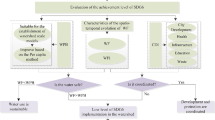
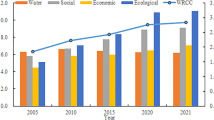
Abstract
Focusing on the efficient allocation and scientific management of water resources in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt (YREB), the total and per capita water ecological footprints (WEFs) and water ecological carrying capacities (WECCs) in each province and municipality from 2004 to 2018 were evaluated through an improved water ecological footprint analysis model. Then, the panel data were used to analyze the spatiotemporal variation, and regression discontinuity models were applied to examine the effect of YREB policy on local WEF. Results show that, first, in terms of temporal trend, for the entire YREB, per capita WEFs first increased and then declined with fluctuation, while per capita WECCs fluctuated in a small range, which is further evident in that only Zhejiang had both a low level and a significant downward trend in per capita WEFs. Second, in terms of spatial features, per capita WEFs were lower in the upstream area and higher in the downstream area (except for Zhejiang), and per capita WECCs were roughly higher in the southern area and lower in the northern area. Third, China’s YREB policy had a negative impact on local WEF, which was specifically more significant in developed regions than in develo** regions and more effective with agriculture than with industry. The findings of this study indicate that the YREB can achieve a harmonious situation of economic development and ecological protection, but attention is needed to ensure industrial water savings and policy implementation in backward areas.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arenas-Sánchez, A., Rico, A., & Vighi, M. (2016). Effects of water scarcity and chemical pollution in aquatic ecosystems: State of the art. Science of the Total Environment, 572, 390–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.211
Bu, J., Li, C., Wang, X., et al. (2020). Assessment and prediction of the water ecological carrying capacity in Changzhou city. China. J. Clean. Prod., 277, 123988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123988
Cai, H., Nan, Y., Zhao, Y., et al. (2020). Impacts of winter heating on the atmospheric pollution of northern China’s prefectural cities: Evidence from a regression discontinuity design. Ecological Indicators, 118, 106709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106709
Chen, Y., Zhang, S., Huang, D., et al. (2017). The development of China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt: How to make it in a green way? Science Bulletin, 62(9), 648–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2017.04.009
Cui, X., Wu, X., He, X., et al. (2018). Regional suitability of virtual water strategy: Evaluating with an integrated water-ecosystem-economy index. Journal of Cleaner Production, 199, 659–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.192
Dadmand, F., Naji-Azimi, Z., Motahari Farimani, N., et al. (2020). Sustainable allocation of water resources in water-scarcity conditions using robust fuzzy stochastic programming. Journal of Cleaner Production, 276, 123812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123812
Dai, D., Sun, M., Xu, X., et al. (2019). Assessment of the water resource carrying capacity based on the ecological footprint: A case study in Zhangjiakou City. North China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. r., 26(11), 11000–11011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04414-9
Fang, W., Sun, C., & Guo, W. (2015). Analysis of influende factor of water resources ecological footprint in Dongguan based on LMDI method. Journal of Water Resource Engineering and Management, 26(3), 115–123. (in Chinese).
Geng, C. X., & Cui, Z. Y. (2020). Analysis of spatial heterogeneity and driving factors of capital allocation efficiency in energy conservation and environmental protection industry under environmental regulation. Energ. Policy., 137, 111081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111081
Guan, D., Su, Y., Su, W. et al. 2015. Assessment and forecast on ecological footprint of water resources in Guizhou Province. Journal of Chongqing University 38(4):112–120. https://doi.org/10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2015.04.016(in Chinese).
Hahn, J., Todd, P., & Wilbert, V. (2001). Identification and estimation of treatment effects with a regression-discontinuity design. Econometrica, 69(1), 201–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-0262.00183
Hansen, M. H., Li, H., & Svarverud, R. (2018). Ecological civilization: Interpreting the Chinese past, projecting the global future. Global Environmental Change, 53, 195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2018.09.014
Huang, L. N., Zhang, W. X., Jiang, C. L., et al. (2008). Ecological footprint method in water resources assessment. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(3), 1279–1286. (in Chinese).
