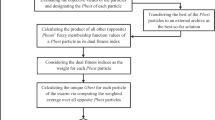
Abstract
In this paper, a new version of the multi-objective particle swarm optimizer named the Diversity-enhanced fuzzy multi-objective particle swarm optimization (f-MOPSO/Div) algorithm is proposed. This algorithm is an improved version of our recently proposed f-MOPSO. In the proposed algorithm, a new characteristic of the particles in the objective space, which we named the “extremity,” is also evaluated, along with the Pareto dominance, to appoint proper guides for the particles in the search space. Three improvements are applied to the f-MOPSO to mitigate its shortcomings, generating f-MOPSO/Div: (1) selecting the global best solution based on the diversity of the extreme solutions, (2) impeding the particles to be trapped in the local optima using a mutation scheme based on the dynamic probability, and (3) removing the pre-optimization process. To validate f-MOPSO/Div, it was compared with some other popular multi-objective algorithms on 14 standard low- and high-dimensional test problem suites. After the comparative results indicated the outperformance of the proposal, the f-MOPSO/Div was applied to solve an optimal conjunctive water use management problem, in a semi-arid study area in west-central Iran, over a 13-year long-term planning period with two main objectives: (1) maximizing the aquifer sustainability as an environmental goal, and (2) maximizing the crop yields as a socio-economic goal. As the results suggest, the cumulative groundwater level drawdown is considerably decreased over the whole planning period to make the aquifer sustainable, while the water productivity is held at a desirable level, demonstrating the superiority of the f-MOPSO/Div when also applied to solve a large-scale real-world optimization problem.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abido, M. A. (2010). Multiobjective particle swarm optimization with nondominated local and global sets. Natural Computing, 9, 747–766.
Afshar, A., Zahraei, A., & Marino, M. A. (2010). Large-scale nonlinear conjunctive use optimization problem: decomposition algorithm. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, ASCE, 136(1), 59–71.
Agrawal, S., Dashora, Y., Tiwari, M., & Son, Y.–. J. (2008). Interactive particle swarm: a Pareto-adaptive metaheuristic to multiobjective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Part A: Systems and Humans, 38, 258–277.
Balling, R., & Wilson, S. (2001). The maxi-min fitness function for multiobjective evolutionary computation: application to city planning, In: Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference (GECCO’2001), pp. 1079–1084.
Ben Said, L., Bechikh, S., & Ghedira, K. (2010). The r-dominance: a new dominance relation for interactive evolutionary multicriteria decision making. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 14, 801–818.
Burt, O. R. (1964). The economics of conjunctive use of ground and surface water. Hilgardia., 36(2), 25–41.
Deb, K., & Deb, D. (2014). Analyzing mutation schemes for real-parameter genetic algorithms. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing, 4(1), 1–28.
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., & Meyarivan, T. (2002). A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 6(2), 182–197.
Drechsler, N., Drechsler, R., & Becker, B. (2001). Multi-objective optimization based on relation favour. In Evolutionary multi-criterion optimization (pp. 154–166). Berlin: Springer.
Durillo, J. J., García-Nieto, J., Nebro, A. J., Coello, C. A. C., Luna, F., & Alba, E. (2009). Multi-objective particle swarm optimizers: An Experimental Comparison. In: Ehrgott M., Fonseca C.M., Gandibleux X., Hao JK., Sevaux M. (eds) Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization. EMO 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5467. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01020-0_39.
Garza-Fabre, M., Pulido, G. T., & Coello, C. A. C. (2009). Ranking methods for many-objective optimization, In: Aguirre A.H., Borja R.M., Garciá C.A.R. (eds) MICAI 2009: Advances in Artificial Intelligence. MICAI 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. vol 5845. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-05258-3_56.
Goulart, F., & Campelo, F. (2016). Preference-guided evolutionary algorithms for many-objective optimization. Information Sciences, 329, 236–255.
Hollander, H. M., Mull, R., & Panda, S. N. (2009). A concept for managed aquifer recharge using ASR-walls for sustainable use of groundwater resources in an alluvial coastal aquifer in Eastern India. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 34, 270–278.
Ireland, D., Lewis, A., Mostaghim, S., & Lu, J. W. (2006). Hybrid particle guide selection methods in multi-objective particle swarm optimization, In Proceedings of the second IEEE international, Conference on e-science and grid computing 2006, (e-Science'06).
Jahandideh-Tehrani, M., Bozorg-Haddad, O., & Loáiciga, H. A. (2020). Application of particle swarm optimization to water management: an introduction and overview. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 281.
Kaur, R., Paul, M., & Malik, R. (2007). Impact assessment and recommendation of alternative conjunctive water use strategies for salt affected agricultural lands through a field scale decision support system- A case study. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 129, 257–270.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization, In Proc International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, IEEE Piscataway NJ, pp. 1942-1948.
