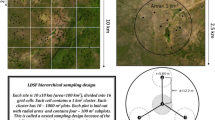
Abstract
Today’s agri-food systems face the triple challenge of addressing food security, adapting to climate change, and reducing the climate footprint by reducing the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG). In agri-food systems, changes in land use and land cover (LULC) could affect soil physicochemical properties, particularly soil organic carbon (SOC) stock. However, the impact varies depending on the physical, social, and economic conditions of a given region or watershed. Given this, a study was conducted to quantify the impact of LULC and slope gradient on SOC stock and C sequestration rate in the Anjeni watershed, which is a highly populated and intensively cultivated area in Northwest Ethiopia. Seventy-two soil samples were collected from 0–15 and 15–30 cm soil depths representing four land use types and three slope gradients. Soil samples were selected systematically to match the historical records (30 years) for SOC stock comparison. Four land use types were quantified using Landsat imagery analysis. As expected, plantation forest had a significantly (p < 0.05) higher SOC (1.94 Mg ha−1) than cultivated land (1.38 Mg ha−1), and gentle slopes (1–15%) had the highest SOC (1.77 Mg ha−1) than steeper slopes (> 30%). However, higher SOC stock (72.03 Mg ha−1) and SOC sequestration rate (3.00 Mg ha−1 year−1) were recorded when cultivated land was converted to grassland, while lower SOC stock (8.87 Mg ha−1) and sequestration rate (0.77 Mg ha−1 year−1) were recorded when land use changed from cultivation to a plantation forest. The results indicated that LULC changes and slope gradient had a major impact on SOC stock and C sequestration rate over 30 years in a highly populated watershed. It is concluded that in intensively used watersheds, a carefully planned land use that involves the conversion of cultivated land to grassland could lead to an increase in soil C sequestration and contributes to reducing the carbon footprint of agri-food systems.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abera, Y., & Belachew, T. (2011). Effects of landuse on soil organic carbon and nitrogen in soils of bale, Southeastern Ethiopia. Tropical and Subtropical Agroecosystems, 14, 229–235.
Agidew, A. meta A., & Singh, K. N. (2017). The implications of land use and land cover changes for rural household food insecurity in the Northeastern highlands of Ethiopia: The case of the Teleyayen sub-watershed. Agric. Food Secur., 6, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40066-017-0134-4
Alemu, B. (2015). The Effect of Land Use Land Cover Change on Land Degradation in the Highlands of Ethiopia. ISSN 2224–3216 (Paper) ISSN 2225–0948 (Online). Journal of Environment and Earth Science, 5(1), 1–13. www.iiste.org
Alemu, W. G., Amare, T., Yitaferu, B., Selassie, Y. G., Wolfgramm, B., & Hurni, H. (2013). Impacts of Soil and Water Conservation on Land Suitability to Crops: The Case of Anjeni Watershed, Northwest Ethiopia. Journal of Agricultural Science, 5, 95–109. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v5n2p95
Amanuel, W., Yimer, F., & Karltun, E. (2018). Soil organic carbon variation in relation to land use changes: The case of Birr watershed, upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. Journal of Ecology and Environmen, 42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41610-018-0076-1
Amare, T. (2018). Impact of Sustainable Land Management Practices on Soil Organic Carbon Content of Three Watersheds in Ethiopia. Ethiopian Journal of Natural Resources, 17, 61–83.
