Abstract
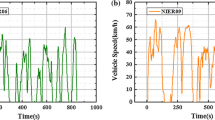
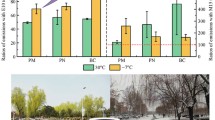
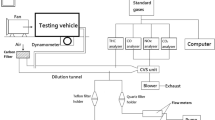
The increasing number of vehicles are emitting a large amount of particles into the atmosphere, causing serious harm to the ecological environment and human health. This study conducted the Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Cycle (WLTC) to investigate the emission characteristics of particle number (PN) of China-VI gasoline vehicles with different gasoline. The gasoline with lower aromatic hydrocarbons and olefins reduced particulate matter (PM) and PN emissions by 24% and 52% respectively. The average PN emission rate of the four vehicles during the first 300 s (the cold start period) was 7.2 times that of the 300 s–1800s. Additionally, because the particle transmission time and instrument response time, the test results of instantaneous emissions of PN were not synchronized with vehicle specific power (VSP). By calculating the Spearman correlation coefficient between pre-average vehicle specific power (PAVSP) and the test results of PN instantaneous emissions, the delay time was determined as 10s. After the PN emissions results were corrected, the PN emissions were found to be more related to VSP. By analyzing the influence of driving status on emission, this study found that vehicles in acceleration mode increased PN emissions by 76% compared to those in constant speed mode.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Abhishek, D., & Orathai, C. (2023). Assessment of health burden due to the emissions of fine particulate matter from motor vehicles: A case of Nakhon Ratchasima province, Thailand. The Science of the Total Environment, 872, 162128–162128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162128
Alashaab, A., Saleh, H., Abo-Serie, E., & Rabee, B. (2016). Gaseous fuel for lower emissions during the cold start and warming up of spark ignition engines. International Journal of Global Warming, 10(1/2/3), 115–132. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGW.2016.077909
An, F., Barth, M., Norbeck, J., & Ross, M. (1997). Development of comprehensive modal emissions model: Operating under hot-stabilized conditions. Transportation Research Record, 1587(1), 52–62. https://doi.org/10.3141/1587-07
Banerjee, T., & Christian, R. (2017). On-field and laboratory measurement of nanoparticle emission in the wake of gasoline vehicle. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8(6), 1179–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2017.05.007
Banerjee, T., & Christian, R. (2019). Effect of operating conditions and speed on nanoparticle emission from diesel and gasoline driven light duty vehicles. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 10(6), 1852–1865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2019.07.017
Chen, L., Liang, Z., Zhang, X., & Shuai, S. (2017). Characterizing particulate matter emissions from GDI and PFI vehicles under transient and cold start conditions. Fuel, 189, 131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.055
Davis, N., Lents, J., Osses, M., Nikkila, N., & Barth, M. (2005). Development and application of an international vehicle emissions model. Transportation Research Record, 1939(1), 156–165. https://doi.org/10.1177/0361198105193900118
USEPA. (2009). Technical guidance on the use of MOVES2010 for emission inventory preparation in state implementation plans and transportation conformity. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Retrieved March 30, 2024, from https://purl.fdlp.gov/GPO/LPS123823
Fang, G., Kao, C., Zhuang, Y., & Huang, P. (2021). Ambient air particulates and hg(p) concentrations and dry depositions estimations, distributions for various particles sizes ranges. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 56(6), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2021.1918976
Frey, C., Rouphail, H., Zhai, M. N., Tiago, N., Farias, L., & Gonçalo, A. G. (2007). Comparing real-world fuel consumption for diesel- and hydrogen-fueled transit buses and implication for emissions. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 12(4), 281–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2007.03.003
Gallus, J., Kirchner, U., Vogt, R., Christoph, B., & Thorsten, B. (2016). On-road particle number measurements using a portable emission measurement system (PEMS). Atmospheric Environment, 124, 37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.11.012
Gao, J., Wang, Y., Chen, H., Laurikko, J., Liu, Y., Pellikka, A. P., & Li, Y. (2022). Variations of significant contribution regions of NOx and PN emissions for passenger cars in the real-world driving. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 424(PC), 127590. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2021.127590
Giechaskiel, B., Lähde, T., & Drossinos, Y. (2019). Regulating particle number measurements from the tailpipe of light-duty vehicles: The next step? Environmental Research, 172, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.02.006
Hannelore, B., Eva, B., Eli, S., Bijnens, E., et al. (2019). Ambient black carbon particles reach the fetal side of human placenta. Nature Communications, 10(1), 3866. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11654-3
Huang, J., Gao, J., Wang, Y., Yang, C., & Chaochen, M. (2022). Real-world pipe-out emissions from gasoline direct injection passenger cars. Processes, 11(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/PR11010066
Ioannis, M., Elisavet, S., Agathangelos, S., & Eugenia, B. (2020). Environmental and health impacts of air pollution: A review. Frontiers in Public Health, 8, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00014
Jiménez, P. J. L. (1999). Understanding and quantifying motor vehicle emissions with vehicle specific power and TILDAS remote sensing. Thesis (Ph.D.), Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Karavalakis, G., Daniel, S., Diep, V., Robert, R., Maryam, H., Akua, A., & A., & Thomas, D, D. (2015). Evaluating the effects of aromatics content in gasoline on gaseous and particulate matter Emissions from SI-PFI and SIDI vehicles. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(11), 7021–7031. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5061726
Ko, J., Kim, K., Chung, W., Myung, C., & Park, S. (2019). Characteristics of on-road particle number (PN) emissions from a GDI vehicle depending on a catalytic stripper (CS) and a metal-foam gasoline particulate filter (GPF). Fuel, 238, 363–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.091
Lents, J., & Davis, N. (2004). IVE model users manual. ISSRC.
