Abstract
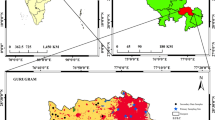
The lack of quality water resources for irrigation is one of the main threats for sustainable farming. This pioneering study focused on finding the best area for farming by looking at irrigation water quality and analyzing its location using a fuzzy logic model on a Geographic Information System platform. In the tribal-prone areas of Khagrachhari Sadar Upazila, Bangladesh, 28 surface water and 39 groundwater samples were taken from shallow tube wells, rivers, canals, ponds, lakes, and waterfalls. The samples were then analyzed for irrigation water quality parameters like electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), soluble sodium percentage (SSP), residual sodium bicarbonate (RSBC), magnesium hazard ratio (MHR), Kelley’s ratio (KR), and permeability index (PI). Fuzzy Irrigation Water Quality Index (FIWQI) was employed to determine the irrigation suitability of water resources. Spatial maps for parameters like EC, KR, MH, Na%, PI, SAR, and RSBC were developed using fuzzy membership values for groundwater and surface water. The FIWQI results indicate that 100% of the groundwater and 75% of the surface water samples range in the categories of excellent to good for irrigation uses. A new irrigation suitability map constructed by overlaying all parameters showed that surface water (75%) and some groundwater (100%) in the northern and southwestern portions are fit for agriculture. The western and central parts are unfit for irrigation due to higher bicarbonate and magnesium contents. The Piper and Gibbs diagram also indicated that the water in the study area is magnesium-bicarbonate type and the primary mechanism of water chemistry is controlled by the weathering of rocks, respectively. This research pinpoints the irrigation spatial pattern for regional water resource practices, identifies novel suitable areas, and improves sustainable agricultural uses in tribal-prone areas.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Abdel-Rahman, G. N. E. (2022). Heavy metals, definition, sources of food contamination, incidence, impacts and remediation: A literature review with recent updates. Egyptian Journal of Chemistry, 65(1), 419–437.
Adimalla, N., & Venkatayogi, S. (2018). Geochemical characterization and evaluation of groundwater suitability for domestic and agricultural utility in semi-arid region of Basara, Telangana State South India. Applied Water Science, 8, 44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0682-1
Adimalla, N., & Wu, J. H. (2019). Groundwater quality and associated health risks in a semi-arid region of south India: Implication to sustainable groundwater management. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 25, 191–216.
Adimalla, N. (2019). Groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and potential health risks assessment: a case study from semi-arid region of South India. Exposure and Health, 11(2), 109–123.
Ahmed, M. J., Haque, M. R., Ahsan, A., et al. (2010). Physicochemical assessment of surface and groundwater quality of the greater Chittagong region of Bangladesh. Pakistan Journal of Analytical & Environmental Chemistry, 11(2), 1–11.
Akter, T., Ghosh, S., Sarker, S., Rahman, M. M., & Nabi, K. M. (2019). Quantitative assessment of ionic status in pond water for irrigation and aquaculture usage in the selected sites of Mymensingh areas, Bangladesh. Research in Agriculture Livestock and Fisheries, 6, 301–313. https://doi.org/10.3329/ralf.v6i2.43053
APHA. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (19th ed.). American Public Health Association Inc.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation.
Aravinthasamy, P., Karunanidhi, D., Subba Rao, N., et al. (2020). Irrigation risk assessment of groundwater in a non-perennial river basin of South India: Implication from irrigation water quality index (IWQI) and geographical information system (GIS) approaches. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 13, 1125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06103-1
Arun, P. V. (2013). A comparative analysis of different DEM interpolation methods. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 16(2), 133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2013.09.001
Ayers, R. S., & Westcot, D. W. (1985). Water quality for agriculture. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper, 29, 1–144.
Banerjee, P., & Prasad, B. (2020). Determination of concentration of total sodium and potassium in surface and ground water using a fame photometer. Applied Water Science, 10, 113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01188-1
BBS. (2015). Population and housing census 2011, Zila report: Khagrachhari, Bangladesh bureau of statistics, statistics and informatics division, ministry of planning, government of the people’s republic of Bangladesh.
Bonham-Carter, G. F. (1994). Geographic information systems for geo-scientists: Modelling with GIS. Pergamon Press.
Burrough, P. A., McDonnell, R. A., & Lloyd, C. D. (2015). Principles of geographical information systems. Oxford University Press.
