Abstract
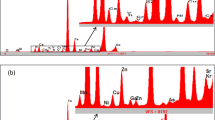
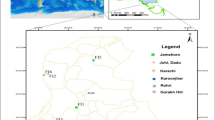
Soil factors, especially metal elements in the soil, play a significant role in forming and accumulating secondary metabolites, which determine the medicinal properties of medicinal herbs. In this study, the concentrations of some metal elements (K, Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, and Cr) in Cam Mountain and Tinh Bien Town, An Giang Province, Vietnam, were determined using the XRF method. We simultaneously determined the total phenolic and flavonoid content of some medicinal herbs collected from the collected soil sample areas, thereby assessing the influence of these elements on the formation of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. The results showed that K, Mn, and Cr were mainly concentrated in the topsoil and transition layers; Fe and Cu elements tended to concentrate in the transition layer and the subsoil when surveying the soil profile. K, Mn, Cu, and Cr concentrations were more focused in Tinh Bien area, while Fe and Zn had higher concentrations at Cam Mountain. Additionally, results from evaluating the relationship between the content of the elements in the soil and the content of two active compounds also showed the correlation regression model between Zn and flavonoid expression by level 4 at the 5% significance level. Thus, the nonlinear model is suitable for evaluating the relationship between the content of metal elements in the soil and the active compound in medicinal plants.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
Abbreviations
- CM:
-
Cam Mountain
- O. indicum :
-
Oroxylum indicum
- P. fruticosa :
-
Polyscias fruticosa
- R. nasutus :
-
Rhinacanthus nasutus
- S. octophylla :
-
Schefflera octophylla
- S. torvum :
-
Solanum torvum
- TB:
-
Tinh Bien
- Z. zerumbet :
-
Zingiber zerumbet
References
Archontoulis, S. V., & Miguez, F. E. (2015). Nonlinear regression models and applications in agricultural research. Agronomy Journal, 107(2), 786–798. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2012.0506
Babu, P. V. A., Liu, D., & Gilbert, E. R. (2013). Recent advances in understanding the anti-diabetic actions of dietary flavonoids. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 24(11), 1777–1789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.06.003
Boroom, N., & Grouh, M. S. H. (2012). Macroelements nutrition (NPK) of medicinal plants: A review. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 6(12), 2249–2255. https://doi.org/10.5897/JMPR11.019
Chi, V. V. (1991). Medicinal plants in An Giang province. The An Giang Committee of Science and Technology: An Giang.
Choy, K. W., Murugan, D., Leong, X.-F., Abas, R., Alias, A., & Mustafa, M. R. (2019). Flavonoids as natural anti-inflammatory agents targeting nuclear factor-kappa B (NFκB) signaling in Cardiovascular diseases: A mini review. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10(1295). https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01295
Corliss, W. R. (1963). Neutron activation analysis (Vol. 7). US Atomic Energy Commission, Division of Technical Information.
Crozier, A., Jaganath, I. B., & Clifford, M. N. (2009). Dietary phenolics: Chemistry, bioavailability and effects on health. Natural Product Reports, 26(8), 1001–1043. https://doi.org/10.1039/B802662A
Drzewiecka, K., Mleczek, M., Gąsecka, M., Magdziak, Z., Budka, A., Chadzinikolau, T., et al. (2017). Copper and nickel co-treatment alters metal uptake and stress parameters of Salix purpurea×viminalis. Journal of Plant Physiology, 216, 125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2017.04.020
Esfahani, A. N., & Mirzaei, M. (2019). Flavonoid derivatives for monoamine oxidase–A inhibition. Advanced Journal of Chemistry-Section B, 1(1), 17–22. https://doi.org/10.33945/SAMI/AJCB.2019.1.4
Farhadi, F., Khameneh, B., Iranshahi, M., & Iranshahy, M. (2019). Antibacterial activity of flavonoids and their structure–activity relationship: An update review. Phytotherapy Research, 33(1), 13–40. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6208
Gąsecka, M., Mleczek, M., Jutrzenka, A., Goliński, P., & Stuper-Szablewska, K. (2017). Phenolic compounds in leaves of Salix species and hybrids growing under different soil conditions. Chemistry and Ecology, 33(3), 196–212. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2017.1289186
Gąsecka, M., Mleczek, M., Siwulski, M., & Niedzielski, P. (2016). Phenolic composition and antioxidant properties of Pleurotus ostreatus and Pleurotus eryngii enriched with selenium and zinc. European Food Research and Technology, 242(5), 723–732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-015-2580-1