Amare, T., Hergarten, C., Hurni, H., Wolfgramm, B., Yitaferu, B., & Selassie, Y. G. (2013). Prediction of Soil Organic Carbon for Ethiopian Highlands Using Soil Spectroscopy. ISRN Soil Science, 2013, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/720589
Anokye, J., Logah, V., & Opoku, A. (2021). Soil carbon stock and emission: estimates from three land-use systems in Ghana. Ecological Processes, 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-020-00279-w
Assefa and Bork. (2014). Deforestation and Forest Management in Southern Ethiopia: Investigations in the Chencha and Arbaminch Areas 284–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-013-0182-x
Assefa, F., Elias, E., Soromessa, T., & Ayele, G. T. (2020). Effect of Changes in Land-Use Management Practices on Soil Physicochemical Properties in Kabe Watershed, Ethiopia. Air, Soil and Water Research, 13. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178622120939587
Betemariyam, M., Negash, M., & Worku, A. (2020). Comparative Analysis of Carbon Stocks in Home Garden and Adjacent Coffee Based Agroforestry Systems in Ethiopia. Small-Scale, 19, 319–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11842-020-09439-4
Bizuhoraho, T., Kayiranga, A., Manirakiza, N., & Mourad, K. A. (2018). The Effect of Land Use Systems on Soil Properties; A case study from Rwanda. Sustainable Agriculture Research, 7, 30. https://doi.org/10.5539/sar.v7n2p30
Blake, G. R., & Hartge, K. H. (2018). Bulk density. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 1 Physical and Mineralogical Methods, 9, 363–375. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.1.2ed.c13
Blake, G. R. R., & Hartge, K. H. H. (1986). Bulk Density, in: Klute, A. (Ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1. Physical and Mineralogical Methods, SSSA Book Series SV - 5.1. ASA, SSSA, Madison, USA, pp. 363–375. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.1.2ed.c13
Boix-Fayos, C., de Vente, J., Albaladejo, J., & Martínez-Mena, M. (2009). Soil carbon erosion and stock as affected by land use changes at the catchment scale in Mediterranean ecosystems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 133, 75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.05.013
Bouyoucos, G. J. (1962). Hydrometer Method Improved for Making Particle Size Analyses of Soils1. Agronomy Journal, 54, 464–465. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1962.00021962005400050028x
Brandt, M., Rasmussen, K., Peñuelas, J., Tian, F., Schurgers, G., Verger, A., Mertz, O., Palmer, J. R. B., & Fensholt, R. (2017). Human population growth offsets climate-driven increase in woody vegetation in sub-Saharan Africa. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 4–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-017-0081
Bremner, J. M., & Mulvaney, C. S. (1982). Nitrogen-Total, in: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties. ASA, SSSA, Madison, Wisconsin USA, pp. 595–624. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.3.c37
Chapman, H. D. (1965). Cation Exchange Capacity. In: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2.: Chemical and Microbiological Properties. ASA, SSSA, Madison, USA, pp. 891–901. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.c6
Chemistry, S. (2014). Introduction to Soil Chemistry. Introduction to Soil Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118773383
Fite, T. (2017). Influence of Different Land Use Types and Soil Depths on Selected Soil Properties Related to Soil Fertility in Warandhab Area, Horo Guduru Wallaga Zone, Oromiya, Ethiopia. International Journal of Environmental Sciences & Natural Resources, 4. https://doi.org/10.19080/ijesnr.2017.04.555634
Getahun, Y. S., & Haj, V. L. (2015). Assessing the Impacts of Land Use-Cover Change on Hydrology of Melka Kuntrie Subbasin in Ethiopia, Using a Conceptual Hydrological Model. Journal of Waste Water and Treatment Analysis, 6. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7587.1000210
Gete, Z. (2000). Landscape Dynamics and Soil Erosion Process Modelling in the North Western Ethiopia highlands. Univesity of Berne, Switzerland.
Girmay, G., Singh, B. R., Mitiku, H., Borresen, T., & Lal, R. (2008). Carbon stocks in Ethiopian soils in relation to land use and soil management. Land Degradation & Development, 19, 351–367. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.844
Hartemink, A., McSweeney, K. (Eds.), & Soil Carbon. (2014). Progress in soil science. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-04084-4_48
Hassan, Z., Shabbir, R., Ahmad, S. S., Malik, A. H., Aziz, N., Butt, A., & Erum, S. (2016). Dynamics of land use and land cover change (LULCC) using geospatial techniques: a case study of Islamabad Pakistan. Springerplus 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2414-z
Henry, M., Valentini, R., & Bernoux, M. (2009). Soil carbon stocks in ecoregions of Africa. Biogeosciences Discuss., 6, 797–823. https://doi.org/10.5194/bgd-6-797-2009
Hu, Y., Zhen, L., & Zhuang, D. (2019). Assessment of Land-Use and Land- Cover Change in Guangxi, China. Scientific Reports, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38487-w
Ibrahim, T., Tesfay, F., & Geremew, B. (2021). Spatio-Temporal Dynamic of Land Use and Land Cover in Andit Tid Watershed, Wet Frost/Afro-Alpine Highland of Ethiopia. Edelweiss Applied Science and Technology, 5, 33–38. https://doi.org/10.33805/2576-8484.192
IPCC. (2003). Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Special Report; Land Use, Land-Use Change and Forestry. Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES) for the IPCC ©, Kanagawa Japan.
Jacob, M., Romeyns, L., Frankl, A., Asfaha, T., Beeckman, H., & Nyssen, J. (2016). Land use and cover dynamics since 1964 in the afro-alpine vegetation belt: Lib Amba mountain in north Ethiopia 653, 641–653.