Chidambaram, S., Prasanna, M. V., Venkatramanan, S., Nepolian, M., Pradeep, K., Banajarani Panda Thivya, C., & Thilagavathi, R. (2022). Groundwater quality assessment for irrigation by adopting new suitability plot and spatial analysis based on fuzzy logic technique. Environmental Research, 204, 111729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111729
Demir, V., Dere, T., Ergin, S., Cakır, Y., & Celik, F. (2015). Determination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in drinking water of Tunceli, Turkey. Water Resources, 42, 508–516.
DOE. (1997). The environment conservation rules, 1997. Department of environment, ministry of environment and forest, government of the people’s republic of Bangladesh. https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/bgd19918.pdf.
Eaton, F. M. (1950). Significance of carbonates in irrigation waters. Soil Science, 69, 123–134.
Elbeltagi, A., Pande, C. B., Kouadri, S., & Islam, A. R. M. T. (2022). Applications of various data-driven models for the prediction of groundwater quality index in the Akot basin, Maharashtra, India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–15.
Esri. (2023). Fuzzy overlay (spatial analyst). https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/tool-reference/spatial-analyst/fuzzy-overlay.htm. Accessed 13 Mar.
Ghosh, A. B., Bajaj, J. C., Hasan, R., & Singh, D. (1983). Soil and water testing methods: A laboratory manual (pp. 31–36). IARI.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, 170(3962), 1088–1090. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
Grzebisz, W. (2011). Magnesium–food and human health. Journal of Elementology, 16(2). https://doi.org/10.5601/jelem.2011.16.2.13
Gugulothu, S., Subbarao, N., Das, R., et al. (2022). Geochemical evaluation of groundwater and suitability of groundwater quality for irrigation purpose in an agricultural region of South India. Applied Water Science, 12, 142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01583-w
Hao, O. J., Chen, J. M., Huang, L., & Buglass, R. L. (1996). Sulfate-reducing bacteria. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 26(2), 155–187.
Helal, U. S. M., Saiful, H., Rahman, M. S., Hossain, M. F., & Laiju, M. M. (2003). Quality assessment of well and pond water for irrigation in different aquifers of Khagrachhari in Bangladesh. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 6(20), 1720–1724.
Hossain, S., Khan, R., Anik, A. H., Siddique, M. A. B., Tamim, U., Islam, A. R. M. T., Idris, A. M., & Khaleque, M. A. (2023). Natural and anthropogenic contributions to the elemental compositions and subsequent ecological consequences of a Transboundary River’s sediments (Punarbhaba, Bangladesh). Environmental Research, 216, 114444.
Islam, M. S., Islam, M. A., Alam, M. S., & Reshma, B. Z. (1998). Effect of shrimp farming on physico-chemical qualities of water in some medium saline areas in greater Khulna district. Bangladesh Journal of Fisheries, 21, 82–92.
Islam, M. J., Shah, Md., Helal Uddin, M. W., Zaman, R. I. M., & Rahman, M. S. (2003). Toxicity assessment of ground water in different aquifers of Khagrachari in Bangladesh. Asian Journal of Plant Sciences, 2, 257–260. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajps.2003.257.260
Islam, M. S., Saito, T., & Kurasaki, M. (2015). Phytofiltration of arsenic and cadmium using Micranthemum umbrosum: Phytotoxicity, uptake kinetics and mechanism. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 112, 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.11.006
Islam, M. S., Islam, M. S., Mamun, M. A. H., Islam, S. M. A., & Eaton, D. W. (2016). Total and dissolved metals in the industrial wastewater: A case study from Dhaka Metropolitan, Bangladesh. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring and Assessment, 5, 74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2016.04.001
Islam, A. R. M. T., Shen, S., Bodrud-Doza, M. D., & Safiur Rahman, M. (2017b). Assessing irrigation water quality in Faridpur district of Bangladesh using several indices and statistical approaches. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 10(19), 418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3199-2
Islam, A. R. M. T., Shen, S., Haque, M. A., et al. (2018a). Assessing groundwater quality and its sustainability in Joypurhat district of Bangladesh using GIS and multivariate statistical approaches. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 20(5), 1935–1959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-017-9971-3
Islam, A. R. M. T., Shen, S., Haque, M. A., Bodrud-Doza, M., Maw, K. W., & Habib, M. A. (2018b). Assessing groundwater quality and its sustainability in Joypurhat district of Bangladesh using GIS and multivariate statistical approaches. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 20, 1935–1959.