Li, G., Zeng, Q., & Pan, X. (2016). Disease burden of ischaemic heart disease from short-term outdoor air pollution exposure in Tian**, 2002–2006. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, 23(16), 1774–1782. https://doi.org/10.1177/2047487316651352
Liu, F., Zhao, F., Liu, Z., & Hao, H. (2020). The impact of purchase restriction policy on Car ownership in China's four major cities. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7454307
Liu, H., & Barth, M. (2012). Identifying the effect of vehicle operating history on vehicle running emissions. Atmospheric Environment, 59, 22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.05.045
Liu, J., Ge, Y., Wang, X., Hao, L., Tan, J., Peng, Z., Zhang, C., Gong, H., & Huang, Y. (2017). On-board measurement of particle numbers and their size distribution from a light-duty diesel vehicle: Influences of VSP and altitude. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 57, 238–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.11.023
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (MEE). (2016). Limits and measurement methods for emissions from light-duty vehicles (CHINA 6), : China Environment Press. Retrieved May 28, 2024, from https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgg/201612/t20161223_369497.htm
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China (MEE). (2022). China Vehicle Environmental Management Annual Report. Retrieved July 9, 2023, from https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/ydyhjgl/202212/t20221207_1007111.shtml
Pan, M., Huang, R., Liao, J., Jia, C., Zhou, X., Huang, H., & Huang, X. (2019). Experimental study of the spray, combustion, and emission performance of a diesel engine with high n -pentanol blending ratios. Energy Conversion and Management, 194, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.04.054
Sandhu, S. G., & Frey, C. H. (2013). Effects of errors on vehicle emission rates from portable emissions measurement systems. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2340(1), 10–19. https://doi.org/10.3141/2340-02
Tang, G., Wang, S., Du, B., Cui, L., Huang, Y., & **ao, W. (2022). Study on pollutant emission characteristics of different types of diesel vehicles during actual road cold start. Science of the Total Environment, 823, 153598. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.153598
Wang, Y., Zheng, R., Qin, Y., Peng, J., Li, M., Lei, J., Wu, Y., Hu, M., & Shuai, S. (2016). The impact of fuel compositions on the particulate emissions of direct injection gasoline engine. Fuel, 166, 543–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.11.019
Wei, J., Zenghui, Y., Yejian, Q., Chenfang, W., & Chen, B. (2019). Comparative effects of olefin content on the performance and emissions of a modern GDI engine. Energy & Fuels, 33(11), 10499–11050. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.9b01894
World Health Organization. (2021). WHO global air quality guidelines: Particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), ozone, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide. Retrieved July 29, 2023, from https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240034228.
Wu, R., Zhong, L., Huang, X., Xu, H., Liu, S., Feng, B., Wang, T., Song, X., Bai, Y., Wu, F., Wang, X., & Huang, W. (2018). Temporal variations in ambient particulate matter reduction associated short-term mortality risks in Guangzhou, China: A time-series analysis (2006–2016). Science of the Total Environment, 645, 491–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.091
Xu, J., Tu, R., Wang, A., Zhai, Z., & Hatzopoulou, M. (2020). Generation of spikes in ultrafine particle emissions from a gasoline direct injection vehicle during on-road emission tests. Environmental Pollution, 267(prepublish), 115695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115695
Yang, D., Hua, Z., Wang, Z., Zhao, S., & Li, J. (2021). Changes in anthropogenic particulate matters and resulting global climate effects since the industrial revolution. International Journal of Climatology, 1, 315–330. https://doi.org/10.1002/JOC.7245
Yang, J., Roth, P., Zhu, H., Thomas, D. D., & Karavalakis, G. (2019). Impacts of gasoline aromatic and ethanol levels on the emissions from GDI vehicles: Part 2. Influence on particulate matter, black carbon, and nanoparticle emissions. Fuel, 252, 812–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.04.144
Zhang, X., Zhang, L., Li, J., Zou, X., **g, X., & Li, W. (2022). Combustion and emission characteristics of diesel with different distillation ranges on the China-VI diesel engine. Fuel, 325, 124876. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUEL.2022.124876
Zhao, H., **g, D., Wang, Y., Shuai, S., & Pang, C. (2017). Effects of aromatic and olefin on the formations of PAHs in GDI engine (p. 2390). SAE Technical Paper Series. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120131
Zhou, H., Zhao, H., Wu, M., Li, J., Wang, J., Feng, Q., Long, Z., Yu, S., Peng, H., Wang, X., & **, T. (2019). Influence of different bin-grou** methods on the estimation of emission factors in model IVE in Chinese. China Environmental Science, 39(02), 560–564. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2019.0067
Funding
This study was sponsored by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFC3703600), and International Clean Energy Talent Program 2017 of China Scholarship Council (201702660024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
iaohan Miao (First Author):Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Writing - Original Draft; **n Zhang:Data Curation, Writing - Original Draft; Chang Wang: Data Curation, Formal Analysis; **gyuan Li (Corresponding Author):Resources, Supervision; Jie Zhao:Visualization, Investigation; Liang Qu:Visualization, Review; Yu Liu:Resources, Supervision; Songbo Qi:Review & Editing; Honglin Li:Review & Editing; Mengqi Fu:Investigation, Formal Analysis; Taosheng ** (Corresponding Author):Conceptualization, Funding Acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing - Review & Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1873 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, X., Zhang, X., Wang, C. et al. Effects of fuel and driving conditions on particle number emissions of China-VI gasoline vehicles: based on corrections to test results. Environ Monit Assess 196, 591 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12756-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12756-2