Abstract
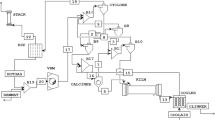
Uncertainties in the process industries are the biggest challenge for smooth operation. This study is based on the use of artificial intelligence based surrogate modeling for predicting and optimizing emissions in combustion sections of cement manufacturing plants under uncertainty. Uncertainties in feed flow rate, kiln air flow rate, tertiary air flow rate, and coal flow rate in the combustion sections of the plant are the subject of the study. Initially, an Aspen Plus model of the kiln and calciner units of the cement plant was developed and converted into a dynamic mode to generate 700 data samples with 10% uncertainty. Then, genetic algorithm (GA), particle swarm optimization (PSO), and GA-PSO frameworks were used to optimize the process conditions using Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models as surrogates. The GA-PSO framework exhibited an advantage over GA and PSO in predicting and optimizing CO2, and CO emissions. Besides, ANN models were used as a surrogate within the SOBOL and Fourier Amplitude Sensitivity Test frameworks for performing sensitivity analysis of the process. The sensitivity analysis was performed to identify the process conditions with the highest sensitivity toward the emissions. Based on sensitivity analysis, total coal and tertiary air were found to be more influencing parameters on process output. This study provides a baseline for real-time predicting and optimizing emissions at the cement plant.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Akram, A. U., Ahmad, I., Chughtai, A., & Kano, M. (2018). Exergy analysis and optimization of naphtha reforming process with uncertainty. International Journal of Exergy, 26(3), 247–262. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEX.2018.093138
Ali, M. B., Saidur, R., & Hossain, M. S. (2011). A review on emission analysis in cement industries. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15(5), 2252–2261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.02.014
Angelopoulos, A., Michailidis, E. T., Nomikos, N., Trakadas, P., Hatziefremidis, A., Voliotis, S., & Zahariadis, T. (2020). Tackling faults in the industry 4.0 era—a survey of machine-learning solutions and key aspects. Sensors (switzerland), 20(1), 1–34. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010109
Ayvaz, S., & Alpay, K. (2021). Predictive maintenance system for production lines in manufacturing : A machine learning approach using IoT data in real-time. Expert Systems with Applications, 173, 114598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114598
Bakdi, A., Kouadri, A., & Bensmail, A. (2017). Fault detection and diagnosis in a cement rotary kiln using PCA with EWMA-based adaptive threshold monitoring scheme. Control Engineering Practice, 66, 64–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2017.06.003
Barnett, J. W., Bilchak, C. R., Wang, Y., Benicewicz, B. C., Murdock, L. A., Bereau, T., & Kumar, S. K. (2020). Designing exceptional gas-separation polymer membranes using machine learning. Science Advances, 6(20), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz4301
Battisti, R., Alberto, C., Manenti, F., Antonio, R., Machado, F., & Marangoni, C. (2020). Machine learning modeling and genetic algorithm-based optimization of a novel pilot-scale thermosyphon-assisted falling film distillation unit. Separation and Purification Technology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118122
Chen, H., Zhang, X., Hong, P., Hu, H., & Yin, X. (2016). Recognition of the temperature condition of a rotary kiln using dynamic features of a series of blurry flame images. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 12(1), 148–157. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2015.2500891
Fatahi, R., Khosravi, R., Siavoshi, H., Yazdani, S., Hadavandi, E., & Chelgani, S. C. (2021). Ventilation prediction for an industrial cement raw ball mill by bnn—a “conscious lab” approach. Materials, 14(12), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123220
Gaudio, M. T., Coppola, G., Zangari, L., Curcio, S., Greco, S., & Chakraborty, S. (2021). Artificial intelligence-based optimization of industrial membrane processes. Earth Systems and Environment, 5(2), 385–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-021-00220-x
Guo, H., Wu, S., Tian, Y., Zhang, J., & Liu, H. (2021). Bioresource technology application of machine learning methods for the prediction of organic solid waste treatment and recycling processes : A review. Bioresource Technology, 319, 124114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124114
Hoffman, Z. (2003). Simulation and economic evaluation of coal gasification with set reforming process for power production. Louisiana State University.
