Abstract
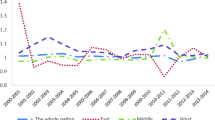
The gap between the efficient state of resources and the inefficient state of real allocation is significant, and how to quantify factor allocation efficiency is a key issue. Factor distortions and inter-factor mismatches can have significant effects on economic growth. Energy is one of the major production factors. Properly incorporating it into the framework is especially critical to measuring the efficiency of factor allocation in the industrial sector. We used Dagum's decomposition of the Gini coefficient and spatial Markov chain to reveal the dynamic spatial pattern of energy factor allocation using input–output data for China's industrial economic sectors from 2003 to 2017. The results showed that the distortions of the energy factor were more severe than those of labor factor during the study period and did not improve significantly. The primary driver of distortions was between-group inequality, with the enormous difference between Eastern–Western regions. Spatial factors played an influential role in the evolution of the distorted state of energy factors, and neighbors with low distortion levels can lead to more efficient resource allocation. These findings can assist decision-makers develop policies to improve factor allocation efficiency from a spatial perspective.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Some or all data, models, or code generated or used during the study are available from the corresponding author by request.
References
Amjadi, G., & Lundgren, T. (2022). Is industrial energy inefficiency transient or persistent? Evidence from Swedish manufacturing. Applied Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.118324
Aoki, S. (2012). A simple accounting framework for the effect of resource misallocation on aggregate productivity. Journal of the Japanese and International Economies, 26(4), 473–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjie.2012.08.001
Bai, J. H., & Bian, Y. C. (2016). Factor market distortion and the efficiency losses of Chinese innovative production. China Industrial Economics, 11(1), 39–55. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2016.11.005
Brandt, L., Tombe, T., & Zhu, X. (2013). Factor market distortions across time, space and sectors in China. Review of Economic Dynamics, 16(1), 39–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.red.2012.10.002
Celik, M. A. (2023). Does the cream always rise to the top? The misallocation of talent in innovation. Journal of Monetary Economics, 133, 105–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoneco.2022.11.003
Chen, S. Y. (2017). Misallocation, economic growth performance and the market entry of firms: A dual perspective of state and non-state sectors. Academic Monthly, 1, 42–56+65. https://doi.org/10.19862/j.cnki.xsyk.2017.01.006
Chen, S. Y., & Chen, D. K. (2017). Dynamic evolution of resource allocation efficiency in China: A new approach incorporating energy factors. Social Sciences in China, 04, 67–83.
Chen, S. Y., & Santos-Paulino, A. U. (2013). Energy consumption restricted productivity re-estimates and industrial sustainability analysis in post-reform China. Energy Policy, 57, 52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.08.060
Choi, B. (2020). Productivity and misallocation of energy resources: Evidence from Korea’s manufacturing Sector. Resource and Energy Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reseneeco.2020.101184
Goldsmith, R. W. (1951). A perpetual inventory of national wealth. Research Papers in Economics, 5–73.
Gong, G., & Hu, G. L. (2013). Efficiency of resource allocation and manufacturing total factor productivity in China. Economic Research Journal, 1(4), 4–15.
Hsieh, C. T., & Klenow, P. J. (2009). Misallocation and manufacturing TFP in China and india. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 124(4), 1403–1448. https://doi.org/10.1162/qjec.2009.124.4.1403
Jia, K. (2015). Supply-side reforms during the “13th Five-Year Plan” period. Journal of Chinese Academy of Governance, 6, 12–21. https://doi.org/10.14063/j.cnki.1008-9314.2015.06.002
Jiang, H. M. (2020). Energy price distortion and real trade gains from China’s manufacturing industry. Contemporary Finance & Economics, 2, 116–124. https://doi.org/10.13676/j.cnki.cn36-1030/f.2020.02.011
Jiang, W., & Zhang, L. P. (2015). Misallocation effect of subsidies disparity: Based on TFP dispersion approach. China Industrial Economics, 2, 31–43. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2015.02.004
**, L. Q., Lin, J. Z., & Ding, S. S. (2015). Effect of administrative monopoly on resources misallocation caused by ownership differences. China Industrial Economics, 4, 31–43. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2015.04.004
Liu, G., Liu, Y., & Zhang, C. (2018). Factor allocation, economic growth and unbalanced regional development in China. World Economy, 41(9), 2439–2463. https://doi.org/10.1111/twec.12572
Li, H., Lee, W., & Ko, B. (2017). What determines misallocation in innovation? A study of regional innovation in China. Journal of Macroeconomics, 52, 221–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmacro.2017.04.005
Li, Y., Ji, Q., Wang, Z., **ong, Z., & Zhan, S. (2022). Green energy mismatch, industrial intelligence and economics growth: Theory and empirical evidence from China. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 24(10), 11785–11816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01919-7
Melitz, M. J. (2003). The impact of trade on intra-industry reallocations and aggregate industry productivity. Econometrica, 71(6), 1695–1725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.**teco.2004.07.001
Restuccia, D., & Rogerson, R. (2017). The causes and costs of misallocation. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 31(3), 151–174. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.31.3.151
Shan, H. J. (2008). Reestimating the capital stock of China: 1952–2006. The Journal of Quantitative & Technical Economics, 10, 17–31.
Shen, X. B., & Lin, B. Q. (2021). Does industrial structure distortion impact the energy intensity in China? Sustainable Production and Consumption, 25, 551–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2020.12.012
Sun, C. W., & Lin, B. Q. (2014). Energy resource allocation efficiency and energy conservation potential of China’s Industrial Sectors. The Journal of Quantitative & Technical Economics, 5, 86–99. https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2014.05.006
Wang, N., & Shi, J. C. (2015). Measure the degree of factor price distortion in China. The Journal of Quantitative & Technical Economics, 9, 149–161. https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2015.09.010
Wang, W., & Qi, L. Q. (2017). Volatility and heterogeneity of total factor productivity growth in China’s equipment manufacturing industry. The Journal of Quantitative & Technical Economics., 10, 111–127. https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2017.10.007
Watanabe, M., & Tanaka, K. (2007). Efficiency analysis of Chinese industry: A directional distance function approach. Energy Policy, 35(12), 6323–6331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.07.013
**e, R., Yao, S., Han, F., & Zhang, Q. (2022). Does misallocation of land resources reduce urban green total factor productivity? An analysis of city-level panel data in China. Land Use Policy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.106353
Yang, M., Yang, F., & Sun, C. (2018). Factor market distortion correction, resource reallocation and potential productivity gains: An empirical study on China’s heavy industry sector. Energy Economics, 69, 270–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.11.021
Zhao, W. Q., Hu, J., & Zhao, S. G. (2020). Factor allocation efficiency of energy industry and industry upgrading in China. The Journal of Quantitative & Technical Economics, 12, 146–162. https://doi.org/10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2020.12.008
Funding
Funding was provided by Chinese National Funding of Social Sciences (Grant No. 20ZDA092).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We confirm that this work is original and has not been published elsewhere, nor is it currently under consideration for publication elsewhere. All authors have read and approved the submitted manuscript and agree to its submission to this journal. We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Wang, Z., Ji, Y. et al. Dynamic evolution of spatial distribution of energy factor allocation efficiency: industrial sector in China. Environ Dev Sustain (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04493-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-04493-w