Abstract
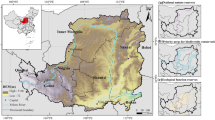
Revealing the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and key driving processes behind the habitat quality is of great significance for the scientific management of production, living, and ecological spaces in resource-based cities, as well as for the efficient allocation of resources. Focusing on the largest coal-mining subsidence area in Jiangsu Province of China, this study examines the spatiotemporal evolution of land use intensity, morphology, and functionality across different time periods. It evaluates the habitat quality characteristics of the Pan’an Lake area by utilizing the InVEST model, spatial autocorrelation, and hotspot analysis techniques. Subsequently, by employing the GTWR model, it quantifies the influence of key factors, unveiling the spatially varying characteristics of their impact on habitat quality. The findings reveal a notable surge in construction activity within the Pan’an Lake area, indicative of pronounced human intervention. Concurrently, habitat degradation intensifies, alongside an expanding spatial heterogeneity in degradation levels. The worst habitat quality occurs during the periods of coal mining and large-scale urban construction. The escalation in land use intensity emerges as the primary catalyst for habitat quality decline in the Pan’an Lake area, with other factors exhibiting spatial variability in their effects and intensities across different stages.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Ai, M. S., Chen, X., & Yu, Q. (2024). Spatial correlation analysis between human disturbance intensity (HDI) and ecosystem services value (ESV) in the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration. Ecological Indicators, 158. doi:ARTN 111555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.111555.
Aneseyee, A. B., Noszczyk, T., Soromessa, T., & Elias, E. (2020). The InVEST habitat quality model associated with land use/cover changes: A qualitative case study of the Winike watershed in the Omo-Gibe Basin, Southwest Ethiopia. Remote Sensing, 12(7). doi:ARTN. 1103 https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071103.
Artmann, M., Inostroza, L., & Fan, P. L. (2019). From urban sprawl to compact green cities—Advancing multi-scale and multi-dimensional analysis. Ecological Indicators, 96, 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.10.058
Bao, J. L., Gao, S., & Ge, J. X. (2019). Salt and wetland: Traditional development landscape, land use changes and environmental adaptation on the Central Jiangsu Coast, China, 1450–1900. Wetlands, 39(5), 1089–1102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-019-01144-z
Baral, H., Keenan, R. J., Sharma, S. K., Stork, N. E., & Kasel, S. (2014). Spatial assessment and map** of biodiversity and conservation priorities in a heavily modified and fragmented production landscape in north-central Victoria, Australia. Ecological Indicators, 36, 552–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.09.022
Cai, Y. B., Zhang, H., Pan, W. B., Chen, Y. H., & Wang, X. R. (2013). Land use pattern, socio-economic development, and assessment of their impacts on ecosystem service value: Study on natural wetlands distribution area (NWDA) in Fuzhou city, southeastern China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(6), 5111–5123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2929-x
Chen, C. Y., Liu, J., & Bi, L. L. (2023a). Spatial and temporal changes of habitat quality and its influential factors in China based on the InVEST model. Forests, 14(2). doi:ARTN 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14020374.
Chen, Y. D., Chang, J., Li, Z. X., Ming, L., Li, C. K., & Li, C. (2023b). Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal analysis of urban compactness and land-use efficiency in resource-based areas: A case study of Shanxi Province, China. Land, 12(9). doi:ARTN 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12091658.
Gao, Y., Ma, L., Liu, J. X., Zhuang, Z. Z., Huang, Q. H., & Li, M. C. (2017). Constructing ecological networks based on habitat quality assessment: A case study of Changzhou, China. Scientific Reports, 7. doi:ARTN 46073. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46073.
Haase, D., Haase, A., & Rink, D. (2014). Conceptualizing the nexus between urban shrinkage and ecosystem services. Landscape and Urban Planning, 132, 159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2014.09.003
Hou, W., Zhou, W., Li, J. Y., & Li, C. (2022). Simulation of the potential impact of urban expansion on regional ecological corridors: A case study of Taiyuan, China. Sustainable Cities and Society, 83. doi:ARTN 103933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.103933.
