Abstract
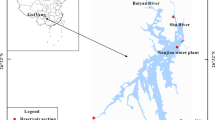
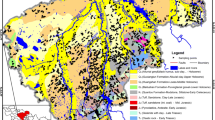
The aim of this research was the analysis of the effect of a dam height raise on the water quality of a tropical reservoir used for drinking water purposes in South East Asia. Analyses of iron, manganese, pH and ammonia were performed over a 5-year period from daily water sampling at the reservoir. In addition, high-frequency monitoring data of nitrate, ammonium, pH and blue-green algae were obtained using a monitoring probe. The results showed that due to the raising of the reservoir water level, previously oxic sediments became submerged, triggering an increase in iron and manganese in particular due to the establishment of reducing conditions. Manganese concentrations with values up to 4 mg L−1 are now exceeding guideline values. The analysis strongly indicated that both iron and manganese have a seasonal component with higher iron and manganese concentrations during the wet season. Over a three-year period afterwards, concentrations did not go back to pre-raise levels. The change in water quality was accompanied by a change in pH from previous values of around 5 to pH values of around 6.5. Geochemical simulations confirmed the theory that the increasing concentrations of iron and manganese are due to the dissolution of MnO2 and ferric oxyhydroxides oxidising organic matter in the process. This study showed that changes in reservoir water levels with the establishment of reducing conditions can have long-term effects on the water quality of a reservoir.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data can be made available upon reasonable written request to the corresponding author and with approval by the Brunei Government.
References
American Public Health Association. (1992). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Washington. ISBN 0–87553–207–1.
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation. (2018). 1020 quality assurance In: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Lipps WC, Baxter TE, Braun-Howland E, editors. Washington DC: APHA Press. https://doi.org/10.2105/SMWW.2882.005
Atta, S. K., Mohammed, S. A., Van Cleemput, O., & Zayed, A. (1996). Transformations of iron and manganese under controlled E(h), E(h)-pH conditions and addition of organic matter. Soil Technol., 9, 223–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0933-3630(96)00013-X
Azffri, S.L., Azaman, A., Sukri, R.S., Jaafar, S.M., Ibrahim, M.F., Schirmer, M., Gödeke, S.H. (2022a). Soil and groundwater investigation for sustainable agricultural development: A case study from Brunei Darussalam. Sustainability , 14, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031388
Azffri, S.L., Ibrahim, M.F. & Gödeke, S.H. (2022b). Electrical resistivity tomography and induced polarization study for groundwater exploration in the agricultural development areas of Brunei Darussalam. Environmental Earth Sciences, 81, 233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10284-1
Azhar, A. S. B., Latiff, A. H. A., Lim, L. H., & Gӧdeke, S. H. (2019). Groundwater investigation of a coastal aquifer in Brunei Darussalam using seismic refraction. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(6), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8203-6
Baharim, N. H., Ismail, R., & Omar, M. H. (2011). Effects of thermal stratification on the concentration of iron and manganese in a tropical water supply reservoir. Sains Malaysiana, 40(8), 821-825.
Björnerås, C., Škerlep, M., Floudas, D., Persson, P., & Kritzberg, E. S. (2019). High sulfate concentration enhances iron mobilization from organic soil to water. Biogeochemistry, 144, 245–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-019-00581-6
Bouchard, M., Laforest, F., Vandelac, L., Bellinger, D., & Mergler, D. (2007). Hair Manganese and Hyperactive Behaviours: Pilot Study of School-Age Children Exposed through Tap Water Environmental Health Perspectives, 115(1), 122–127. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9504
Bouchard, M. F., Sauvé, S., Barbeau, B., Legrand, M., Brodeur, M. È., Bouffard, T., & Mergler, D. (2011). Intellectual impairment in school-age children exposed to manganese from drinking water. Environmental health perspectives, 119(1), 138-143.https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1002321
Brunei Meteorological Department. (2020). Rainfall Data from 2015 to 2020. Unpublished report.
BTKS. (2020). Bahagian Kaji Tanah dan Kaji Selidik. Soil report of the Mengkubau reservoir area. Unpublished Report.