Islam, M. S., Hosen, M. M. L., & Uddin, M. N. (2019). Phytodesalination of saline water by using Ipomoea aquatica, Alternanthera philoxeroides and Ludwigia adscendens. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16(2), 965–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1705-z
Islam, M. S., Nakagawa, K., Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M., Khan, A. S., Goni, M. A., & Berndtsson, R. (2022a). Spatial distribution and source identification of water quality parameters of an industrial seaport riverbank area in Bangladesh. Water, 14(9), 1356.
Islam, M. S., Haque, K. A., Jahan, N., Atikullah, M., Uddin, M. N., Naser, A. M., Faruk-E-Azam, A. K. M., & Islam, M. S. (2022b). Soil salinity mitigation by naturally grown halophytes in seawater affected coastal Bangladesh. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology., 19, 11013–11022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-03912-7
Islam, A. R. M. T., Mia, M. Y., Haque, M. E., Jannat, J. N., Jion, M. M. M. F., Islam, M. S., Siddique, M. A. B., Idris, A. M., Senapathi, V., Talukdar, S., & Rahman, A. (2023). Analysis of self-organizing maps and explainable artificial intelligence to identify hydrochemical factors that drive drinking water quality in Haor region. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166927
Islam, A. R. M. T., Shen, S., Bodrud-Doza, M., Atiqur Rahman, M., & Das, S. (2017a). Assessment of trace elements of groundwater and their spatial distribution in Rangpur district, Bangladesh. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 10(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2886-3
Islam, M.S., Akter, R., Rahman, M.M., Kurasaki, M. 2022c. Phytoremediation: Background, principle, and application, plant species used for phytoremediation. In: Tanaka, S., Kurasaki, M., Morikawa, M., Kamiya, Y. (eds) Design of materials and technologies for environmental remediation. The handbook of environmental chemistry, vol 115:199–224, Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/698_2021_831
Jannat, J. N., Khan, M. S. I., Islam, H. T., Islam, M. S., Khan, R., Siddique, M. A. B., Varol, M., Tokatli, C., Pal, S. C., Islam, A., Idris, A. M., Malafia, G., & Islam, A. R. M. T. (2022). Hydrochemical assessment of fluoride and nitrate in groundwater from east and west coasts of Bangladesh and India. Journal of Cleaner Production, 372, 133675.
Karanth, K. R. (1987). Groundwater assessment, development and management. Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company.
Kelley, W. P. (1963). Use of saline irrigation water. Soil Science, 95, 355–391.
Latifa, G. A., Majumder, K. A., Kabir, M. H., & Chakma, A. (2019). Water quality and fish diversity of Chengi river of Khagrachhari district. Bangladesh Journal of Zoology, 47(2), 343–353.
Li, J., & Heap, A. D. (2011). A review of comparative studies of spatial interpolation methods in environmental sciences: Performance and impact factors. Ecological Informatics, 6(3), 228–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2010.12.003
Li, P., Wu, J., Qian, H., et al. (2014). Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: A case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(4), 693–712.
Li, P., He, S., Yang, N., & **ang, G. (2018). Groundwater quality assessment for domestic and agricultural purposes in Yan’an City, northwest China: Implications to sustainable groundwater quality management on the Loess Plateau. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77, 1–16.
Mallik, S., Mishra, U., & Paul, N. (2021). Groundwater suitability analysis for drinking using GIS based fuzzy logic. Ecological Indicators, 121, 107179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107179
Mckone, T.E., Deshpande, A.W., 2005. Can fuzzy logic bring complex environmental problems into focus? Environmental Science & Technology 39. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0531632.
Mia, M. Y., Islam, A. R. M. T., Jannat, J. N., Jion, M. M. M. F., Sarker, A., Tokatli, C., Siddique, M. A. B., Ibrahim, S. M., & Senapathi, V. (2023). Identifying factors affecting irrigation metrics in the Haor basin using integrated Shannon’s entropy, fuzzy logic and automatic linear model. Environmental Research, 115688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115688
Mostafa, M. G., Uddin, S. H., & Haque, A. B. M. H. (2017). Assessment of hydro-geochemistry and groundwater quality of Rajshahi City in Bangladesh. Applied Water Science, 7, 4663–4671.