Jacobson, A., Dhanota, J., Godfrey, J., Jacobson, H., Rossman, Z., Stanish, A., Walker, H., & Riggio, J. (2015). A novel approach to map** land conversion using Google Earth with an application to East Africa. Environmental Modelling and Software, 72, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.06.011
Jakšić, S., Ninkov, J., Milić, S., Vasin, J., Živanov, M., Jakšić, D., & Komlen, V. (2021). Influence of slope gradient and aspect on soil organic carbon content in the region of Niš, Serbia. Sustainability, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158332
**, Z., Charlock, T., & Rutledge, K. (2006). A parameterization of spectral and broadband ocean surface albedo. In: 12th Conference on Cloud Physics, and 12th Conference on Atmospheric Radiation. pp. 6493–6499. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JC00629.K.
Jobbagy, E. G., & Jackson, R. B. (2000). The Vertical Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon and Its Relation to Climate and Vegetation. Ecological Applications, 10, 423. https://doi.org/10.2307/2641104
Kakaire, J., Makokha, G. L., Mwanjalolo, M., Mensah, A. K., & Menya, E. (2016). Effects of Mulching on Soil Hydro-Physical Properties in Kibaale Sub-catchment, South Central Uganda. Applied Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 3, 127–135. https://doi.org/10.12691/aees-3-5-1
Kejela, K. (1995).The soils of the Anjeni Area – Gojam Research Unit, Ethiopia Research Report 27. Soil Conservation Research Project, Centre for Development and Environment, University of Berne.
Kelliher, F. M., Ross, D. J., Law, B. E., Baldocchi, D. D., & Rodda, N. J. (2004). Limitations to carbon mineralization in litter and mineral soil of young and old ponderosa pine forests. Forest Ecology and Management, 191, 201–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2003.12.005
Lal, R., Negassa, W., & Lorenz, K. (2015). Carbon sequestration in soil. Current Opinion in Environment Sustainability, 15, 79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosust.2015.09.002
Lambin, E. F., Turner, B. L., Geist, H. J., Agbola, S. B., Angelsen, A., Bruce, J. W., Coomes, O. T., Dirzo, R., Fischer, G., Folke, C., George, P. S., Homewood, K., Imbernon, J., Leemans, R., Li, X., Moran, E. F., Mortimore, M., Ramakrishnan, P. S., Richards, J. F., … Xu, J. (2001). The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Global Environmental Change, 11, 261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-3780(01)00007-3
Landon, J. R. (2013). Booker Tropical Soil Manual. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315846842
Liu, Z., Shao, M., & Wang, Y. (2011). Effect of environmental factors on regional soil organic carbon stocks across the Loess Plateau region, China. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 142, 184–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.05.002
Medinets, S., Skiba, U., Rennenberg, H., & Butterbach-Bahl, K. (2015). A review of soil NO transformation: Associated processes and possible physiological significance on organisms. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 80, 92–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.09.025
Mekuria, W., Getnet, K., Noble, A., Hoanh, C. T., McCartney, M., & Langan, S. (2013). Economic valuation of organic and clay-based soil amendments in small-scale agriculture in Lao PDR.Field Crops Research, 149, 379–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.05.026
Meshesha, D. T., Tsunekawa, A., Tsubo, M., Ali, S. A., & Haregeweyn, N. (2014). Land-use change and its socio-environmental impact in Eastern Ethiopia’s highland. Regional Environmental Change, 14, 757–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-013-0535-2
Meshesha, D. T., Tsunekawa, A., & Tsubo, M. (2012). Continuing land degradation: cause–effect in Ethiopia's Central Rift Valley. 143, 130–143.