Brient, L., Lengronne, M., Bertrand, E., Rolland, D., Sipel, A., Steinmann, D., Baudin, I., Legeas, M., Le Rouzic, B., & Bormans, M. (2008). A phycocyanin probe as a tool for monitoring cyanobacteria in freshwater bodies. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 10(2), 248–255. https://doi.org/10.1039/bMonitoring
Bryant, L. D., Hsu-Kim, H., Gantzer, P. A., & P. A., Little, J.C. (2011). Solving the problem at the source: Controlling Mn release at the sediment-water interface via hypolimnetic oxygenation. Water Research, 45(19), 6381–6392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.09.030
Burdige, D. J. (1993). The biogeochemistry of manganese and iron reduction in marine sediments. Earth-Science Reviews, 35, 249–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(93)90040-E
BS ISO 11271. (2002). Soil quality — Determination of redox potential — Field method. ISBN 0580406776.
Canfield, D. E., Jørgensen, B. B., Fossing, H., Glud, R., Gundersen, J., Rasing, N. B., Thamdrup, B., Hansen, J. W., Nielsen, L. P., & Hall, P. O. J. (1993). Pathways of organic carbon oxidation in three continental margin sediments. Marine Geology, 113, 27–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-3227(93)90147-N
Chen, S., Carey, C. C., Little, J. C., Lofton, M. E., McClure, R. P., & Lei, C. (2017). A coupled three-dimensional hydrodynamic model for predicting hypolimnetic oxygenation and epilimnetic mixing in a shallow eutrophic reservoir. Water Resource, 5, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR019279.
Chittoor Viswanathan, V., Jiang, Y., Berg, M., Hunkeler, D., & Schirmer, M. (2016). An integrated spatial snap-shot monitoring method for identifying seasonal changes and spatial changes in surface water quality. Journal of Hydrology, 539, 567–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.05.017
Cleveland, R. B., Cleveland, W. S., McRae, J. E., & Terpenning, I. (1990). STL: A seasonal-trend decomposition based on Loess. Journal of Official Statistics, 6(1), 3–73.
Davison, W. (1993). Iron and manganese in lakes. Earth-Science Reviews, 34(2), 119–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(93)90029-7
Department of Water Services. (2018). Internal report on the water consumption per person in Brunei Darussalam, Unpublished Internal Report.
Dong, W., Bhattacharyya, A., Fox, P. M., Bill, M., Dwivedi, D., Carrero, S., Conrad, M., & Nico, P. S. (2020). Geochemical controls on release and speciation of Fe(II) and Mn(II) from hyporheic sediments of East River. Colorado. Frontiers in Water, 2(November), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/frwa.2020.562298
Dubbin, W. E., & Bullough, F. (2017). Dissolution of Al-Substituted Goethite in the Presence of Ferrichrome and Enterobactin at pH 6.5. Aquatic Geochemistry, 23(1), 61-74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-016-9304-4
Eccles, R., Zhang, H., Hamilton, D., & Maxwell, P. (2020). Trends in water quality in a subtropical Australian river-estuary system: Responses to damming, climate variability and wastewater discharges. Journal of Environmental Management, 269, 110796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110796
Ekström, S. M., Regnell, O., Reader, H. E., Nilsson, P. A., Löfgren, S., & Kritzberg, E. S. (2016). Increasing concentrations of iron in surface waters as a consequence of reducing conditions in the catchment area. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences, 121, 479–493. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JG003141.
FAO. (2011). Irrigation in Southern and Eastern Asia in figures, AQUASTAT Survey – FAO. Water Report 37, 978-92-5-107282-0.
