Abstract
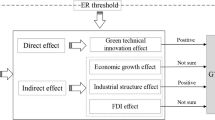
The environmental protection tax law (EPTL) is China’s inaugural formally legislated market-based environmental tax regime. Whether the EPTL can improve green total factor energy efficiency (GTFEE) is of great importance for China’s sustainable development. Utilizing a sample of China’s 284 prefecture-level cities from 2015 to 2019 and the difference-in-differences method, this study explores the impact of China’s environmental protection tax law (EPTL) on green total factor energy efficiency (GTFEE). Results show that: (1) The EPTL exerts a significant negative impact on GTFEE, a conclusion reinforced by a series of robustness checks; (2) two potential mechanisms are reduced green technology innovation and shifted industrial structure; (3) heterogeneity analysis underscores that the negative effects are more significant in eastern regions, old industrial cities, and cities under high fiscal pressure; and (4) based on the spatial difference-in-differences method, the subsequent analysis reveals a negative spatial spillover effect of the EPTL on GTFEE of neighboring cities. Derived from the above conclusions, this study provides policy recommendations for the long-term formulation of the EPTL.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
The “Green Paradox” refers the notion that an increase in taxes could exacerbate existing environmental and climate issues, as such a tax might incentivize producers to shift their production to the present moment, thereby undermining the intended purpose of the environmental tax.
References
Alpay, E., Buccola, S., & Kerkvliet, J. (2002). Productivity growth and environmental regulation in Mexican and U.S. food manufacturing. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 84(4), 887–901. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8276.00041
Antonietti, R., & Fontini, F. (2019). Does energy price affect energy efficiency? Cross-country panel evidence. Energy Policy, 129, 896–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2019.02.069
Bashir, M. F., Ma, B., Bilal, Komal, B., & Bashir, M. A. (2021). Analysis of environmental taxes publications: a bibliometric and systematic literature review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(16), 20700–20716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12123-x
Bashir, M. F., Ma, B., Shahbaz, M., & Jiao, Z. (2020). The nexus between environmental tax and carbon emissions with the roles of environmental technology and financial development. PLOS ONE, 15(11), e0242412. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0242412
Bashir, M. F., Ma, B., Shahbaz, M., Shahzad, U., & Vo, X. V. (2021). Unveiling the heterogeneous impacts of environmental taxes on energy consumption and energy intensity: Empirical evidence from OECD countries. Energy, 226, 120366. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2021.120366
Bezdek, R. H., Wendling, R. M., & DiPerna, P. (2008). Environmental protection, the economy, and jobs: National and regional analyses. Journal of Environmental Management, 86(1), 63–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2006.11.028
Bjørner, T. B., & Jensen, H. H. (2002). Energy taxes, voluntary agreements and investment subsidies—A micro-panel analysis of the effect on Danish industrial companies’ energy demand. Resource and Energy Economics, 24(3), 229–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0928-7655(01)00049-5
Blackman, A. (2008). Can voluntary environmental regulation work in develo** countries? Lessons from case studies. Policy Studies Journal, 36(1), 119–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1541-0072.2007.00256.X
Cai, W., & Ye, P. (2020). How does environmental regulation influence enterprises’ total factor productivity? A quasi-natural experiment based on China’s new environmental protection law. Journal of Cleaner Production, 276, 124105. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2020.124105
Cai, X., Lu, Y., Wu, M., & Yu, L. (2016). Does environmental regulation drive away inbound foreign direct investment? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Journal of Development Economics, 123, 73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JDEVECO.2016.08.003
Cairns, R. D. (2014). The green paradox of the economics of exhaustible resources. Energy Policy, 65, 78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2013.10.047
Camisón, C. (2010). Effects of coercive regulation versus voluntary and cooperative auto-regulation on environmental adaptation and performance: Empirical evidence in Spain. European Management Journal, 28(5), 346–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EMJ.2010.03.001
Candau, F., & Dienesch, E. (2017). Pollution haven and corruption paradise. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 85, 171–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEEM.2017.05.005
Chagas, A. L. S., Azzoni, C. R., & Almeida, A. N. (2016). A spatial difference-in-differences analysis of the impact of sugarcane production on respiratory diseases. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 59, 24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.REGSCIURBECO.2016.04.002
Chang, T. P., & Hu, J. L. (2010). Total-factor energy productivity growth, technical progress, and efficiency change: An empirical study of China. Applied Energy, 87(10), 3262–3270. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2010.04.026
Chen, Z., Yu, B., Yang, C., Zhou, Y., Yao, S., Qian, X., et al. (2021). An extended time series (2000–2018) of global NPP-VIIRS-like nighttime light data from a cross-sensor calibration. Earth System Science Data, 13(3), 889–906.