Muriithi, F. K. (2016). Author’ s Accepted Manuscript commercial horticulture Applications: Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2016.01.002
Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1982). Total Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Organic Matter. In: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Propertie. ASA, SSSA, Madison, USA, pp. 593–579. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.2ed.c29
Nesic, L., Vasin, J., Belic, M., Ciric, V., Gligorijevic, J., Milunovic, K., & Sekulic, P. (2015). The colloid fraction and cation-exchange capacity in the soils of Vojvodina, Serbia. Journal Ratarstvo i Povrtarstvo, 52, 18–23. https://doi.org/10.5937/ratpov52-7720
Obodai, J., Amaning, K., Nii, S., & Lumor, M. (2019). Remote Sensing Applications : Society and Environment Land use / land cover dynamics using landsat data in a gold mining basin-the. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 13, 247–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2018.10.007
Olsen, S. R., & Dean, L. A. (1965). Phosphorus. In: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Propertie. ASA, SSSA, Madison, WI, pp. 1035–1049. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.c32
Ontl, T. A., Janowiak, M. K., Swanston, C. W., Daley, J., Handler, S., Cornett, M., Hagenbuch, S., Handrick, C., McCarthy, L., & Patch, N. (2020). Forest management for carbon sequestration and climate adaptation. Journal of Forestry, 118, 86–101. https://doi.org/10.1093/jofore/fvz062
Padbhushan, R., Kumar, U., Sharma, S., Rana, D. S., Kumar, R., Kohli, A., Kumari, P., Parmar, B., Kaviraj, M., Sinha, A. K., Annapurna, K., & Gupta, V. V. S. R. (2022). Impact of Land-Use Changes on Soil Properties and Carbon Pools in India: A Meta-analysis. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 9, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.794866
Pandi, D., Kothandaraman, S., Kasiviswanathan, K. S., & Kuppusamy, M. (2022). A catchment scale assessment of water balance components: A case study of Chittar catchment in South India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 72384–72396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19032-1
Poeplau, C., Kätterer, T., Bolinder, M. A., Börjesson, G., Berti, A., & Lugato, E. (2015). Low stabilization of aboveground crop residue carbon in sandy soils of Swedish long-term experiments. Geoderma, 237, 246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.09.010
Ritchie, M. E. (2014). Plant compensation to grazing and soil carbon dynamics in a tropical grassland. PeerJ, 2014. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.233
Ross, Ribeiro, E., Batjes, N. H., Leenaars, J. G. B., van Oostrum, A., de Jesus, J. M., et al (2015). Towards the standardization and harmonization of world soil data. Proced. Man. ISRIC World Soil Inf. Serv. (WoSIS version 2.0). 1–111.
Selassie, Y. G., Anemut, F., & Addisu, S. (2015). The effects of land use types, management practices and slope classes on selected soil physico-chemical properties in Zikre watershed, North-Western Ethiopia. Environmental Systems Research, 4, 0–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-015-0027-0
Sheleme, B. (2017). Topographic positions and land use impacted soil properties along Humbo Larena-Ofa Sere toposequence, Southern Ethiopia. Journal of Soil Science and Environmental Management, 8, 135–147. https://doi.org/10.5897/jssem2017.0643
Singh, P., & Benbi, D. K. (2018). Soil organic carbon pool changes in relation to slope position and land-use in Indian lower Himalayas. Catena, 166, 171–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.04.006
Solomon, N., Hishe, H., Annang, T., Pabi, O., Asante, I. K., & Birhane, E. (2018). Forest Cover Change, Key Drivers and Community Perception in Wujig Mahgo Waren Forest of Northern Ethiopia. Land, 7, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/land7010032
Song, X. P., Hansen, M. C., Stehman, S. V., Potapov, P. V., Tyukavina, A., Vermote, E. F., & Townshend, J. R. (2018). Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature, 560, 639–643. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0411-9
Stavi, I., Ungar, E. D., Lavee, H., & Sarah, P. (2008). Grazing-induced spatial variability of soil bulk density and content of moisture, organic carbon and calcium carbonate in a semi-arid rangeland. Catena, 75, 288–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2008.07.007
Tadesse, T., Haque, T., & Aduayi, E. A. (1991) Soil, plant, water, fertilizer, animal manure and compost analysis manual. ILCA PSD Working Document, B13, International Livestock Center for Africa, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
Thomas, G. W. (1982). Exchangeable Cations. In: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties. ASA, SSSA, Madison, USA, pp. 159–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-31211-6_22
Thomas, G. W. (1996). Soil pH and Soil Acidity. In: Methods Soil Anal Part 3—Chemical Methodss-SSSA Book Series No. 5. Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, pp. 475–490. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.3.c16
Trivedi, P., Singh, B. P., & Singh, B. K. (2018). Soil carbon: Introduction, importance, status, threat, and mitigation. Modulators, Mechanisms and Modeling. Elsevier Inc. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812766-7.00001-9
Warra, H. H., Ahmed, M. A., & Nicolau, M. D. (2015). Impact of land cover changes and topography on soil quality in the Kasso catchment, Bale Mountains of southeastern Ethiopia. Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography, 36, 357–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/sjtg.12124
