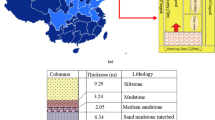
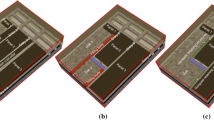
Abstract
To study the stability of roof areas in the process of rapid driving in coal roadways, the deformation law of roof areas under the interaction of different factors is systematically analyzed through mechanical analysis, numerical calculation, and industrial testing, yielding a reasonable selection basis of the critical parameters of roof space stability. The roof is difficult to control when the unsupported roof distance exceeds 2.0 m and the roof thickness is less than 0.9 m. Considering the tunnel excavation safety and effectiveness, the support technology principles of "large-angle control span" and "classification control technology of roadway surrounding rock stability" based on the support "small-step" excavation method were realized in the case study of the 150,802 machine roadway of Liuzhuang Coal Mine, China. The resulting rapid tunneling system made it possible to increase the tunneling speed from 300 to 500 m/month, i.e. by 67%. The whole roadway remained relatively stable, verifying the proposed approach feasibility.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used in the field measurement can be obtained from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Bai JB, **ao TQ, Li L (2011) Difference method for determining goaf roof distance in roadway excavation and its application. J Coal 36:920–924. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2011.06.020
Cai M, Kaiser PK (2014) In-situ rock spalling strength near excavation boundaries. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47:659–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0437-0
Cheluszka P (2015) Computer-aided design of robotised technology for manufacturing working units of mining machines. Int J Min Reclam Environ 29(1):62–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/17480930.2014.955959
Chen Y, Bai JB, Yan S, Hao SP, Dao VD (2016) A method for computing unsupported roof distance in roadway advancement and its in-situ application. Int J Min Sci Technol 26(04):551–556
Chen H, Ye YC, Wang QH (2020) Study on failure mode of direct roof in weak layer of roadway based on Rock beam-block theory. Geomechanics 41:1447–1454. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2019.0294
Chu XW, Wu YZ, Wu ZG (2020) Deformation characteristics of heading roof and determination method of reasonable unsupported roof distance. J Min Saf Eng 37:908–917. https://doi.org/10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2020.05.006
Dogruoz C, Bolukbasi N (2014) Effect of cutting tool blunting on the performances of various mechanical excavators used in low-and medium-strength rocks[J]. Bull Eng Geol Environ 73(3):781–789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-013-0551-y
Hou GY, Li JJ (2020) Whole process analysis of surrounding rock-support interaction under elastic-plastic deformation condition. Geomechanics 33:961–970. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2012.04.025
Huang SJ, Zhao GM, Meng XR, Cheng X, Xu WS, Liu G, Sk Z (2022) Study of prevention and control technology for roadway excavation under the soft and extra-thick coal roof in luling coal mine. Processes 10:1835
Jiao Y (2014) Application of digging anchor integrated machine in coal mine production. Sci Technol Inf 2014:39–40
Kang HP (2016) 60 years’ development and Prospect of bolt support technology in coal mine roadway in China. J China Univ Min Technol 45:1071–1081. https://doi.org/10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000583
Lu HF, Yao DX (2014) Study on stress distribution law and failure depth of layered rock mass in mining floor. J Rock Mech Eng 33:2030–2039. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.10.009
Lu W, Wang L, Song KZ, Sun HB, Chen DM (2022) Safety evaluation of anchoring-grouting rock-support interaction in deep underground excavation based on support vector machine learning. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civil Eng 46(5):3805–3817
Ma P, Qian DY, Zhang N (2020) Application of bolter miner rapid excavation technology in deep underground roadway in inner mongolia: a case study. Sustainability 12:2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072588
Ning S, Su H, Gao J (2015) Research on automatic section precision forming of boom-type roadheader. In: Proceedings of the 2015 international conference on intelligent system research and mechatronics engineering, pp 1250~1256. https://doi.org/10.2991/isrme-15.2015.254
Niu SQ, Yang SS, Li Y (2014) Shear instability mechanism and support method of roof layer of long-span roadway. J Coal 39:325–331. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2013.1404
Ozturk CA, Simdi E (2014) Geostatistical investigation of geotechnical and constructional properties in Kadikoy–Kartal subway, Turkey. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 41:35–45