Naser A.M., Rahman M., Unicomb L., Parvez S.M., Islam M.S., Doza S., Khan G.K., Ahmed K.M., Anand S., Luby S.P., Shamsudduha M., Gribble M.O., Narayan K.M.V., Clasen T.F. 2020. Associations of drinking rainwater with macro-mineral intake and cardiometabolic health: A pooled cohort analysis in Bangladesh, 2016–2019. NPJ Clean Water, 3:20 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-020-0067-5
Nepolian, M., Chidambaram, S., Thivya, C., Paramaguru, P., Pradeep, K., Panda, Banaja Rani, & D. N., & Vasudevan, U. (2016). Assessment of hydrogeochemical and quality studies in groundwater of Villupuram District, Tamilnadu, India. BDL, 116, 10–95.
Nizam, M. U., Shariful, I. M., & Islam, M. S. (2010). Quality assessment of surface water resources of Dumki upazila in Bangladesh for irrigation, aquaculture and livestock consumption. Journal of Agroforestry and Environment, 4, 81–84.
Nuruzzaman, M. (2019). Chemical status of surface water of Bauphal Upazila for irrigation, aquaculture, livestock consumption and industrial uses. MS thesis, department of post harvest technology and marketing. Patuakhali Science and Technology University.
Okorogbona, A. O., Denner, F. D., Managa, L. R., Khosa, T. B., Maduwa, K., Adebola, P. O., Amoo, S. O., Ngobeni, H. M., & Macevele, S. (2018). Water quality impacts on agricultural productivity and environment. Sustainable Agriculture Reviews, 27, 1–35.
Paliwal, K. V. (1972). Irrigation with saline water. Monogram No.2 (New Series) (p. 198). Water Technology Centre.
Paquette, C., Gregory-Eaves, I., & Beisner, B. E. (2022). Environmental drivers of taxonomic and functional variation in zooplankton diversity and composition in freshwater lakes across Canadian continental watersheds. Limnology and Oceanography, 67(5), 1081–1097.
Pathak, D. R., & Bhandary, N. P. (2020). Evaluation of groundwater vulnerability to nitrate in shallow aquifer using multi-layer fuzzy inference system within GIS environment. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 11, 100470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100470
Paul, R., Brindha, K., Gowrisankar, G., Tan, M. L., & Singh, M. K. (2019). Identification of hydrogeochemical processes controlling groundwater quality in Tripura, Northeast India using evaluation indices, GIS, and multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78, 1–16.
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 25(6), 914–928. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR025i006p00914
Prasanna, M. V., Chidambaram, S., Hameed, A. S., & Srinivasamoorthy, K. (2011). Hydrogeochemical analysis and evaluation of groundwater quality in the Gadilam river basin, Tamil Nadu India. Journal of Earth System Science, 120(1), 85–98.
Rahman, M. S., Saha, N., Islam, A. T., Shen, S., & Bodrud-Doza, M. (2017). Evaluation of water quality for sustainable agriculture in Bangladesh. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 228, 1–16.
Rao, N. S., Dinakar, A., Sravanthi, M., et al. (2021). Geochemical characteristics and quality of groundwater evaluation for drinking, irrigation, and industrial purposes from a part of hard rock aquifer of South India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 31941–31961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12404-z
Rao, N. S., Dinakar, A., & Sun, L. (2022a). Estimation of groundwater pollution levels and specific ionic sources in the groundwater, using a comprehensive approach of geochemical ratios, pollution index of groundwater, unmix model and land use/land cover–A case study. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 248, 103990.
Rao, N. S., Sunitha, B., Das, R., & Kumar, B. A. (2022b). Monitoring the causes of pollution using groundwater quality and chemistry before and after the monsoon. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c, 128, 103228.
Rao, N. S., Das, R., Sahoo, H. K., & Gugulothu, S. (2024). Hydrochemical characterization and water quality perspectives for groundwater management for urban development. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 24, 101071.
Ravindra, B., Subba Rao, N., & Dhanamjaya Rao, E. N. (2023). Groundwater quality monitoring for assessment of pollution levels and potability using WPI and WQI methods from a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 25, 14785–14815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02689-6
Richards, L. A. (Ed.) (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils (No. 60). US Government Printing Office.
Salam, M. A., Rahman, S., Anik, A. R., & Sharna, S. C. (2023). Exploring competitiveness of surface water versus ground water irrigation and their impacts on rice productivity and efficiency: An empirical analysis from Bangladesh. Agricultural Water Management, 283, 108298.
Sasikala, K. R., & Petrou, M. (2001). Generalised fuzzy aggregation in estimating the risk of desertification of a burned forest. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 118(1), 121–137.