Ghorbanpour, M., Asgari Lajayer, H., & Hadian, J. (2016). Influence of copper and zinc on growth, metal accumulation and chemical composition of essential oils in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Journal of Medicinal Plants, 15(59), 132–144. http://jmp.ir/article-1-1473-en.html
Ginwala, R., Bhavsar, R., Chigbu, D. G. I., Jain, P., & Khan, Z. K. (2019). Potential role of flavonoids in treating chronic inflammatory diseases with a special focus on the anti-inflammatory activity of apigenin. Antioxidants, 8(2), 35–62. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8020035
Hammoudi, A., Iosifescu, O., & Bernoux, M. (2015). Mathematical analysis of a nonlinear model of soil carbon dynamics. Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems, 23(4), 453–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12591-014-0227-5
Hegazy, M. H., Alzuaibr, F. M., Mahmoud, A. A., Mohamed, H. F., & Said-Al Ahl, H. A. (2016). The effects of zinc application and cutting on growth, herb, essential oil and flavonoids in three medicinal Lamiaceae plants. European Journal of Medicinal Plants, 12(3), 1–12.
Hien, N. M., Thi, P. T., Ngan, H. T. K., Nhi, N. T. Y., Dung, N. T., & Tri, L. M. (2021). Study on the content of some metals in soil by XRF method and evaluating their effect on the total phenolic and flavonoid content of methanol extracts from two medicinal plants in An Giang Province. VNUHCM Journal of Engineering and Technology, 4(2), 900–909. https://doi.org/10.32508/stdjet.v4i2.798
Hussein, R. A., & El-Anssary, A. A. (2019). Plants secondary metabolites: The key drivers of the pharmacological actions of medicinal plants. Herbal Medicine, 1(3), 11–30. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.76139
ISO. (1995). Soil quality — Extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia. (ISO 11466:1995). International Organization for Standardization. https://www.iso.org/standard/19418.html
Jaakola, L., & Hohtola, A. (2010). Effect of latitude on flavonoid biosynthesis in plants. Plant, Cell & Environment, 33(8), 1239–1247. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02154.x
Jiang, J., Yuan, X., Wang, T., Chen, H., Zhao, H., Yan, X., et al. (2014). Antioxidative and cardioprotective effects of total flavonoids extracted from Dracocephalum moldavica L. against acute ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury in isolated rat heart. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 14, 74–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-013-9221-3
Jiang, N., Doseff, A. I., & Grotewold, E. (2016). Flavones: From biosynthesis to health benefits. Plants, 5(2), 27–51. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants5020027
Jobbagy, E. G., & Jackson, R. B. (2001). The distribution of soil nutrients with depth: Global patterns and the imprint of plants. Biogeochemistry, 53(1), 51–77. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010760720215
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2004). Soil–plant transfer of trace elements—an environmental issue. Geoderma, 122(2–4), 143–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.01.004
Karak, P. (2019). Biological activities of flavonoids: an overview. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 10(4), 1567–1574. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.10(4).1567-74
Khorsandi, F., Yazdi, F. A., & Vazifehshenas, M. R. (2009). Foliar zinc fertilization improves marketable fruit yield and quality attributes of pomegranate. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 11(6), 766–770. https://www.fspublishers.org/published_papers/11926_..pdf
Krauss, M., Wilcke, W., Kobza, J., & Zech, W. (2002). Predicting heavy metal transfer from soil to plant: Potential use of Freundlich-type functions. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 165(1), 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/1522-2624(200202)165:1%3c3::AID-JPLN3%3e3.0.CO;2-B
Kumar, S., & Pandey, A. K. (2013). Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. The Scientific World Journal. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/162750
Laenger, A., Martel, A., Boucher, F., François, X., Dabas, M., Rouillard, J., & Durand, A. (2022). Comparison of geophysical prospecting and geochemical prospecting at the medieval and modern Cistercian Abbey of Carnoët (Finistère, France). Archaeological Prospection, 29(4), 597–606.