Hotellier, E., Pérez-Olivares, J. S., & Zama, E. (2020). Optimization of Process-Aware Attack Detection for Industrial Control Systems Security (pp. 889–896).
Huang, L. (2006). The study of physicochemical process simulation and optimum design for cement precalciner. Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Jadoon, U. K., Ahmad, I., Noor, T., Kano, M., Caliskan, H., & Ahsan, M. (2022). An intelligent sensing system for estimation of efficiency of carbon-capturing unit in a cement plant. Journal of Cleaner Production, 377, 134359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134359
Jiang, Y., Chen, H., Zhang, X., Zhou, Y., & Wang, L. (2022). Combustion condition recognition of coal-fired kiln based on chaotic characteristics analysis of flame video. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 18(6), 3843–3852. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2021.3118135
Kahawalage, A. C., & **adasa, M. H. W. N. (2021). Modeling a Cement Precalciner by Machine Learning Methods (pp. 21–23). https://doi.org/10.3384/ecp2118599
Katoch, S., Chauhan, S. S., & Kumar, V. (2021). A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 80(5), 8091–8126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10139-6
Khan, M., Ahmad, I., Ahsan, M., Kano, M., & Caliskan, H. (2022). Prediction of optimum operating conditions of a furnace under uncertainty: An integrated framework of artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Fuel, 330, 125563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125563
Koukkari, P., & Pajarre, R. (2006). Introducing mechanistic kinetics to the Lagrangian Gibbs energy calculation. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 30(6–7), 1189–1196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2006.03.001
Kwon, H., & Choi, Y. (2021). Development and application of machine learning ‐ based prediction model for distillation column, (August 2020), 1970–1997. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22368
Li, M. (2002). Life-cycle inventory (LCI) development for a solid waste/coal blend gasification system for the production of power and chemicals.
Magazzino, C., Mele, M., & Schneider, N. (2021). A machine learning approach on the relationship among solar and wind energy production, coal consumption, GDP, and CO2 emissions. Renewable Energy, 167, 99–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.11.050
Mathiason, G. (2020). Using Machine Learning for Robust Target Prediction in a Basic Oxygen Furnace System, (ML). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-020-01853-5
Mirmozaffari, M., Shadkam, E., Khalili, S. M., Kabirifar, K., Yazdani, R., & Gashteroodkhani, T. (2020). A Novel Artificial Intelligent Approach: Comparison of Machine Learning Tools and Algorithms Based on Optimization DEA Malmquist Productivity Index for Eco-efficiency Evaluation.