Hu, X. S., & Xu, H. Q. (2018). A new remote sensing index for assessing the spatial heterogeneity in urban ecological quality: A case from Fuzhou City, China. Ecological Indicators, 89, 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.02.006
Hu, T. H., Chang, J., Liu, X. X., & Feng, S. S. (2018). Integrated methods for determining restoration priorities of coal mining subsidence areas based on green infrastructure: A case study in the Xuzhou urban area, of China. Ecological Indicators, 94, 164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.11.006
Krellenberg, K., Koch, F., & Kabisch, S. (2016). Urban sustainability transformations in lights of resource efficiency and resilient city concepts. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 22, 51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2017.04.001
Lauf, S., Haase, D., & Kleinschmit, B. (2014). Linkages between ecosystem services provisioning, urban growth and shrinkage—A modeling approach assessing ecosystem service trade-offs. Ecological Indicators, 42, 73–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.01.028
Law, B., Caccamo, G., Roe, P., Truskinger, A., Brassil, T., Gonsalves, L., et al. (2017). Development and field validation of a regional, management-scale habitat model: A koala case study. Ecology and Evolution, 7(18), 7475–7489. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.3300
Li, H. D., Xu, X. J., Zhai, F. F., Zhang, Y. X., & Li, Z. G. (2023). Spatiotemporal evolution of habitat quality in typical resource—Depleted cities in China based on land use changes. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 32(6), 5677–5690. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/168718
Li, Z. X., Chang, J., Wang, Z. Y., Chen, Y. D., & Li, C. (2024). Stability of regional ecological supply-demand is enhanced by complex network modeling: Evidence from the Xuzhou metropolitan area, China. Ieee Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 17, 1857–1873. https://doi.org/10.1109/Jstars.2023.3342985
Li, X. Y., Dong, W., Liu, Y., & Yang, Y. (2022). Tracking the urban expansion and its driving mechanisms behind **njiang production and construction corps (XPCC): Evidence from morphology and landscapes. Habitat International, 126. doi:ARTN 102599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2022.102599.
Lourenço, I. B., Guimaraes, L. F., Alves, M. B., & Miguez, M. G. (2020). Land as a sustainable resource in city planning: The use of open spaces and drainage systems to structure environmental and urban needs. Journal of Cleaner Production, 276. doi:ARTN 123096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123096.
Moreira, M., Fonseca, C., Vergílio, M., Calado, H., & Gil, A. (2018). Spatial assessment of habitat conservation status in a Macaronesian island based on the InVEST model: A case study of Pico Island (Azores, Portugal). Land Use Policy, 78, 637–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.07.015
Newbold, T., Hudson, L. N., Hill, S. L. L., Contu, S., Lysenko, I., Senior, R. A., et al. (2015). Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature, 520(7545), 45-+. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14324.
Paredes-Arquiola, J., Solera, A., Martinez-Capel, F., Momblanch, A., & Andreu, J. (2014). Integrating water management, habitat modelling and water quality at the basin scale and environmental flow assessment: Case study of the Tormes River, Spain. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 59(3–4), 878–889. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2013.821573
Qiu, S., Yu, Q., Niu, T., Fang, M. Z., Guo, H. Q., Liu, H. J., et al. (2022). Study on the landscape space of typical mining areas in Xuzhou City from 2000 to 2020 and optimization strategies for carbon sink enhancement. Remote Sensing, 14(17). doi:ARTN 4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14174185.
Song, Y. A., Wang, M., Sun, X. F., & Fan, Z. M. (2021). Quantitative assessment of the habitat quality dynamics in Yellow River Basin, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(9). doi:ARTN 614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09404-4.
Wang, B. X., & Cheng, W. M. (2022). Effects of land use/cover on regional habitat quality under different geomorphic types based on InVEST model. Remote Sensing, 14(5). doi:ARTN 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051279.
Wang, C., Shi, J., Ni, Y. K., Zhou, Y. Y., Yang, X. Q., Wei, S. J., et al. (2020). Semi-supervised learning-based remote sensing image scene classification via adaptive perturbation training. Igarss 2020 - 2020 Ieee International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 541–544. https://doi.org/10.1109/Igarss39084.2020.9323430.
Wang, D., Ji, X., Li, C., & Gong, Y. X. (2021). Spatiotemporal variations of landscape ecological risks in a resource-based city under transformation. Sustainability, 13(9). doi:ARTN 5297. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13095297.
Wang, B., Wang, Y. X., & Wu, X. F. (2023). Impact of land use compactness on the habitat services from green infrastructure in Wuhan, China. Urban Forestry and Urban Greening, 84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2023.127927.
Weber, D., Schaepman-Strub, G., & Ecker, K. (2018). Predicting habitat quality of protected dry grasslands using Landsat NDVI phenology. Ecological Indicators, 91, 447–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.03.081
Wei, Q. Q., Abudureheman, M., Halike, A., Yao, K. X., Yao, L., Tang, H., et al. (2022). Temporal and spatial variation analysis of habitat quality on the PLUS-InVEST model for Ebinur Lake Basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 145. doi:ARTN 109632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109632.
Wu, J. S., Li, X. C., Luo, Y. H., & Zhang, D. N. (2021a). Spatiotemporal effects of urban sprawl on habitat quality in the Pearl River Delta from 1990 to 2018. Scientific Reports, 11(1). doi:ARTN 13981. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92916-3.
Wu, L. L., Sun, C. G., & Fan, F. L. (2021b). Estimating the characteristic spatiotemporal variation in habitat quality using the InVEST model—A case study from Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Remote Sensing, 13(5). doi:ARTN 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13051008.