White, P. J., & Brown, P. H. (2010). Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Annals of Botany, 105, 1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq085
Wiesmeier, M., Urbanski, L., Hobley, E., Lang, B., von Lützow, M., Marin-Spiotta, E., van Wesemael, B., Rabot, E., Ließ, M., Garcia-Franco, N., Wollschläger, U., Vogel, H. J., & Kögel-Knabner, I. (2019). Soil organic carbon storage as a key function of soils - A review of drivers and indicators at various scales. Geoderma, 333, 149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.07.026
Wubie, M. A., & Assen, M. (2020). Effects of land cover changes and slope gradient on soil quality in the Gumara watershed, Lake Tana basin of North-West Ethiopia. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 6, 85–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00660-5
Wubie, M. A., Assen, M., & Nicolau, M. D. (2016). Patterns, causes and consequences of land use/cover dynamics in the Gumara watershed of lake Tana basin, Northwestern Ethiopia. Environmental Systems Research, 5, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-016-0058-1
**ong, X., Grunwald, S., Myers, D. B., Ross, C. W., Harris, W. G., & Comerford, N. B. (2014). Science of the Total Environment Interaction effects of climate and land use / land cover change on soil organic carbon sequestration. Science of the Total Environment, 493, 974–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.088
Yared, M., Kibebew, K., Bobe, B., & Muktar, M. (2018). Soil organic carbon stock under different land use types in Kersa Sub Watershed, Eastern Ethiopia. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 13, 1248–1256. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajar2018.13190
Yuan, Z., **, X., Guan, Q., & Meshack, A. O. (2021). Converting cropland to plantation decreases soil organic carbon stock and liable fractions in the fertile alluvial plain of eastern China. Geoderma Regional, 24, e00356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2021.e00356
Yuan, Z. Q., Fang, C., Zhang, R., Li, F. M., Javaid, M. M., & Janssens, I. A. (2019). Topographic influences on soil properties and aboveground biomass in lucerne-rich vegetation in a semi-arid environment. Geoderma, 344, 137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.03.003
Zeleke, G., & Hurni, H. (2001). Implications of land use and land cover dynamics for mountain resource degradation in the Northwestern Ethiopian highlands. Mountain Research and Development, 21, 184–191. https://doi.org/10.1659/0276-4741(2001)021[0184:IOLUAL]2.0.CO;2
Zhao, J., Yang, Y., Zhao, Q., & Zhao, Z. (2017). Effects of ecological restoration projects on changes in land cover: A case study on the Loess Plateau in China. Science and Reports, 7, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44496
Zhu, M., Feng, Q., Qin, Y., Cao, J., Zhang, M., Liu, W., Deo, R. C., Zhang, C., Li, R., & Li, B. (2019). The role of topography in sha** the spatial patterns of soil organic carbon. Catena, 176, 296–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.01.029
Acknowledgements
The first author thanks Haramaya University Africa Center of Excellence for Climate Smart Agriculture and Biodiversity Conservation (ACE Climate SABC), Debre Berhan University, CGIAR’s research program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), and the Global Research Alliance on Agricultural Greenhouse Gases (GRA) through their CLIFF-GRADS program for the financial support. The authors also thank Dr. Woubet Alemu, for providing us with the necessary data, Dr. Fikrey Tesfay for the continuous supervision and support during data collection and laboratory analysis, Debre Berhan Agricultural Research Center, and Anjeni area farmers for the laboratory work and support during data collection respectively.
Funding
This laboratory work is supported by CGIAR’s research program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), Africa Centre of Excellence for Climate-Smart Agriculture and Biodiversity Conservation, Haramaya University, Haramaya, Ethiopia and the Global Research Alliance on Agricultural Greenhouse Gases (GRA) through their CLIFF-GRADS program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bethel Geremew: data curation, conceptualization, methodology, writing — original draft, formal analysis and investigation visualization. Tsegaye Tadesse: data curation, writing — review and editing and supervision. Bobe Bedadi: data curation, writing — review and editing, project administration, resources and supervision. Hero T. Gollany: writing — review and editing, resources and supervision. Kindie Tesfaye: data curation, writing — review and editing and supervision. Abebe Aschalew: writing — reviewing and editing and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors declare that the manuscript is original and has not been published in any journal.
Consent to participate
The authors have participated in the preparation and submission of this paper for a publication in Environmental Monitoring and Assessment.
Consent for publication
The authors declare their consent to publication of the manuscript in “Environmental Monitoring and Assessment” journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Geremew, B., Tadesse, T., Bedadi, B. et al. Impact of land use/cover change and slope gradient on soil organic carbon stock in Anjeni watershed, Northwest Ethiopia. Environ Monit Assess 195, 971 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11537-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11537-7