Shao, Z., Huq, M. E., Cai, B., Altan, O., & Li, Y. (2020). Integrated remote sensing and GIS approach using fuzzy-AHP to delineate and identify groundwater potential zones in semi-arid Shanxi Province. Environmental Modelling & Software., 134, 104868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2020.104868
Sharma, D., Tiwari, A., Sood, S., Meher, P. K., & Kumar, A. (2022). Identification and validation of candidate genes for high calcium content in finger millet [Eleusine coracana (L) Gaertn] through genome-wide association study. Journal of Cereal Science, 107, 103517.
Subba Rao, N. (2018). Groundwater quality from a part of Prakasam District, Andhra Pradesh India. Applied Water Science, 8, 30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0665-2
Tandon, H. L. S. (1995). Methods of analysis of soils, plants, waters, fertilisers & organic manures. Fertiliser development and consultation organisation.
Thapa, R., Gupta, S., Reddy, D. V., et al. (2017). An evaluation of irrigation water suitability in the Dwarka river basin through the use of GIS-based modelling. Environment and Earth Science, 76, 471.
Thivya, C., Chidambaram, S., Singaraja, C., Thilagavathi, R., Prasanna, M. V., Anandhan, P., & Jainab, I. (2013). A study on the significance of lithology in groundwater quality of Madurai district, Tamil Nadu (India). Environment, Development and Sustainability, 15, 1365–1387.
Todd, D. K., & Mays, L. W. (2004). Groundwater hydrology. John Wiley & Sons.
Trivedy, P. K., & Goel, P. K. (2006). Chemical and biological methods for water pollution studies. Environmental publications.
Uddin, M., Alam, M., Mobin, M., & Miah, M. (2014). An assessment of the river water quality parameters: A case of Jamuna River. Journal of Environmental Science, 7(1), 249–256.
United News of Bangladesh. (2019). Acute water scarcity in Khagrachhari district, United News of Bangladesh, Khagrachhari. Published: 12:35. https://www.newagebd.net/article/71522/acute-water-scarcity-in-khagrachhari.
Venkatramanan, S., Chung, S. Y., Rajesh, R., Lee, S. Y., Ramkumar, T., & Prasanna, M. V. (2015). Comprehensive studies of hydrogeochemical processes and quality status of groundwater with tools of cluster, grou** analysis, and fuzzy set method using GIS platform: A case study of Dalcheon in Ulsan CityKorea. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 11209–11223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4290-4
Wang, B., Feng, P., Li Liu, D., & Waters, C. (2020). Modelling biophysical vulnerability of wheat to future climate change: A case study in the eastern Australian wheat belt. Ecological Indicators, 114, 106290.
WHO (World Health Organization). (2022). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Incorporating first and second addenda (4th ed.). Geneva. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240045064
Wilcox, L. V. (1955). Classifcation and use of irrigation waters. US Department of Agriculture.
Wu, Y.-H. (Eva), Hung, M.-C., Wu, Y.-H. (Eva), & Hung, M.-C. (2016). Comparison of spatial interpolation techniques using visualization and quantitative assessment. In Applications of Spatial Statistics. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/65996
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Information and Control, 8, 338–353.
Zaman, M. W., & Rahman, M. M. (1996). Ionic toxicity of industrial process waters in someselected sites off’ Sirajgonj in Bangladesh. Bangladesh Journal of Environmental Sciences., 2, 27–34.
Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, T., Liu, J., You, Z., & Wang, C. (2023). Plasma membrane-associated calcium signaling modulates cadmium transport. New Phytologist, 238(1), 313–331. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.18698
Funding
This work is financially supported (partially) by Research and Training Center (RTC), Patuakhali Science and Technology University (PSTU), Dumki, Patuakhali-8602, Bangladesh. Md. Shariful Islam has received the research support and partial grant from PSTU to conduct this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Md. Shariful Islam, Udoy Jibon Tripura, Md. Saiful Islam, Abu Reza Md. Towfiqul Islam, S. M. Rabbi Al Zihad, and Mst. Moriom Khatun. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Udoy Jibon Tripura, Md. Mahadi Hasan, and Tuba Yasmin Lubna and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read, review, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M., Tripura, U.J., Islam, M.S. et al. Appraising water resources for irrigation and spatial analysis based on fuzzy logic model in the tribal-prone areas of Bangladesh. Environ Monit Assess 196, 641 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12799-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12799-5