Lambert, J. D., Hong, J., Yang, G.-Y., Liao, J., & Yang, C. S. (2005). Inhibition of carcinogenesis by polyphenols: Evidence from laboratory investigations. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 81(1), 284S-291S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/81.1.284S
Larit, F., Elokely, K. M., Chaurasiya, N. D., Benyahia, S., Nael, M. A., León, F., et al. (2018). Inhibition of human monoamine oxidase A and B by flavonoids isolated from two Algerian medicinal plants. Phytomedicine, 40, 27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2017.12.032
Machado, R. C., Andrade, D. F., Babos, D. V., Castro, J. P., Costa, V. C., Sperança, M. A., et al. (2020). Solid sampling: Advantages and challenges for chemical element determination—A critical review. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 35(1), 54–77. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9JA00306A
Magalingam, K. B., Radhakrishnan, A., & Haleagrahara, N. (2013). Rutin, a bioflavonoid antioxidant protects rat pheochromocytoma (PC-12) cells against 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced neurotoxicity. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 32(1), 235–240. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1375
Manvar, D., Mishra, M., Kumar, S., & Pandey, V. N. (2012). Identification and evaluation of anti hepatitis C virus phytochemicals from Eclipta alba. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 144(3), 545–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.09.036
Marchant, B., Saby, N., Lark, R., Bellamy, P., Jolivet, C., & Arrouays, D. (2010). Robust analysis of soil properties at the national scale: Cadmium content of French soils. European Journal of Soil Science, 61(1), 144–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2009.01212.x
Minister of Natural Resources and Environment. (2015). QCVN 03-MT:2015/BTNMT on national technical regulation on the allowable limits of heavy metals in the soils. http://www.iph.org.vn/attachments/article/1010/QCVN%2003.2015_Kim%20loai%20nang%20trong%20dat.pdf
Mykhailenko, O., Gudžinskas, Z., Kovalyov, V., Desenko, V., Ivanauskas, L., Bezruk, I., & Georgiyants, V. (2020). Effect of ecological factors on the accumulation of phenolic compounds in Iris species from Latvia. Lithuania and Ukraine. Phytochemical Analysis, 31(5), 545–563. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2918
Nile, S. H., Keum, Y. S., Nile, A. S., Jalde, S. S., & Patel, R. V. (2018). Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and enzyme inhibitory activity of natural plant flavonoids and their synthesized derivatives. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 32(1), e22002. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22002
Pande, P., Chand, S., Pandey, A., & Patra, D. (2011). Effect of sole and conjoint application of iron and manganese on herb yield, nutrient uptake, oil quality vis-a-vis their optimal level in spearmint (Mentha spicata Linn. emend. Nathh. cv.‘Arka’). Indian Journal of Natural Products and Resources, 242–249. http://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/12149
Purdue Department of Chemistry. (2020). Epsilon 4 X-ray fluorescence spectrometer – Basic data collection and analysis of an unknown sample using the Omnian procedure Retrieved Aug 30, 2022 from https://www.chem.purdue.edu/xray/docs/Epsilon%204%20Basic%20Instructions%20Omnian.pdf
Radušienė, J., Karpavičienė, B., & Stanius, Ž. (2012). Effect of external and internal factors on secondary metabolites accumulation in St. John’s worth. Botanica Lithuanica, 18(2), 101–108. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10279-012-0012-8
Senhou, A., Chouak, A., Cherkaoui, R., Lferde, M., Elyahyaoui, A., El Khoukhi, T., et al. (2002). Comparison of 14 MeV-NAA, k0-NAA and ED-XRF for air pollution bio-monitoring. Journal of Radioanalytical Nuclear Chemistry, 253(2), 247–252. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1019697725334
Shakya, A. K. (2016). Medicinal plants: Future source of new drugs. International Journal of Herbal Medicine, 4(4), 59–64. https://www.florajournal.com/archives/2016/vol4issue4/PartA/4-2-13-120.pdf
Shaltout, A. A., Dabi, M. M., Ibrahim, M. M., Al-Ghamdi, A. S., & Elnagar, E. (2020). Applicability of low-cost binders for the quantitative elemental analysis of urinary stones using EDXRF based on fundamental parameter approach. Biological Trace Element Research, 195(2), 417–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01884-3
Shuai, W., Qizhen, J., Genyuan, C., Zhang, L., & Chunhui, M. (2013). Anti-aging effects of the flavonoids of Oxytropis glabra DC. on Mice. Medicinal Plant, 4(7), 42–45.