Copeland, B. R., & Taylor, M. S. (2004). Trade, growth, and the environment. Journal of Economic Literature, 42(1), 7–71. https://doi.org/10.1257/002205104773558047
de Miguel, C., Labandeira, X., & Löschel, A. (2015). Frontiers in the economics of energy efficiency. Energy Economics, 52, S1–S4. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2015.11.012
Diao, M., Leonard, D., & Sing, T. F. (2017). Spatial-difference-in-differences models for impact of new mass rapid transit line on private housing values. Regional Science and Urban Economics, 67, 64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2017.08.006
Du, K., Cheng, Y., & Yao, X. (2021). Environmental regulation, green technology innovation, and industrial structure upgrading: The road to the green transformation of Chinese cities. Energy Economics, 98, 105247. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2021.105247
Dubé, J., Legros, D., Thériault, M., & des Rosiers, F. (2014). A spatial difference-in-differences estimator to evaluate the effect of change in public mass transit systems on house prices. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 64, 24–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRB.2014.02.007
Fan, H., Zivin, J. S. G., Kou, Z., Liu, X., & Wang, H. (2019). Going green in China: Firms’ responses to stricter environmental regulations. National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w26540
Ferman, B. (2023). Inference in difference-in-differences: How much should we trust in independent clusters? Journal of Applied Econometrics, 38(3), 358–369. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.2955
Fisher-Vanden, K., Hu, Y., Jefferson, G., Rock, M., & Toman, M. (2016). Factors influencing energy intensity in four Chinese industries. The Energy Journal, 37(China Special Issue), 153–178. https://doi.org/10.5547/01956574.37.SI1.KFIS
Fullerton, D., & Metcalf, G. E. (1997). Environmental taxes and the double-dividend hypothesis: Did you really expect something for nothing? National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper Series, No. 6199. https://doi.org/10.3386/w6199
Gao, X., Liu, N., & Hua, Y. (2022). Environmental protection tax law on the synergy of pollution reduction and carbon reduction in China: Evidence from a panel data of 107 cities. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 33, 425–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.07.006
Gao, Y., Yao, X., Wang, W., & Liu, X. (2019). Dynamic effect of environmental tax on export trade: Based on DSGE mode. Energy and Environment, 30(7), 1275–1290. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305X19842380
Geng, Y., Liu, W., Li, K., & Chen, H. (2021). Environmental regulation and corporate tax avoidance: A quasi-natural experiment based on the eleventh five-year plan in China. Energy Economics, 99, 105312. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2021.105312
Haider, S., & Mishra, P. P. (2021). Does innovative capability enhance the energy efficiency of Indian iron and steel firms? A Bayesian stochastic frontier analysis. Energy Economics, 95, 105128. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2021.105128
Han, F., & Li, J. (2020). Assessing impacts and determinants of China’s environmental protection tax on improving air quality at provincial level based on Bayesian statistics. Journal of Environmental Management, 271, 111017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111017
Hancevic, P. I. (2016). Environmental regulation and productivity: The case of electricity generation under the CAAA-1990. Energy Economics, 60, 131–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2016.09.022
Hao, Y., Gai, Z., & Wu, H. (2020). How do resource misallocation and government corruption affect green total factor energy efficiency? Evidence from China. Energy Policy, 143, 111562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111562
He, P., Sun, Y., Niu, H., Long, C., & Li, S. (2021). The long and short-term effects of environmental tax on energy efficiency: Perspective of OECD energy tax and vehicle traffic tax. Economic Modelling, 97, 307–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECONMOD.2020.04.003
He, P., Sun, Y., Shen, H., Jian, J., & Yu, Z. (2019). Does environmental tax affect energy efficiency? An empirical study of energy efficiency in OECD countries based on DEA and Logit model. Sustainability, 11(14), 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU11143792
He, Y., Zhu, X., & Zheng, H. (2022). The influence of environmental protection tax law on total factor productivity: Evidence from listed firms in China. Energy Economics, 113, 106248. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2022.106248
Heckert, M. (2015). A spatial difference-in-differences approach to studying the effect of greening vacant land on property values. Source: Cityscape, 17(1), 51–60. https://doi.org/10.2307/26326921