Fidel, R. B., Laird, D. A., & Spokas, K. A. (2018). Sorption of ammonium and nitrate to biochars is electrostatic and pH-dependent. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35534-w
Fukushima, T., Matsushita, B., Subehi, L., Setiawan, F., & Wibowo, H. (2017). Will hypolimnetic waters become anoxic in all deep tropical lakes?. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45320
Gantzer, P. A., Bryant, L. D., & L ittle, J. C. (2009). Controlling soluble iron and manganese in a water-supply reservoir using hypolimnetic oxygenation. Water Research, 43(5), 1285–1294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.019
Gerling, A. B., Browne, R. G., Gantzer, P. A., Mobley, M. H., Little, J. C., & Carey, C. C. (2014). First report of the successful operation of a side stream supersaturation hypolimnetic oxygenation system in a eutrophic, shallow reservoir. Water Research, 67, 129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.09.002
Gharbi, O., Al-Sammarraie, M., Cheneviere, P. Julien, P., Goedeke, S, Amir, A., Al-Shahwani, S., Al-Mohannadi, N. (2014). Core flood analysis of acid stimulation in carbonates: towards effective diversion and water production mitigation. IPTC 2014, Doha. https://doi.org/10.2523/IPTC-17608-MS
Gӧdeke, S., Geistlinger, H., Fischer, A., Richnow, H. H., Wachter, T., & Schirmer, M. (2008). Simulation of a reactive tracer experiment using stochastic hydraulic conductivity fields. Environmental Geology, 55(6), 1255–1261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1073-3
Gӧdeke, S., Malik, O. A., Lai, D., Bretzler, A., Schirmer, M., & Mansor, N. H. (2020). Water Quality investigation in Brunei Darussalam: Investigation of the influence of climate change. Environmental Earth Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09157-2
González, E. J., Ortaz, M., Peñaherrera, C., & De Infante, A. (2004). Physical and chemical features of a tropical hypertrophic reservoir permanently stratified. Hydrobiologia, 522(1–3), 301–310. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000029983.53568.d2
Gotoh, S., & Patrick, W. H., Jr. (1972). Transformation of manganese in a waterlogged soil as affected by redox potential and pH. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 36, 738–742. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1972.03615995003600050018x
Grealish, G. J., & Fitzpatrick, R. W. (2013). Acid sulphate soil characterization in N egara B runei D arussalam: a case study to inform management decisions. Soil Use and Management, 29(3), 432–444. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12051
Han, X., & Webber, M. (2020). Extending the China water machine: Constructing a dam export industry. Geoforum, 112, 63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2020.03.010
Heal, K. V., Kneale, P. E., & McDonald, A. T. (2002). Teneur en manganèse de l’écoulement en bassins versants d’altitude: Variations temporelles et contrǒles de la mobilisation. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 47, 769–780. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626660209492979
Hong, W. J., Shamsuddin, N., Abas, E., Apong, R. A., Masri, Z., Suhaimi, H., Gödeke, S. H., & Noh, M. N. A. (2021). Water quality monitoring with Arduino based sensors. Environments, 8, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8010006
Holloway, C. J., Santos, I. R., Tait, D. R., Sanders, C. J., Rose, A. L., Schnetger, B., Brumsack, H. J., Macklin, P. A., Sippo, J. Z., & Maher, D. T. (2016). Manganese and iron release from mangrove porewaters: A significant component of oceanic budgets? Marine Chemistry, 184, 43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2016.05.013
Holt, C. C. (1957). Forecasting seasonals and trends by exponentially weighted moving averages. O.N.R. Memorandum No. 52. Carnegie Institute of Technology, Pittsburgh USA.
Huisman, J., Codd, G. A., Paerl, H. W., Ibelings, B. W., Verspagen, J. M. H., & Visser, P. M. (2018). Cyanobacterial blooms. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 16, 471–483. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0040-1
Hutchison, C. S. (2005). Geology of North-West Borneo: Sarawak, Brunei and Sabah. Elsevier.
Hyndman, R. J., & Khandakar, Y. (2008). Automatic time series forecasting: The forecast package for R. Journal of Statistical Software, 26(3), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v027.i03
Ito, Y., & Momii, K. (2015). Impacts of regional warming on long-term hypolimnetic anoxia and dissolved oxygen concentration in a deep lake. Hydrological Processes, 29, 2232–2242. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10362
Iyare, P. U. (2019). The effects of manganese exposure from drinking water on school-age children: A systematic review. Neurotoxicology, 73, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2019.02.013
Jeirani, Z., Sedeghi, A., Soltan, J., Roshani, B., & Rindall, B. (2015). Effectiveness of advanced oxidation processes for the removal of manganese and organic compounds in membrane concentrate. Separation and Purification Technology, 149, 110–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.05.009
Kendall, C., Elliott, E. M., & Wankel, S. D. (2007). Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems. Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science, 2(1), 375-449. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470691854.ch12
Khatri, N., Tyagi, S., & Rawtani, D. (2017). Recent strategies for the removal of iron from water. A review. Journal of Water Processing Engineering, 19, 291–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2017.08.015
Kirchherr, J., Charles, K. J., & Walton, M. J. (2016). Multi-causal pathways of public opposition to dam projects in Asia: A fuzzy set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA). Global Environmental Change, 41, 33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.08.001
Komatsu, E., Fukushima, T., & Harasawa, H. (2007). (2007) A modeling approach to forecast the effect of long-term climate change on lake water quality. Ecological Modelling, 209, 351–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2007.07.021
Kritzberg, E. S., & Ekström, S. M. (2012). Increasing iron concentrations in surface waters—A factor behind brownification? Biogeosciences, 9, 1465–1478. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-9-1465-2012
Krueger, K. M., Vavrus, C. E., Lofton, M. E., McClure, R. P., Gantzer, P., Carey, C. C., & Schreiber, M. E. (2020). Iron and manganese fluxes across the sediment-water interface in a drinking water reservoir. Water Research, 182, 116003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116003
Li, N., Huang, T., Mao, X., Zhang, H., Li, K., Wen, G., Lv, X., & Deng, L. (2019). Controlling reduced iron and manganese in a drinking water reservoir by hypolimnetic aeration and artificial destratification. Science of the Total Environment, 685, 497–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.445
Likens, G. (2009). Encyclopedia of inland waters, 1st Edition. Academic Press ISBN 978–0–12–370626–3.