Mittal, S., Pathak, S., Dhawan, H., & Upadhyayula, S. (2021). A machine learning approach to improve ignition properties of high-ash Indian coals by solvent extraction and coal blending. Chemical Engineering Journal, 413, 127385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127385
Modirzadeh, S. A., Nasseri, M., Ahadi, M. S., & Sangachin, F. P. (2021). Assessing GHG mitigation goals of INDCs (NDCs) considering socio-economic and environmental indicators of the parties. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 26(8), 36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-021-09975-0
Mujumdar, K. S., Ganesh, K. V., Kulkarni, S. B., & Ranade, V. V. (2007). Rotary Cement Kiln Simulator (RoCKS): Integrated modeling of pre-heater, calciner, kiln, and clinker cooler. Chemical Engineering Science, 62(9), 2590–2607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2007.01.063
Mzili, T., Mzili, I., & Riffi, M. E. (2023). Artificial rat optimization with decision-making: A bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving the traveling salesman problem. Decision Making: Applications in Management and Engineering, 6(2), 150–176. https://doi.org/10.31181/dmame622023644
Mzili, T., Riffi, M. E., Mzili, I., & Dhiman, G. (2022). A novel discrete rat swarm optimization (Drso) algorithm for solving the traveling salesman problem. Decision Making: Applications in Management and Engineering, 5(2), 287–299. https://doi.org/10.31181/dmame0318062022m
Okoji, A. I., Anozie, A. N., Omoleye, J. A., Okoji, A. I., Anozie, A. N., & Evaluation, J. A. O. (2021). Predicting exergy efficiency of the cement raw meal production process Evaluation of optimization techniques for predicting exergy efficiency of the cement raw meal production process. Cogent Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2021.1930493
Okoji, A. I., Anozie, A. N., Omoleye, J. A., Taiwo, A. E., & Babatunde, D. E. (2023). Evaluation of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system-genetic algorithm in the prediction and optimization of NOx emission in cement pre-calcining kiln. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(19), 54835–54845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26282-0
Oyepata, J. S., & Obodeh, O. (2015). Cement production optimization modeling : A case study BUA plant. Journal of Engineering and Technology Research, 7, 53–58. https://doi.org/10.5897/JETR2015.0545
Oyepata, J. S., & Osarugue, O. T. (2022). The Impact of Fossil Fuels and Agricultural Wastes Used as Energy Mix on Cement Production : Using Particle Swarm Optimization model The Impact of Fossil fuels and Agricultural Wastes Used as Energy Mix on Cement Production : Using Particle Swarm Optimizer, (December) (pp. 11–20). https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7443937
Qayyum Chohan, H., Ahmad, I., Mohammad, N., Manca, D., & Caliskan, H. (2022). An integrated approach of artificial neural networks and polynomial chaos expansion for prediction and analysis of yield and environmental impact of oil shale retorting process under uncertainty. Fuel, 329, 125351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125351
Qian, J., Zhao, Z., Zhang, Q., Werner, M., Petty, R., Abraham, S., & Lu, M. (2021). Machine learning-assisted optical thermometer for continuous temperature analysis inside molten metal. Sensors and Actuators, a: Physical, 322, 112626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.112626
Ramasamy, V., Sidharthan, R. K., Kannan, R., & Muralidharan, G. (2019). Optimal tuning of model predictive controller weights using genetic algorithm with interactive decision tree for industrial cement kiln process. Processes. https://doi.org/10.3390/PR7120938
Ran, Q., Bu, F., Razzaq, A., Ge, W., Peng, J., Yang, X., & Xu, Y. (2023). When will China’s industrial carbon emissions peak? Evidence from machine learning. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26333-6
Roddam, A. W. (2005). Statistics for the quality control chemistry laboratory. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (statistics in Society), 168(2), 464. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-985X.2005.358\_13.x
Ruiz, E., Ferreño, D., Cuartas, M., Lloret, L., Ruiz Del Árbol, P. M., López, A., et al. (2021). Machine learning methods for the prediction of the inclusion content of clean steel fabricated by electric arc furnace and rolling. Metals. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060914
Sadeghian, M., & Fatehi, A. (2011). Identification, prediction, and detection of the process fault in a cement rotary kiln by locally linear neuro-fuzzy technique. Journal of Process Control, 21(2), 302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprocont.2010.10.009
Saltelli, A., Tarantola, S., Campolongo, F., & Ratto, M. (2004). Sensitivity analysis in practice: a guide to assessing scientific models (vol. 1). Wiley Online Library.
Samad, A., Ahmad, I., Kano, M., & Caliskan, H. (2023). Prediction and optimization of exergetic efficiency of reactive units of a petroleum refinery under uncertainty through artificial neural network-based surrogate modeling. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 177, 1403–1414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2023.07.046
Sanchez, M., Exposito, E., & Aguilar, J. (2020). Autonomic computing in manufacturing process coordination in industry 4.0 context. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 19, 100159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jii.2020.100159
Shi, X., Huang, G., Hao, X., Yang, Y., & Li, Z. (2021). A synchronous prediction model based on multi-channel cnn with a moving window for coal and electricity consumption in the cement calcination process. Sensors. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134284
Sobol, I. M. (1990). On sensitivity estimation for nonlinear mathematical models. Matematicheskoe Modelirovanie, 2(1), 112–118.
