Abstract
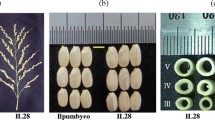
Grain weight (GW), one of the yield components of rice (Oryza sativa L.), is an important trait for improving rice productivity. In the 1990s, New Plant Type (NPT) rice breeding focused on improving the yield potential of rice varieties by introducing unique traits from Tropical Japonica Group cultivars. To reveal the genetic factors responsible for yield-related traits of NPT varieties, we previously developed 334 introgression lines with variations in traits inherited from NPT varieties in the genetic background of an Indica Group cultivar, ‘IR 64’. Three of the NPT varieties—‘IR65600-87-2-2-3’, ‘IR69093-41-2-3-2’, and ‘IR71195-AC1’—had heavier GW than ‘IR 64’. To identify the genetic basis for the heavier GW in these lines, here we performed QTL analysis in F2 (BC4F2 equivalent) populations. We detected one each QTL for GW on chromosome 5 in the three populations, and developed three near-isogenic lines (NILs) with a QTL for GW, qGW5 (qGW5.1-YP1, qGW5.2-YP5, and qGW5.3-YP10), through marker-assisted selection. These three NILs were confirmed to have heavier GW than ‘IR 64’. These NILs are useful materials in research and breeding for improvement of rice productivity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brondani C, Rangel PHN, Brondani RPV, Ferreira ME (2002) QTL map** and introgression of yield-related traits from Oryza glumaepatula to cultivated rice (Oryza sativa) using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:1192–1203
Fan C, **ng Y, Mao H, Lu T, Han B, Xu C, Li X, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112:1164–1171
Fujita D, Santos RE, Ebron LA, Telebanco-Yanoria MJ, Kato H, Kobayashi S, Uga Y, Araki E, Takai T, Tsunematsu H, Imbe T, Khush GS, Brar DS, Fukuta Y, Kobayashi N (2009) Development of introgression lines of an indica-type rice variety, IR64, for unique agronomic traits and detection of the responsible chromosomal regions. Field Crops Res 114:244–254
Fujita D, Santos RE, Ebron LA, Telebanco-Yanoria MJ, Kato H, Kobayashi S, Uga Y, Araki E, Takai T, Tsunematsu H, Imbe T, Khush GS, Brar DS, Fukuta Y, Kobayashi N (2010) Characterization of introgression lines for yield-related traits with Indica-type rice variety IR64 genetic background. JARQ 44:277–290
Fujita D, Santos RE, Ebron LA, Fukuta Y, Kobayashi N (2011) Plant Breeding 130(5):526–532 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2011.01864.x
Fujita D, Tagle AG, Ebron L, Fukuta Y, Kobayashi N (2012) Characterization of near-isogenic lines carrying QTL for high spikelet number with the genetic background of an indica rice variety IR64 (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 62:18–26
Fujita D, Trijatmiko KR, Tagle AG, Sapasap MV, Koide Y, Sasaki K, Tsakirpaloglou N, Gannaban RB, Nishimura T, Yanagihara S, Fukuta Y, Koshiba T, Slamet-Loedin IH, Ishimaru T, Kobayashi N (2013) NAL1 allele from a rice landrace greatly increases yield in modern indica cultivars. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:20431–20436
Guo T, Chen K, Dong NQ, Shi CL, Ye WW, Gao JP, Shan JX, Lin HX (2018) GRAIN SIZE AND NUMBER1 negatively regulates the OsMKKK10-OsMKK4-OsMPK6 cascade to coordinate the trade-off between grain number per panicle and grain size in rice. Plant Cell 30:871–888
Hu J, Wang Y, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu J, Yu H, Shi Z, Pan J, Zhang D, Kang S, Zhu L, Dong G, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhang G, **e L, **ong G, Li J, Qian Q (2015) A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant 8:1455–1465
Hu Z, Lu SJ, Wang MJ, He H, Sun L, Wang H, Liu XH, Jiang L, Sun JL, **n X, Kong W, Chu C, Xue HW, Yang J, Luo X, Liu JX (2018) A novel QTL qTGW3 encodes the GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase OsGSK5/OsSK41 that interacts with OsARF4 to negatively regulate grain size and weight in rice. Mol Plant 11:736–749
Ishimaru K, Hirotsu N, Madoka Y, Murakami N, Hara N, Onodera H, Kashiwagi T, Ujiie K, Shimizu B, Onishi A, Miyagawa H, Katoh E (2013) Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield. Nat Genet 45:707–711
Khush GS (1987) Rice breeding: past, present and future. J Genet 66:195–216
Khush GS (1995) Breaking the yield frontier of rice. GeoJournal 35:329–332
Khush GS, Virk PS (2005) Selection criteria. In: IR varieties and their impact, International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Philippines, pp 6–15
Koide Y, Fujita D, Tagle AG, Sasaki K, Ishimaru T, Fukuta Y, Kobayashi N (2013) QTL for spikelet number from a high-yielding rice variety Hoshiaoba detected in an introgression line with the genetic background of an indica rice variety IR64. Euphytica 192(1):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-0882-6
Kosambi D (1943) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugenet 12:172–175
Li J, Thomson M, McCouch SR (2004) Fine map** of a grain-weight quantitative trait locus in the pericentromeric region of rice chromosome 3. Genetics 168:2187–2195