Salsani A, Daneshian J, Shariati S et al (2014) Predicting roadheader performance by using artificial neural network. Neural Comput Appl 24(7–8):1823–1831
Tian JY (2017) Study on support optimization of rectangular coal roadway under horizontal stress. Kunming University of Technology, Kunming
Wang JH (2014) China mechanized road header status and bolt support technology in mine seam roadway. Coal Sci Tech 31:6–10
Wang XF, Zhang DS, Shao P, Zhang W (2011) Rapid tunneling technology of deep soft rock bolt shotcrete support roadway. J Min Saf Eng 28:415–419
Wang H, Wang BK, Zhang XF (2021) Key technology research and engineering practice of intelligent rapid excavation in coal mine. J Coal 412:1–17. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.jj21.0412
Wang Q, Su X, ** Y, Sun CY, Yu SY, Zhao WZ, Feng YL (2023) Experimental Investigation of reservoir fluid interlayer crossflow through fracture during the drainage stage of coal measure gas well. Nat Resour Res 32:1283–1298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10187-3
Wu PQ (2017) Study on self stability law and construction scheme optimization of goaf roof in rapid coal roadway excavation. China Univ Min Technol 34:1585–1593
**a ZY, Tan ZY, Zhang JF (2021) Study on instability mechanism of extraction structure under undercut space based on thin plate theory in block caving method. Shock Vib. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5548213
**e ZZ, Zhang N, Qian D (2018) Rapid excavationand stability control of deep roadways for an underground coal minewith high production in Inner Mongolia. Sustainability 10:1160
Xue Q (2006) Elasticity. Peking University Press, Bei**g
Yan WF, Shi L (2018) Development status of coal roadway driving technology and equipment in China. Coal Min Mach 39:1–3. https://doi.org/10.13436/j.mkjx.201812001
Yang S, Hua XZ, Yang P, Liu X (2021) Determination and engineering practice of unsupported roof distance for rapid excavation of roadway with thick and hard basic roof. Geotechn Geol Eng 37:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-021-01820-0
Yang H, Lin H, Chen Y, Wang Y (2022a) Influence of wing crack propagation on the failure process and strength of fractured specimens. Bull Eng Geol Env 81:71
Yang P, Huang ZG, Liu X, Yang S (2022b) Filling wall mechanical analysis of gob-side entry retaining with composite roof. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-09468-7
Yang P, Pang DD, Liu J, Huang ZG, Xu WS, Dou ZS (2023) Experiment on deformation and failure characteristics of sandstone at different unloading rates. Alex Eng J 75:209–219
Yuan XP (2021) Application of all-in-one digging anchor machine in roadway excavation of Chang** Mine. Coal Chem Ind 44:71–73. https://doi.org/10.19286/j.cnki.cci.2021.03.023
Zhang ZQ (2018) Study on temporal and spatial evolution characteristics and support mechanism of surrounding rock stress shell of deep roadway. China University of mining and Technology, Bei**g
Zhang GF (2019) Application and improvement analysis of coal mine excavation anchor integrated machine. Energy Technol Manag 44:139–140
Zhao YL, Liu Q, Zhang C, Liao J, Lin H, Wang Y (2021) Coupled seepage-damage effect in fractured rock masses: model development and a case study. Int J of Rock Mech Min Sci 144:104822
Zhu HZ (2019) Reasonable reservation of unsupported roof distance and construction optimization in rapid tunneling of coal roadway. Coal Chem Ind 42:27–34. https://doi.org/10.19286/j.cnki.cci.2019.05.008
Zya B, Chang LC, Hz A (2019) Mechanism of rock burst caused by fracture of key strata during irregular working face mining and its prevention methods. Int J Min Sci Technol 29:889–897
Funding
We acknowledge the financial support for this work provided by The Tiandi Technology Co., Ltd., For The Provided Funding Of The Science And Technology Innovation And Entrepreneurship Fund (2021-2-TD-ZD008) (Research On Self-Relief Technology And Equipment Of Bedding Directional Hydraulic Slitting); The State Key Laboratory Open Fund Project (SKLMRDPC20KF01) (Prevention And Control Technology Of Cross-Cutting, Longitudinal Breaking, Unloading And Energy Dissipation For Coal-Rock Composite Dynamic Disasters In Deep Mines); Key project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China Regional Innovation and Development Joint Fund (U21A20110), risk identification and precise prevention and control of coal and rock dynamic disasters in deep high gas soft coal seams.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, X. Roof Stability Mechanism and Support Technology Optimization of Tunneling Roadway. Geotech Geol Eng 42, 561–574 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02589-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02589-0