Lorieri, D., & Elsenbeer, H. (1997). Aluminium, iron and manganese in near-surface waters of a tropical rainforest ecosystem. Science of the Total Environment, 205, 13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(97)00089-2
Luo, Z., Shao, Q., Zuo, Q., & Cui, Y. (2020). Impact of land use and urbanization on river water quality and ecology in a dam dominated basin. Journal of Hydrology, 584, 124655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124655
Madigan, M. T., Martinki, J. P., Parker, J. (2003). Brock Mikrobiologie Spektrum Akademischer Verlag GmbH Heidelberg 3-8274-0566-1.
Marshall, D. J., Abdelhady, A. A., Wah, D. T. T., Mustapha, N., Gӧdeke, S. H., De Silva, L. C., & Hall-Spencer, J. M. (2019). Biomonitoring acidification using marine gastropods. Science of the Total Environment, 692, 833–843. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.07.041
Neal, C., Lofts, S., Evans, C. D., Reynolds, B., Tip**, E., & Neal, M. (2008). Increasing iron concentrations in UK upland waters. Aquatic Geochemistry, 14(3), 263–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-008-9036-1
Norrman, J., Sparrenbom, C. J., Berg, M., Dang, D. N., Jacks, G., Harms-Ringdahl, P., Pham, Q. N., & Rosqvist, H. (2015). Tracing sources of ammonium in reducing groundwater in a well field in Hanoi (Vietnam) by means of stable nitrogen isotope (δ15N) values. Applied Geochemistry, 61, 248–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.06.009
Pais, I., & Jones, J. B. (1997). The Handbook of Trace Elements (p. 9781884015342). Taylor & Francis.
Parkhurst, D. L., & Appelo, C. A. J. (2013). Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. US Geological Survey Techniques and Methodss, 6(A43), 497. https://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/06/a43/
Patrick, W. H., & Turner, F. T. (1968). Effect of redox potential on manganese transformation in waterlogged soil. Nature, 220, 476–478. https://doi.org/10.1038/220476a0
Karim, K. N. P. D., Cheng, C. S. S., Zulkefle, N. I., & Tsikouras, B. (2019). Geochemical distribution and behaviour of mercury and arsenic in the Brunei-Muara District, Brunei Darussalam. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 311, No. 1, p. 012087). IOP Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/311/1/012087
Pons, L. J. (1973). Outline of the genesis, characteristics, classification and improvement of acid sulphate soils. In Proceedings of the 1972 (Wageningen, Netherlands) International Acid Sulphate Soils Symposium (Vol. 1, pp. 3-27).
Prabakaran, K., Eswaramoorthi, S., Nagarajan, R., Anandkumar, A., & Franco, F. M. (2020). Geochemical behaviour and risk assessment of trace elements in a tropical river. Northwest Borneo. Chemosphere, 252, 126430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126430
R Core Team. (2021). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Stumm, W., Morgan, J. J. (1981). Aquatic chemistry – 2nd Edition, 780 pp, New York-London-Sydney-Toronto (Wiley).