Son, K., Lee, J., Hwang, H., Jeon, W., Yang, H., Sohn, I., Kim, Y., & Um, H. (2021). Slag foaming estimation in the electric arc furnace using machine learning-based long short-term memory networks. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 12, 555–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.02.085
Strušnik, D., Agrež, M., Avsec, J., & Golob, M. (2021). Optimization of an old 200 MW coal-fired boiler with urea injection through the use of supervised machine learning algorithms to achieve cleaner power generation. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125200
Wang, D., Tan, D., & Liu, L. (2018). Particle swarm optimization algorithm: An overview. Soft Computing, 22(2), 387–408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2474-6
Wang, Y., Pan, Z., Yuan, X., Yang, C., & Gui, W. (2019). A novel deep learning-based fault diagnosis approach for chemical process with extended deep belief network. ISA Transactions. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2019.07.001
Xu, J., Fu, D., Shao, L., Zhang, X., & Liu, G. (2021). A soft sensor modeling of cement rotary kiln temperature field based on model-driven and data-driven methods. IEEE Sensors Journal, 21(24), 27632–27639. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3116937
Yeo, C. S. H., **e, Q., Wang, X., & Zhang, S. (2020). Understanding and optimization of thin film nanocomposite membranes for reverse osmosis with machine learning. Journal of Membrane Science, 606, 118135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118135
Zermane, H., & Drardja, A. (2021). Development of an Efficient Cement Production Monitoring System Based on the Improved Random Forest Algorithm. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-914830/v1
Zhang, L., Wang, S., Zhang, X., He, Z., Huang, J., & Qi, L. (2020). Temperature prediction model for rotary kiln-based JITL with regularized extreme learning machine. https://doi.org/10.1109/CAC51589.2020.9326658
Zhang, X., Kexin, Z., Yoo, H., & Lee, Y. (2021). Machine learning-driven discovery ofmetal–organic frameworks for efficient CO2 capture in humid conditions. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c08806
Zhang, Y., & Fjeld, M. (2021a). I Am Told to Be Happy: An Exploration of Deep Learning in Affective Colormaps in Industrial Tomography. In: 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Information Systems (pp. 1–5). Association for Computing Machinery. https://doi.org/10.1145/3469213.3469220.
Zhang, Y., & Fjeld, M. (2021b). “I Am Told to Be Happy”: An Exploration of Deep Learning in Affective Colormaps in Industrial Tomography. https://doi.org/10.1145/3469213.3469220
Zhang, Y., Cao, S. X., Shao, S., Chen, Y., Liu, S. L., & Zhang, S. S. (2011). Aspen Plus-based simulation of a cement calciner and optimization analysis of air pollutants emission. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 13(3), 459–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-010-0328-y
Zhang, Y., & Shuai, S. C. (2011). Aspen Plus-based simulation of a cement calciner and optimization analysis of air pollutants emission. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 13, 459–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-010-0328-y
Funding
The authors declare that no funds were received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Usman: Conceptualization, Methodology, Study design, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing, Visualization. Iftikhar Ahmad: Conceptualization, Methodology, Study design, Software, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Writing—review and editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. Muhammad Ahsan: Formal analysis, Writing—review and editing. Hakan Caliskan: Formal analysis, Writing—review and editing, Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
There is no conflict of interest in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Usman, M., Ahmad, I., Ahsan, M. et al. Prediction and optimization of emissions in cement manufacturing plant under uncertainty by using artificial intelligence-based surrogate modeling. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-05068-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-05068-5