Hering, L., & Poncet, S. (2014). Environmental policy and exports: Evidence from Chinese cities. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 68(2), 296–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEEM.2014.06.005
Hu, X., Liu, J., Yang, H., Meng, J., Wang, X., Ma, J., & Tao, S. (2020). Impacts of potential China’s environmental protection tax reforms on provincial air pollution emissions and economy. Earth’s Future, 8(4), 14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019EF001467
Jacobson, L. S., LaLonde, R. J., & Sullivan, D. G. (1993). Earnings losses of displaced workers. The American Economic Review, 83(4), 685–709.
Jia, R., Shao, S., & Yang, L. (2021). High-speed rail and CO2 emissions in urban China: A spatial difference-in-differences approach. Energy Economics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2021.105271
Jiang, Z., Wang, Z., & Zeng, Y. (2020). Can voluntary environmental regulation promote corporate technological innovation? Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(2), 390–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/BSE.2372
Kirikkaleli, D., Abbasi, K. R., & Oyebanji, M. O. (2023). The asymmetric and long-run effect of environmental innovation and CO2 intensity of GDP on consumption-based CO2 emissions in Denmark. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(17), 50110–50124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25811-1
Lei, Z., Huang, L., & Cai, Y. (2022). Can environmental tax bring strong porter effect? Evidence from Chinese listed companies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(21), 32246–32260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17119-9
Li, B., Han, Y., Wang, C., & Sun, W. (2022). Did civilized city policy improve energy efficiency of resource-based cities? Prefecture-level evidence from China. Energy Policy, 167, 113081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113081
Li, J., & Lin, B. (2017). Ecological total-factor energy efficiency of China’s heavy and light industries: Which performs better? Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 72, 83–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2017.01.044
Li, P., & Chen, Y. (2019). The influence of enterprises’ bargaining power on the green total factor productivity effect of environmental regulation—Evidence from China. Sustainability, 11(18), 4910. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU11184910
Li, P., Lin, Z., Du, H., Feng, T., & Zuo, J. (2021). Do environmental taxes reduce air pollution? Evidence from fossil-fuel power plants in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 295, 113112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113112
Li, X., & Ma, D. (2021). Financial agglomeration, technological innovation, and green total factor energy efficiency. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 60(4), 4085–4095. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AEJ.2021.03.001
Lin, B., & Zhang, A. (2023). Can government environmental regulation promote low-carbon development in heavy polluting industries? Evidence from China’s new environmental protection law. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 99, 106991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106991
Liu, G., Yang, Z., Zhang, F., & Zhang, N. (2022). Environmental tax reform and environmental investment: A quasi-natural experiment based on China’s environmental protection tax law. Energy Economics, 109, 106000. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2022.106000
López-Gamero, M. D., Molina-Azorín, J. F., & Claver-Cortés, E. (2010). The potential of environmental regulation to change managerial perception, environmental management, competitiveness and financial performance. Journal of Cleaner Production, 18(10–11), 963–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2010.02.015
Miller, S., & Vela, M. A. (2013). Are environmentally related taxes effective? SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/SSRN.2367708
Neves, S. A., Marques, A. C., & Patrício, M. (2020). Determinants of CO2 emissions in European Union countries: Does environmental regulation reduce environmental pollution? Economic Analysis and Policy, 68, 114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2020.09.005
Orlov, A., Grethe, H., & McDonald, S. (2013). Carbon taxation in Russia: Prospects for a double dividend and improved energy efficiency. Energy Economics, 37, 128–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2013.01.008
Radulescu, M., Sinisi, C. I., Popescu, C., Iacob, S. E., & Popescu, L. (2017). Environmental tax policy in Romania in the context of the EU: Double dividend theory. Sustainability, 9(11), 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU9111986
