beta-estradiol. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:935–942
Erhardt L (1996) Biochemical markers in acute myocardial infarction—the beginning of a new era? Eur Heart J 17:1781–1782
Hammond J, Le Q, Goodyer C, Gelfand M, Trifiro M, LeBlanc A (2001) Testosterone-mediated neuroprotection through the androgen receptor in human primary neurons. J Neurochem 77:1319–1326
Hofmann C, Shepelev M, Chernoff J (2004) The genetics of Pak. J Cell Sci 117:4343–4354
Jaffer ZM, Chernoff J (2002) p21-activated kinases: three more join the Pak. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34:713–717
Kaur R, Liu X, Gjoerup O, Zhang A, Yuan X, Balk SP, Schneider MC, Lu ML (2005) Activation of p21-activated kinase 6 by MAP kinase kinase 6 and p38 MAP kinase. J Biol Chem 280:3323–3330
Keane RW, Kraydieh S, Lotocki G, Alonso OF, Aldana P, Dietrich WD (2001) Apoptotic and antiapoptotic mechanisms after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:1189–1198
Knaus UG, Morris S, Dong HJ, Chernoff J, Bokoch GM (1995) Regulation of human leukocyte p21-activated kinases through G protein–coupled receptors. Science 269:221–223
Konigsmark BW (1970) Methods for the counting of Neurons. In: Nauta WJH, Ebbesson SOE (eds) Contemporary research methods in neuroanatomy. New York: Springer-Verlag, pp 315–340
Kumar R, Vadlamudi RK (2002) Emerging functions of p21-activated kinases in human cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 193:133–144
Kumar R, Gururaj AE, Barnes CJ (2006) p21-activated kinases in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:459–471
Laird MD, Vender JR, Dhandapani KM (2008) Opposing roles for reactive astrocytes following traumatic brain injury. Neurosignals 16:154–164
Lee SR, Ramos SM, Ko A, Masiello D, Swanson KD, Lu ML, Balk SP (2002) AR and ER interaction with a p21-activated kinase (PAK6). Mol Endocrinol 16:85–99
Lenzlinger PM, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Laurer HL, McIntosh TK (2001) The duality of the inflammatory response to traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol 24:169–181
Li LZ, Bao YJ, Zhao M (2010) 17Beta-estradiol attenuates programmed cell death in cortical pericontusional zone following traumatic brain injury via upregulation of ERalpha and inhibition of caspase-3 activation. Neurochem Int 58:126–133
Liu Y, Wang Y, Cheng C, Chen Y et al (2010) A relationship between p27(kip1) and Skp2 after adult brain injury: implications for glial proliferation. J Neurotrauma 27:361–371
Manser E, Leung T, Salihuddin H, Zhao ZS, Lim L (1994) A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature 367:40–46
Martin GA, Bollag G, McCormick F, Abo A (1995) A novel serine kinase activated by rac1/CDC42Hs-dependent autophosphorylation is related to PAK65 and STE20. EMBO J 14:1970–1978
Morris GF, Mathews MB (1989) Regulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem 264:13856–13864
Myer DJ, Gurkoff GG, Lee SM, Hovda DA, Sofroniew MV (2006) Essential protective roles of reactive astrocytes in traumatic brain injury. Brain 129:2761–2772
Nadeau S, Hein P, Fernandes KJ, Peterson AC, Miller FD (2005) A transcriptional role for C/EBP beta in the neuronal response to axonal injury. Mol Cell Neurosci 29:525–535
Nekrasova T, Jobes ML, Ting JH, Wagner GC, Minden A (2008) Targeted disruption of the Pak5 and Pak6 genes in mice leads to deficits in learning and locomotion. Dev Biol 322:95–108
Nortje J, Menon DK (2004) Traumatic brain injury: physiology, mechanisms, and outcome. Curr Opin Neurol 17:711–718
Patel T, Gores GJ, Kaufmann SH (1996) The role of proteases during apoptosis. FASEB J 10:587–597
Pearl-Yafe M, Halperin D, Scheuerman O, Fabian I (2004) The p38 pathway partially mediates caspase-3 activation induced by reactive oxygen species in Fanconi anemia C cells. Biochem Pharmacol 67:539–546
Pike CJ, Carroll JC, Rosario ER, Barron AM (2009) Protective actions of sex steroid hormones in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neuroendocrinol 30:239–258
Qu J, Li X, Novitch BG, Zheng Y, Kohn M, **e JM, Kozinn S, Bronson R, Beg AA, Minden A (2003) PAK4 kinase is essential for embryonic viability and for proper neuronal development. Mol Cell Biol 23:7122–7133
Schrantz N, da Silva Correia J, Fowler B, Ge Q, Sun Z, Bokoch GM (2004) Mechanism of p21-activated kinase 6-mediated inhibition of androgen receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 279:1922–1931
Tatsumi K, Haga S, Matsuyoshi H, Inoue M, Manabe T, Makinodan M, Wanaka A (2005) Characterization of cells with proliferative activity after a brain injury. Neurochem Int 46:381–389
Trivedi AK, Bararia D, Christopeit M, Peerzada AA, Singh SM, Kieser A, Hiddemann W, Behre HM, Behre G (2007) Proteomic identification of C/EBP-DBD multiprotein complex: JNK1 activates stem cell regulator C/EBPalpha by inhibiting its ubiquitination. Oncogene 26:1789–1801
Urrea C, Castellanos DA, Sagen J, Tsoulfas P, Bramlett HM, Dietrich WD (2007) Widespread cellular proliferation and focal neurogenesis after traumatic brain injury in the rat. Restor Neurol Neurosci 25:65–76
Wells CM, Jones GE (2010) The emerging importance of group II PAKs. Biochem J 425:465–473
Wen X, Li X, Liao B, Liu Y, Wu J, Yuan X, Ouyang B, Sun Q, Gao X (2009) Knockdown of p21-activated kinase 6 inhibits prostate cancer growth and enhances chemosensitivity to docetaxel. Urology 73:1407–1411
Yang F, Li X, Sharma M, Zarnegar M, Lim B, Sun Z (2001) Androgen receptor specifically interacts with a novel p21-activated kinase, PAK6. J Biol Chem 276:15345–15353
Zhao ZS, Manser E (2005) PAK and other Rho-associated kinases–effectors with surprisingly diverse mechanisms of regulation. Biochem J 386:201–214
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30770488, No. 30870320, No. 31070723 and No. 81070275); Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu province (No. BK2009156, No. BK2009157, No. BK2009161, and No. BK2010169); Nature Science Foundation of Jiangsu Colleges and Universities Grant (09KJB320011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wei Zhao and Jiao Yang are contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Yang, J., Shi, W. et al. Upregulation of p21-activated Kinase 6 in rat brain cortex after traumatic brain injury. J Mol Hist 42, 195–203 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9324-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9324-8