Jia, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, R.. (2016). Ecological footprint of water resources in the Shiyang River Basin from 2001–2011. Acta Prataculturae Sinica; 25(2), 10–17. https://doi.org/10.11686/cyxb2015125 (in Chinese).
Liu, Y., Li, T., Zhao, W., Wang, S., et al. (2019). Landscape functional zoning at a county level based on ecosystem services bundle: Methods comparison and management indication. Journal of Environmental Management, 249, 109315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109315
Luo, Q., Luo, L., Zhou, Q., et al. (2019). Does China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt policy impact on local ecosystem services? Science of the Total Environment, 676, 231–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.135
Lv, H., Yang, L., Zhou, J., et al. (2020). Water resource synergy management in response to climate change in China: From the perspective of urban metabolism. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 163, 105095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105095
Nunes, P., Pinheiro, F., & Brito, M. C. (2019). The effects of environmental transport policies on the environment, economy and employment in Portugal. Journal of Cleaner Production, 213, 428–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.166
Pan, D., Hong, W., & Kong, F. (2020). Efficiency evaluation of urban wastewater treatment: Evidence from 113 cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt of China. Journal of Environmental Management, 270, 110940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110940
Peng, L., **a, J., Li, Z., et al. (2020). Spatio-temporal dynamics of water-related disaster risk in the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2000 to 2015. Resources, Conservation & Recycling, 161, 104851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104851
Rees, W. E. (1992). Ecological footprints and appropriated carrying capacity: What urban economics leaves out. Environment and Urbanization, 4(2), 121–130. https://doi.org/10.1177/095624789200400212
Ren, J., Li, H., Wu, X., et al. (2016). Analysis of water efficiency of capital cities in Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. China Population, Resources and Environment, 26(5), 101–107. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2016.05.012 (in Chinese).
She, Y., Liu, Y., Jiang, L., et al. (2019). Is China’s River Chief Policy effective? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 220, 919–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.031
Song, M., Wang, R., & Zeng, X. (2018). Water resources utilization efficiency and influence factors under environmental restrictions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 184, 611–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.259
Su, Y., Gao, W., Guan, D., et al. (2018). Dynamic assessment and forecast of urban water ecological footprint based on exponential smoothing analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 195, 354–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.184
Sun, C., Zhang, Z., 2017. Assessment of water ecological footprint size, depth, and spatial pattern in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica 37(21), 7048–7060. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201608101640 (in Chinese).
Sun, F. Y., Mejia, A., Zeng, P., et al. (2019). Projecting meteorological, hydrological and agricultural droughts for the Yangtze River basin. Science of the Total Environment, 696, 134076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134076
Sun, J. X., Yu, X., **ao, Q. S., et al. (2018). Utilization characteristics and sustainability evaluation of water resources in China. Water, 10(9), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091142
Tan, F., & Bi, J. (2018). An inquiry into water transfer network of the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 176, 288–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.129
Tan, X., & Zheng, Q. (2009). Dynamic analysis and forecast of water resources ecological footprint in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(7), 3559–3568. (in Chinese).