Singh, A. K. (2016). Experimental Methodologies for the characterization of nanoparticles. In Engineered Nanoparticles: Structure, Properties and Mechanisms of Toxicity, 4, 125–170. Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801406-6.00004-2
Song, C. -Z., Liu, M. -Y., Meng, J. -F., Chi, M., **, Z. -M., & Zhang, Z. -W. (2015). Promoting effect of foliage sprayed zinc sulfate on accumulation of sugar and phenolics in berries of Vitis vinifera cv. Merlot growing on zinc deficient soil. Molecules, 20(2), 2536–2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20022536
Takahashi, G. (2015). Sample preparation for X-ray fluorescence analysis III. Pressed and loose powder methods. Rigaku Journal, 31(1), 26–30. https://www.rigaku.com/journal/winter-2015-volume-31-no-1/26-30
Tang, J., Diao, P., Shu, X., Li, L., & **ong, L. (2019). Quercetin and quercitrin attenuates the inflammatory response and oxidative stress in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells: In vitro assessment and a theoretical model. BioMed Research International, 2019, 7039802–7039809. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7039802
Thuy, T. N., Man, D. M., & Van, P. H. T. (2019). Local knowledge in natural collection and use of medicinal plants resources in An Giang Province. AGU International Journal of Sciences, 7(1), 74–84. https://apps.agu.edu.vn/qlkh/storage/app/agu/1575000220-10-truong-ngoc-thuypdf.pdf
Vereecken, H., Schnepf, A., Hopmans, J. W., Javaux, M., Or, D., Roose, T., et al. (2016). Modeling Soil Processes: Review, Key Challenges, and New Perspectives. Vadose Zone Journal, 15(5). https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2015.09.0131
Waterhouse, A. L. (2002). Determination of total phenolics. Current protocols in food analytical chemistry, 6(1), I1-1. 1.8. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142913.fai0101s06
Wink, M. (2015). Modes of action of herbal medicines and plant secondary metabolites. Medicines, 2(3), 251–286. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines2030251
Zawisza, B., Musielak, M., de Beer, D., Joubert, E., & Walczak, B. (2021). Non-destructive elemental analysis of herbal teas from South Africa. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 102, 104041–104050.
Zhanbin, L., Qinling, Z., & Peng, L. (2013). Distribution characteristics of available trace elements in soil from a reclaimed land in a mining area of north Shaanxi, China. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 1(1), 65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-6339(15)30051-4
Zhang, H.-W., Hu, J.-J., Fu, R.-Q., Liu, X., Zhang, Y.-H., Li, J., et al. (2018). Flavonoids inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis and autophagy through downregulation of PI3Kγ mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K/ULK signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29308-7
Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Ding, Z., Wang, H., Song, L., Jia, S., & Ma, D. (2017). Zinc stress affects ionome and metabolome in tea plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 111, 318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.12.014
Zhu, A. X., Band, L., Vertessy, R., & Dutton, B. (1997). Derivation of soil properties using a soil land inference model (SoLIM). Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61(2), 523–533. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1997.03615995006100020022x
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of time and facilities from Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology (HCMUT) for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nguyen Minh Hien designed the experiments. Huynh Thi Kim Ngan, Nguyen Minh Hien, and Pham Tan Thi contributed to collecting soil and medicinal samples, preparing, and measuring soil samples as well as processing data. Nguyen Minh Hien and Pham Tan Thi contributed to the preparation of soil and medicinal samples and sample measurement. Nguyen Minh Hien and Huynh Thi Kim Ngan performed the statistical analysis. All authors participated in writing the manuscript and reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, H.M., Huynh, N.T.K., Ha, L.T. et al. Utilizing X-ray fluorescence (XRF) method to evaluate the content of metal elements in soil and their effects on the total phenolic and flavonoid contents of some medicinal plants. Environ Monit Assess 195, 963 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11585-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11585-z