Suhip, M. A. A. B. H., Gӧdeke, S. H., Cobb, A. R., & Sukri, R. S. (2020). Seismic refraction study, single well test and physical core analysis of anthropogenic degraded Peat at the Badas Peat Dome. Brunei Darussalam. Eng. Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105689
Tittel, J., Büttner, O., Friese, K., Lechtenfeld, O. J., Schuth, S., Tümpling, W. Von, & Musolff, A. (2022). Iron exports from catchments are constrained by redox status and topography global biogeochemical cycles. 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021GB007056
USEPA. (2003). Health effects support document for manganese. EPA 822-R-03–003, Washington DC.
WHO. (2003). Iron in drinking water. Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/08. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003.
WHO. (2008). Guidelines for drinking water quality. World Health Organisation, Geneva, Switzerland.
WHO. (2011a). Manganese in drinking water—Background document for development of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/104. Geneva: World Health Organization.
WHO. (2011b). Nitrate and nitrite in drinking water—Background document for development of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO/SDE/WSH/07.01/16/Rev/1. Geneva: World Health Organization.
WHO. (2017). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, incorporating the 1st addendum, 4th edition, Geneva Switzerland, page 223, 631 pp ISBN: 978-92-4-154995-0.
Winters, P. R. (1976) Forecasting sales by exponentially weighted moving averages. In: Mathematical Models in Marketing. Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems (Operations Research), Vol 132. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-51565-1_116
Wu, H., Chen, J., Xu, J., Zeng, G., Sang, L., Liu, Q., Yin, Z., Dai, J., Yin, D., Liang, J., & Ye, S. (2019). Effects of dam construction on biodiversity: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 221, 480–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.001
Yule, G. U. (1926). Why do we sometimes get nonsense-correlations between time-series? – A study in sampling and the nature of time-series. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 89(1), 1–63.
Yusri, N. I. A., Gӧdeke, S. H., Mansor, N. H. (2018). A water quality database for Brunei – The case of Bukit Barun and Layong. IET Conference Publications (CP750). https://doi.org/10.1049/cp.2018.1556
Zubala, T. (2009). Influence of dam reservoir on the water quality in a small upland river. Ecohydrology and Hydrobiology, 9, 165–173. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10104-010-0010-3
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by research grants UBD/CRG#18 as well as UBD/RSCH/URC/RG(b)/2020/17 from the Universiti Brunei Darussalam. The authors thank the Ministry of Development, Department of Water Services, Brunei Darussalam, for the supplied data, as well as for allowing the publication of this study. The authors thank Thomas Rüttimann of Eawag, the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology, for the analyses of water samples. The authors thank David Parkhurst for advice on the geochemical modelling with PhreeqCI. The authors are grateful for the support of Azharil Ulum Siregar and Dk Fatin Farhana Binti Pg Noraffin for fieldwork and data analysis as well as Mohammad Yameany bin Hj Rosli for SEM-EDX analysis.
Funding
This project was funded by research grants UBD/CRG #18 as well as UBD/RSCH/URC/RG(b)/2020/17 from the Universiti Brunei Darussalam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Stefan Gödeke; methodology: Stefan Gödeke, Mario Schirmer, Haziq Jamil; formal analysis and investigation: Nur Hakimah Mansor, Stefan Gödeke, Haziq Jamil; writing – original draft preparation: Stefan Gödeke, Haziq Jamil, Norazanita Shamsuddin; writing – review and editing: all authors; funding acquisition: Universiti Brunei Darussalam; resources: Mario Schirmer, Nur Hakimah Mansor, Anja Bretzler; supervision: Nur Hakimah Mansor, Mario Schirmer.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors have followed Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) guidelines in the preparation of this manuscript. This research did not involve human participants or animals. No formal ethical approval was obtained for this study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have given their consent to publish this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• A tropical reservoir in South East Asia was investigated over a 5-year period.
• Water quality monitoring reveals an increase in iron and manganese due to a rise in the dam height of the reservoir.
• The increase in iron and manganese is linked to the enlarged footprint of the reservoir, with previously oxic sediments becoming submerged during the process and the establishment of reducing conditions.
• Iron and manganese display a seasonal component with increased concentrations during the wet season.
• Geochemical simulations confirmed that the dissolution of MnO2 and FeOOH through the oxidation of organic matter led to increased iron and manganese concentrations in the reservoir.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gӧdeke, S.H., Jamil, H., Schirmer, M. et al. Iron and manganese mobilisation due to dam height increase for a tropical reservoir in South East Asia. Environ Monit Assess 194, 358 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10014-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10014-x