Wu, H. J., Deng, K. L., Dong, Z. F., Meng, X. R., Zhang, L., Jiang, S. Y., et al. (2022). Comprehensive assessment of land use carbon emissions of a coal resource-based city, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 379. doi:ARTN 134706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134706.
**ao, P. N., Zhou, Y., Li, M. Y., & Xu, J. (2023). Spatiotemporal patterns of habitat quality and its topographic gradient effects of Hubei Province based on the InVEST model. Environment Development and Sustainability, 25(7), 6419–6448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02310-w
**ao, Y., Zhong, J. L., Zhang, Q. F., **ang, X., & Huang, H. (2022). Exploring the coupling coordination and key factors between urbanization and land use efficiency in ecologically sensitive areas: A case study of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainable Cities and Society, 86. doi:ARTN 104148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2022.104148.
Xu, J. X., Li, G., & Zhao, H. (2013). Study on the change of landscape ecological quality based on land use: A case study in resource-exhausted mining area. Progress in Environmental Protection and Processing of Resource, Pts, 1–4(295–298), 2679–2683. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.295-298.2679
Xu, J. X., Zhao, H., Yin, P. C., Wu, L. X., & Li, G. (2019). Landscape ecological quality assessment and its dynamic change in coal mining area: A case study of Peixian. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(24). doi:ARTN 708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8747-5.
Yang, X., Liu, S., Jia, C., Liu, Y., & Yu, C. C. (2021). Vulnerability assessment and management planning for the ecological environment in urban wetlands. Journal of Environmental Management, 298. doi:ARTN 113540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113540.
Yang, Y., Cheng, D. Y., Zhang, B., Guan, C. H., Cheng, X. L., & Cheng, T. (2023). Coal resource-based cities at the crossroads: Towards a sustainable urban future. Cities, 140. doi:ARTN 104424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2023.104424.
Yu, P. H., Zhang, S. J., Yung, E. H. K., Chan, E. H. W., Luan, B., & Chen, Y. Y. (2023). On the urban compactness to ecosystem services in a rapidly urbanising metropolitan area: Highlighting scale effects and spatial non-stationary. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 98. doi:ARTN 106975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106975.
Zhang, X. R., Song, W., Lang, Y. Q., Feng, X. M., Yuan, Q. Z., & Wang, J. T. (2020). Land use changes in the coastal zone of China’s Hebei Province and the corresponding impacts on habitat quality. Land Use Policy, 99. doi:ARTN 104957 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104957.
Zhang, W. S., Wang, J. H., Xu, Y., Wang, C., & Streets, D. G. (2022). Analyzing the spatio-temporal variation of the CO emissions from district heating systems with “Coal-to-Gas” transition: Evidence from GTWR model and satellite data in China. Science of the Total Environment, 803. doi:ARTN 150083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150083.
Zhao, L. S., Yu, W. Y., Meng, P., Zhang, J. S., & Zhang, J. X. (2022). InVEST model analysis of the impacts of land use change on landscape pattern and habitat quality in the **aolangdi Reservoir area of the Yellow River basin, China. Land Degradation and Development, 33(15), 2870–2884. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.4361
Zhou, G., Wang, C. M., Li, S. L., Duan, J. J., Ma, Y., **g, B., et al. (2021). Preparation and characteristics analysis of an ecoenvironmental protection cyclic solidification dust-fixing agent extracted from waste shrimp shells to suppress dust in coal resource-based cities. Journal of Environmental Management, 296. doi:ARTN 113224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113224.
Zhou, S. Y., Chang, J., Luo, P. J., Kang, Y., & Li, S. (2023). Landscape dynamics and human disturbance processes in wetlands in a mining city: A case study in Huaibei, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(1). doi:ARTN 192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10795-1.
Zhu, S. X., Li, L., Wu, G. S., Liu, J. L., Slate, T. J., Guo, H. Y., et al. (2022). Assessing the impact of village development on the habitat quality of Yunnan snub-nosed monkeys using the INVEST model. Biology-Basel, 11(10). doi:ARTN 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101487.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Research Center for Transitional Development and Rural Revitalization of China’s Resource-Based Cities for providing data which helps to interpret the results.
Funding
This research was funded by the Assistance Program for Future Outstanding Talents of China University of Mining and Technology (Grant No. 2022WLKXJ056); Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. KYCX22_2572); and Xuzhou Science and Technology Plan Project-Key R&D Program (Grant No. KC21145).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yedong Chen: data curation, writing—original draft, methodology. Jiang Chang: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition. Zixuan Li: data curation, visualization. Li Ming: formal analysis, data curation. Cankun Li: validation, investigation. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.
Consent to participate
All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study.
Consent for publication
All the authors consent to publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Chang, J., Li, Z. et al. Influence of land use change on habitat quality: a case study of coal mining subsidence areas. Environ Monit Assess 196, 535 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12702-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12702-2