Li Y, Fan C, **ng Y, Jiang Y, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, **ao J, He Y, Zhang Q (2011) Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet 43:1266–1269
Liu J, Chen J, Zheng X, Wu F, Lin Q, Heng Y, Tian P, Cheng ZJ, Yu X, Zhou K, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Wang H, Wan J (2017) GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signalling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice. Nat Plants 3:17043
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, ** of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Peng S, Khush GS, Virk P, Tang Q, Zou Y (2008) Progress in ideotype breeding to increase rice yield potential. Field Crops Res 108:32–38
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1988) Extraction of DNA from plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol Manual A6:1–10
Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Ebitani T, Kanegae H, Konishi S, Yano M (2008) Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat Genet 40:1023–1028
Si L, Chen J, Huang X, Gong H, Luo J, Hou Q, Zhou T, Lu T, Zhu J, Shangguan Y, Chen E, Gong C, Zhao Q, **g Y, Zhao Y, Li Y, Cui L, Fan D, Lu Y, Weng Q, Wang Y, Zhan Q, Liu K, Wei X, An K, An G, Han B (2016) OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice. Nat Genet 48:447–456
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630
Song XJ, Kuroha T, Ayano M, Furuta T, Nagai K, Komeda N, Segami S, Miura K, Ogawa D, Kamura T, Suzuki T, Higashiyama T, Yamasaki M, Mori H, Inukai Y, Wu J, Kitano H, Sakakibara H, Jacobsen SE, Ashikari M (2015) Rare allele of a previously unidentified histone H4 acetyltransferase enhances grain weight, yield, and plant biomass in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:76–81
Takano-Kai N, Jiang H, Kubo T, Sweeney M, Matsumoto T, Kanamori H, Padhukasahasram B, Bustamante C, Yoshimura A, Doi K, McCouch SR (2009) Evolutionary history of GS3, a gene conferring grain length in rice. Genetics 182:1323–1334
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2004) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.0. Raleigh, NC, Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University
Wang S, Wu K, Yuan Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Lin X, Zeng R, Zhu H, Dong G, Qian Q, Zhang G, Fu X (2012) Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44:950–954
Wang Y, **ong G, Hu J, Jiang L, Yu H, Xu J, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu E, Xu J, Ye W, Meng X, Liu R, Chen H, **g Y, Wang Y, Zhu X, Li J, Qian Q (2015) Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Nat Genet 47:944–948
Wang A, Hou Q, Si L, Huang X, Luo J, Lu D, Zhu J, Shangguan Y, Miao J, **e Y, Wang Y, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhou C, Li Y, Fan D, Lu Y, Tian Q, Wang Z, Han B (2019) The PLATZ transcription factor GL6 affects grain length and number in rice. Plant Physiol 180:2077–2090
Weng J, Gu S, Wan X, Gao H, Guo T, Su N, Lei C, Zhang X, Cheng Z, Guo X, Wang J, Jiang L, Zhai H, Wan J (2008) Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res 18:1199–1209
** of a grain weight quantitative trait locus on rice chromosome 8 using near-isogenic lines derived from a cross between Oryza sativa and Oryza rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 113:885–894
Yonemaru J, Yamamoto T, Fukuoka S, Uga Y, Hori K, Yano M (2010) Q-TARO: QTL annotation rice online database. Rice 3:194–203
Yoshida S, Parao FT (1976) Climatic influence on yield and yield components of lowland rice in the tropics In: Proceedings of the symposium on climate and rice, International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Philippines, pp 471–494
Young ND, Tanksley SD (1989) Restriction fragment length polymorphism maps and the concept of graphical genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 77:95–101
Yuan H, Gao P, Hu X, Yuan M, Xu Z, ** M, Song W, Zhan S, Zhu X, Tu B, Li T, Wang Y, Ma B, Qin P, Chen W, Li S (2022) Fine map** and candidate gene analysis of qGSN5, a novel quantitative trait locus coordinating grain size and grain number in rice. Theor Appl Genet 135:51–64
Zhang X, Wang JF, Huang J, Lan H, Wang C, Yin C, Wu Y, Tang H, Qian Q, Li J, Zhang H (2012) Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:21534–21539
Zhou SR, Xue HW (2020) The rice PLATZ protein SHORT GRAIN6 determines grain size by regulating spikelet hull cell division. J Integr Plant Biol 62:847–864
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Japanese government (IRRI–Japan Collaborative Research Project). This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP18K05586.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujita, D., Tagle, A.G., Koide, Y. et al. Characterization of QTLs for grain weight from New Plant Type rice cultivars through the development of near-isogenic lines with an IR 64 background. Euphytica 218, 50 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03008-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03008-w