Ramzan, M., Abbasi, K. R., Iqbal, H. A., & Adebayo, T. S. (2023). What’s at stake? The empirical importance of government revenue and debt and renewable energy for environmental neutrality in the US economy. Renewable Energy, 205, 475–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.01.071
Ramzan, M., Abbasi, K. R., Salman, A., Dagar, V., Alvarado, R., & Kagzi, M. (2023b). Towards the dream of go green: An empirical importance of green innovation and financial depth for environmental neutrality in world’s top 10 greenest economies. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 189, 122370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122370
Rao, X., Wu, J., Zhang, Z., & Liu, B. (2012). Energy efficiency and energy saving potential in China: An analysis based on slacks-based measure model. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 63(3), 578–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIE.2011.08.023
Rodríguez, M., Robaina, M., & Teotónio, C. (2019). Sectoral effects of a green tax reform in Portugal. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 104, 408–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2019.01.016
Rubashkina, Y., Galeotti, M., & Verdolini, E. (2015). Environmental regulation and competitiveness: Empirical evidence on the porter hypothesis from European manufacturing sectors. Energy Policy, 83, 288–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2015.02.014
Rubin, D. B. (1974). Estimating causal effects of treatments in randomized and nonrandomized studies. Journal of Educational Psychology, 66(5), 688–701. https://doi.org/10.1037/H0037350
Shao, S., Yang, L., Yu, M., & Yu, M. (2011). Estimation, characteristics, and determinants of energy-related industrial CO2 emissions in Shanghai (China), 1994–2009. Energy Policy, 39(10), 6476–6494. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2011.07.049
Shi, B., Feng, C., Qiu, M., & Ekeland, A. (2018). Innovation suppression and migration effect: The unintentional consequences of environmental regulation. China Economic Review, 49, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHIECO.2017.12.007
Shi, X., & Xu, Z. (2018). Environmental regulation and firm exports: Evidence from the eleventh Five-Year Plan in China. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 89, 187–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEEM.2018.03.003
Song, M., An, Q., Zhang, W., Wang, Z., & Wu, J. (2012). Environmental efficiency evaluation based on data envelopment analysis: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 16(7), 4465–4469. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2012.04.052
Sun, H., Edziah, B. K., Sun, C., & Kporsu, A. K. (2019). Institutional quality, green innovation and energy efficiency. Energy Policy, 135, 111002. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2019.111002
Sunak, Y., & Madlener, R. (2016). The impact of wind farm visibility on property values: A spatial difference-in-differences analysis. Energy Economics, 55, 79–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2015.12.025
Takeda, S. (2007). The double dividend from carbon regulations in Japan. Journal of the Japanese and International Economies, 21(3), 336–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JJIE.2006.01.002
Tan, R., Tang, D., & Lin, B. (2018). Policy impact of new energy vehicles promotion on air quality in Chinese cities. Energy Policy, 118, 33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2018.03.018
Tang, H., Liu, J., & Wu, J. (2020). The impact of command-and-control environmental regulation on enterprise total factor productivity: A quasi-natural experiment based on China’s “Two Control Zone” policy. Journal of Cleaner Production, 254, 120011. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2020.120011
van der Ploeg, F., & Withagen, C. (2012). Is there really a green paradox? Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 64(3), 342–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEEM.2012.08.002
Wang, J., & Zhao, T. (2017). Regional energy-environmental performance and investment strategy for China’s non-ferrous metals industry: A non-radial DEA based analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 163, 187–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2016.02.020
Wang, K., Zheng, L. J., Zhang, J. Z., & Yao, H. (2022). The impact of promoting new energy vehicles on carbon intensity: Causal evidence from China. Energy Economics, 114, 106255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106255
Wang, X., Song, J., Duan, H., & Wang, X. (2021). Coupling between energy efficiency and industrial structure: An urban agglomeration case. Energy, 234, 121304. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2021.121304
