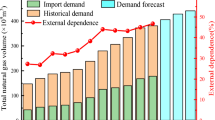
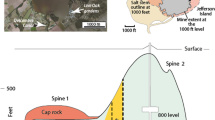
Abstract
Using deep salt caverns for underground energy storage is a globally recognized method of energy storage. The safety of gas storage and the utilization rate of salt mine formation resources are related to the pillar design of salt cavern gas storage. Existing theoretical research on the pillar design of salt cavern gas storage prioritizes universality. This may affect the accuracy of regional research. In this study, triaxial mechanical tests are conducted on salt rock under varying confining pressures. Moreover, a linear dilatancy limit equation is fitted according to the stress state at the dilatancy point. Based on the dilatancy failure mechanism of salt rock pillars, considering the influence of the cavern parameters of the salt rock and internal pressure during gas storage operation, the criteria for pillar failure were improved, and a theoretical method for pillar stability evaluation that is suitable for the **tan area was established. Through the comparison of numerical simulation and theoretical results under different working conditions, the influence laws on pillar stability in terms of pillar width, cavern air pressure and salt hole depth were obtained, and the accuracy of the theoretical method for pillar stability evaluation was verified. Using the pillar stability analysis method to calculate the actual working conditions of a gas storage cavern in **tan, the minimum operating pressure obtained was in line with the field working conditions. This method can provide a reference for future pillar design of salt caverns for gas storage in the **tan area.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aptukov VN (2017) Deformation criterion of salt rock failure. J Min Sci 52(3):448–453. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062739116030645
Búrest P, Brouard B (2003) Safety of salt caverns used for underground storage. Oil Gas Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.2516/ogst:2003023
Chen J, Ren S, Yang C et al (2013) Self-healing characteristics of damaged rock salt under different healing conditions. Materials (basel) 6(8):3438–3450. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6083438
Chen J, Lu D, Liu W et al (2020) Stability study and optimization design of small-spacing two-well (SSTW) salt caverns for natural gas storages. J Energy Storage 27:101131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2019.101131
Cording EJ, Hashash YMA, Oh J (2015) Analysis of pillar stability of mined gas storage caverns in shale formations. Eng Geol 184:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.001
Heusermann S, Fahland S, Eickemeier R (2009) Geomechanical stability and integrity of radioactive waste repositories in salt rock. In: ISRM international symposium on rock mechanics, China
Hou W, Wang H, Yuan L et al (2021) Experimental research into the effect of gas pressure, particle size and nozzle area on initial gas-release energy during gas desorption. Int J Min Sci Technol 31(2):253–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.01.002
Liu W, Zhang X, Li H et al (2020) Investigation on the deformation and strength characteristics of rock salt under different confining pressures. Geotech Geol Eng (dordr) 38(6):5703–5717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01388-1
Nazary Moghadam S, Mirzabozorg H, Noorzad A (2013) Modeling time-dependent behavior of gas caverns in rock salt considering creep, dilatancy and failure. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 33:171–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2012.10.001
Swift GM, Reddish DJ (2005) Underground excavations in rock salt. Geotech Geol Eng (dordr) 23(1):17–42
Wang T, Yan X, Yang H et al (2011) Stability analysis of the pillars between bedded salt cavern gas storages by cusp catastrophe model. Sci China Technol Sci 54(6):1615–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-011-4401-5
Wang T, Yang C, Yan X et al (2015) Allowable pillar width for bedded rock salt caverns gas storage. J Pet Sci Eng 127:433–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2015.01.040
Wang J, Zhang Q, Song Z et al (2020) Creep properties and damage constitutive model of salt rock under uniaxial compression. Int J Damage Mech 29(6):902–922. https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789519891768
Wang H, Zhang B, Yuan L et al (2022a) Analysis of precursor information for coal and gas outbursts induced by roadway tunneling: a simulation test study for the whole process. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 122:104349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2021.104349
Wang S, Wang H, Wu Z et al (2022b) Physical simulation technologies and testing system for cavern shape control from single-well solution mining in rock salt. Rev Sci Instrum 93(12):125101. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0108039
Yan C, XuY G (2007) Analysis on instability of the top pillar between overlap underground chambers induced by danymic loadings with catastrophy theory. Eng Mech 24(4):46–51
Yang C, **g W, Daemen JJK et al (2013) Analysis of major risks associated with hydrocarbon storage caverns in bedded salt rock. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 113:94–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2012.12.017
Yin H, Yang C, Ma H et al (2019) Study on damage and repair mechanical characteristics of rock salt under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(3):659–671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1604-0
Zhang QY, Duan K, Jiao YY et al (2017c) Physical model test and numerical simulation for the stability analysis of deep gas storage cavern group located in bedded rock salt formation. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 94:43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.02.015
Zhang N, Ma L, Wang M et al (2017a) Comprehensive risk evaluation of underground energy storage caverns in bedded rock salt. J Loss Prev Process Ind 45:264–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2016.10.016
Zhang N, Shi X, Wang T et al (2017b) Stability and availability evaluation of underground strategic petroleum reserve (SPR) caverns in bedded rock salt of **tan, China. Energy (oxf) 134:504–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.06.073
Zhang N, Liu W, Zhang Y et al (2020a) Microscopic pore structure of surrounding rock for underground strategic petroleum reserve (SPR) caverns in bedded rock salt. Energies (basel) 13(7):1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13071565
Zhang N, Shi X, Zhang Y et al (2020b) Tightness analysis of underground natural gas and oil storage caverns with limit pillar widths in bedded rock salt. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017
Zhang G, Liu Y, Wang T et al (2021) Pillar stability of salt caverns used for gas storage considering sedimentary rhythm of the interlayers. J Energy Storage 43:103229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2021.103229
Zhengjie L (2018) Stability analysis and application of gas storage pillar in deep salt rock. Dissertation, Shandong University
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (52174081).
Funding
The funding was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52174081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Wang, H., Zhu, H. et al. Long-Term Stability Analysis of Pillars in Salt Cavern Storage Based on the Salt Rock Dilatancy Boundary Evaluation Method. Geotech Geol Eng 41, 3349–3358 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02459-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02459-9