Tan, Y. T., & Mao, X. Q. (2021). Assessment of the policy effectiveness of central inspections of environmental protection on improving air quality in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 288, 125100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125100
Wang, H., Huang, J. J., Zhou, H., Deng, C. B., & Fang, C. L. (2020a). Analysis of sustainable utilization of water resources based on the improved water resources ecological footprint model: A case study of Hubei Province, China. J. Environ. Manage., 262, 110331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110331
Wang, J. F., Ma, Y. P., Qiu, Y., et al. (2019). Spatially differentiated effects of socioeconomic factors on China’s NOx generation from energy consumption: Implications for mitigation policy. Journal of Environmental Management, 250, 109417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109417
Wang, S., Yang, F. L., Xu, L., et al. (2013). Multi-scale analysis of the water resources carrying capacity of the Liaohe Basin based on ecological footprints. Journal of Cleaner Production, 53, 158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.03.052
Wang, Z., Li, W., Li, Y., et al. (2020b). The “Three Lines One Permit” policy: An integrated environmental regulation in China. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 163, 105101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105101
Wang, Z., Zhao, L., & Wang, Y. (2020c). An empirical correlation mechanism of economic growth and marine pollution: A case study of 11 coastal provinces and cities in China. Ocean & Coastal Management, 198, 105380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2020.105380
Wu, P., Cheng, H., & Li, H. (2020). The effectiveness of environmental policy mix: Evidence from the Zhejiang sewage treatment policy. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 3, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6185629
Xu, L., Huang, Y., & Aijun, L. (2011). Study on the carrying capacity of water resources in Jiangsu province based on the principal component analysis. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 20(12), 1468–1474. (in Chinese).
Xu, X., Yang, G., & Tan, Y. (2019). Identifying ecological red lines in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt: A regional approach. Ecological Indicators, 96, 635–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.09.052
Yang, G., Zhang, Y., & Li, X. (2020). Impact of gasoline upgrade policy on particulate matter pollution in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 262, 121336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121336
Yang, Z., Su, W., Zhao, W., et al., 2016. Analysis and forecast of water ecological footprint in karst area based on GRNN model. Carsologica Sinica 35(1), 36–42. https://doi.org/10.11932/karst20160106. (in Chinese)
Yu, B., & Xu, L. (2014). Assessment of sustainable development of urban water ecosystems in Dalian. Resource Science, 36(12), 2578–2583. (in Chinese).
Yu, Y., & Liu, H. (2020). Economic growth, industrial structure and nitrogen oxide emissions reduction and prediction in China. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 11(7), 1042–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.03.011
Zhang, J., Zhang, C., Shi, W., et al. (2019a). Quantitative evaluation and optimized utilization of water resources-water environment carrying capacity based on nature-based solutions. Journal of Hydrology, 568, 96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.10.059
Zhang, W., Du, X., Huang, A., et al. (2019b). Analysis and comprehensive evaluation of water use efficiency in China. Water, 11(12), 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122620
Zhang, Z., Sun, H., Su, Y., (2017). Dynamic characteristics and prediction of ecological footprint and carrying capacity of water resources in arid areas of **njiang. Research of Environmental Sciences 30(12), 1880–1888 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2017.03.32
Zhao, Z., **e, C., Dan, Q., et al., 2015. The valuation and dynamic forecast of ecological footprint of water resources in Tibet. J. Zhejiang Univ. 42(5), 559–566 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2015.05.012
Zhou, X. Y., & Lei, K. (2020). Influence of human-water interactions on the water resources and environment in the Yangtze River Basin from the perspective of multiplex networks. Journal of Cleaner Production, 265, 121783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121783
Zhou, Z., Su, W., & Zheng, Q. (2019). Evolution characteristics of water resource ecological footprint of Guizhou provinve from 2007 to 2016. Bull. Soi. Water. Conserv., 39(2), 227–233. (in Chinese).
Zhu, G., Zhao, C., Zhu, W., et al., 2020. Evaluation of sustainable water resources utilization in Jilin Province based on the ecological footprint model. J. China. Agr. Univ. 25(9), 131–143 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2020.09.14
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51879103, U19A2047) and Key R&D Program of Science and Technology of Hunan Province in China (No. 2017SK2351).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CJ was involved in conceptualization, investigation, writing—original draft; YL performed methodology, formal analysis, writing—review and editing; ZL contributed to funding acquisition, project administration, and supervision; RG done methodology; MH done investigation; JW contributed to writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
**, C., Liu, Y., Li, Z. et al. Ecological consequences of China’s regional development strategy: evidence from water ecological footprint in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ Dev Sustain 24, 13732–13747 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02008-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02008-5