Wang, Y., & Shen, N. (2016). Environmental regulation and environmental productivity: The case of China. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 62, 758–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2016.05.048
Wang, Z., & Feng, C. (2015). A performance evaluation of the energy, environmental, and economic efficiency and productivity in China: An application of global data envelopment analysis. Applied Energy, 147, 617–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2015.01.108
Wu, H., Hao, Y., & Ren, S. (2020). How do environmental regulation and environmental decentralization affect green total factor energy efficiency: Evidence from China. Energy Economics, 91, 104880. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2020.104880
Wu, H., Hao, Y., Ren, S., Yang, X., & **e, G. (2021). Does internet development improve green total factor energy efficiency? Evidence from China. Energy Policy, 153, 112247. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2021.112247
Wu, J., Niu, Y., Peng, J., Wang, Z., & Huang, X. (2014). Research on energy consumption dynamic among prefecture-level cities in China based on DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light. Geographical Research, 33(4), 625–634.
Wu, J., & Tal, A. (2018). From pollution charge to environmental protection tax: A comparative analysis of the potential and limitations of China’s new environmental policy initiative. Journal of Comparative Policy Analysis: Research and Practice, 20(2), 223–236. https://doi.org/10.1080/13876988.2017.1361597
Yang, T., Li, H., Zhang, L., & Chen, T. (2022). The impact of city gas on income inequality in China: A regional heterogeneity analysis. Energy Policy, 169, 113203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113203
Yi, S., Raza Abbasi, K., Hussain, K., Albaker, A., & Alvarado, R. (2023). Environmental concerns in the United States: Can renewable energy, fossil fuel energy, and natural resources depletion help? Gondwana Research, 117, 41–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2022.12.021
Yu, H., Liao, L., Qu, S., Fang, D., Luo, L., & **ong, G. (2021). Environmental regulation and corporate tax avoidance: A quasi-natural experiments study based on China’s new environmental protection law. Journal of Environmental Management, 296, 113160. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2021.113160
Yuan, B., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Flexible environmental policy, technological innovation and sustainable development of China’s industry: The moderating effect of environment regulatory enforcement. Journal of Cleaner Production, 243, 118543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118543
Zhang, D. (2022). Environmental regulation, green innovation, and export product quality: What is the role of greenwashing? International Review of Financial Analysis, 83, 102311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2022.102311
Zhang, J., Liu, Y., Zhou, M., Chen, B., Liu, Y., Cheng, B., et al. (2022). Regulatory effect of improving environmental information disclosure under environmental tax in China: From the perspectives of temporal and industrial heterogeneity. Energy Policy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112760
Zhang, M., Abbasi, K. R., Inuwa, N., Sinisi, C. I., Alvarado, R., & Ozturk, I. (2023). Does economic policy uncertainty, energy transition and ecological innovation affect environmental degradation in the United States? Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 36(2), 2177698. https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677X.2023.2177698
Zhao, X., & Hu, S. (2020). Does market-based electricity price affect China’s energy efficiency? Energy Economics, 91, 104909. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2020.104909
Zhou, C., & Qi, S. (2022). Has the pilot carbon trading policy improved China’s green total factor energy efficiency? Energy Economics, 114, 106268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106268
Zhou, X., & Feng, C. (2017). The impact of environmental regulation on fossil energy consumption in China: Direct and indirect effects. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142, 3174–3183. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2016.10.152
Zhou, Z., Zhang, W., Pan, X., Hu, J., & Pu, G. (2019). Environmental tax reform and the “double dividend” hypothesis in a small open economy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH17010217
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, S., Li, S. Energy efficiency suppression and spatial spillover effect: a quasi-natural experiment based on China’s environmental protection tax law. Environ Dev Sustain (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04146-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04146-4