Laumanns, M., Thiele, L., Deb, K., & Zitzler, E. (2002). Combining convergence and diversity in evolutionary multiobjective optimization. Evolutionary Computation, 10, 263–282.
Li, L., Wang, W., & Xu, X. (2017). Multi-objective particle swarm optimization based on global margin ranking. Information Sciences, 375, 30–47.
Lin, Q., Li, J., Du, Z., Chen, J., & Ming, Z. (2015). A novel multi-objective particle swarm optimization with multiple search strategies. European Journal of Operational Research, 247(3), 732–744.
Liu, Y., Gong, D., Sun, X., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Many-objective evolutionary optimization based on reference points. Applied Soft Computing, 50, 344–355.
Liu, J., Zhang, H., He, K., & Jiang, S. (2018). Multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm based on objective space division for the unequal-area facility layout problem. Expert Systems with Applications, 102, 179–192.
McPhee, J., & Yeh, W. W.-G. (2004). Multi objective optimization for sustainable groundwater management in semiarid regions. J Water Res Plan Manage, ASCE, 130(6), 490–497.
Mostaghim, S., & Teich, J. (2003a). Strategies for finding good local guides in multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO). In IEEE Swarm Intelligence Symposium. IIN April IEEE Service Center Piscataway NJ, pp. 26-33.
Mostaghim, S., & Teich, J. (2003b). The role of ε-dominance in multiobjective particle swarm optimization methods., In Proceedings of IEEE congress on evolutionary computation CEC'2003, Canberra, Australia pp. 1764-1771.
Nebro, A., Durillo, J. J., Garcia-Nieto, J., Barba-Gonzalez, C., Del Ser, J., Coello, C. A. C., Benitez-Hidalgo, A., & Aldana-Montes, J. F. (2018). Extending the speed-constrained multi-objective PSO (SMPSO) with reference point base preference articulation. International Conference on Parallel problem Solving from Nature, Springer, Cham, 298-310.
Peralta, R. C., Forghani, A., & Fayad, H. (2014). Multiobjective genetic algorithm conjunctive use optimization for production, cost and energy with dynamic return flow. J Hydrol, 511, 776–785.
Qu, B., Li, C., Liang, J., Yan, L., Yu, K., & Zhu, Y. (2020). A self-organized speciation based multi-objective particle swarm optimizer for multimodal multi-objective problems. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 86, 105886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105886.
Rezaei, F., Safavi, H. R., Mirchi, A., & Madani, K. (2017a). f-MOPSO: an alternative multi-objective PSO algorithm for conjunctive water use management. Journal of Hydro-environment Research, 14, 1–18.
Rezaei, F., Safavi, H. R., & Zekri, M. (2017b). A hybrid fuzzy-based multi-objective PSO algorithm for conjunctive water use and optimal multi-crop pattern planning. Water Resources Management, 31(4), 1139–1155.
Safavi, H. R., & Rezaei, F. (2015). Conjunctive use of surface and ground water using fuzzy neural network and genetic algorithm. IJSTC, 39(C2), 365–377.
Safavi, H. R., Darzi, F., & Marino, M. A. (2010). Simulation-optimization modeling of conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater. Water Resour Manage, 24, 1965–1988.
Sahoo, N. C., Ganguly, S., & Das, D. (2011). Simple heuristics-based selection of guides for multi-objective PSO with an application to electrical distribution system planning. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 24, 567–585.
Sierra, M. R., & Coello, C. A. C. (2005). Improving PSO-based multi-objective optimization using crowding, mutation and ε-dominance. In Proceedings of Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization.
Srivastava, P., & Singh, R. M. (2017). Agricultural land allocation for crop planning in a canal command area using fuzzy multiobjective goal programming. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 143, 04017007. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0001175.
Sun, Q., Xu, G., Ma, C., & Chen, L. (2017). Optimal crop-planting area considering the agricultural drought degree. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 143, 04017050. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0001245.
Tayebikhorami, S., Nikoo, M. R., & Sadegh, M. (2019). A fuzzy multi-objective optimization approach for treated wastewater allocation. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 468.
Thiele, L., Miettinen, K., Korhonen, P. J., & Molina, J. (2009). A preference-based evolutionary algorithm for multi-objective optimization. Evolutionary Computation, 17, 411–436.
Wang, R., **ong, J., Ishibuchi, H., Wu, G., & Zhang, T. (2017). On the effect of reference point in MOEA/D for multi-objective optimization. Applied Soft Computing, 58, 25–34.
Wong, Y. J., Arumugasamy, S. K., Chung, C. H., Selvarajoo, A., & Sethu, V. (2020). Comparative study of artificial neural network (ANN), adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and multiple linear regression (MLR) for modeling of Cu (II) adsorption from aqueous solution using biochar derived from rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum) peel. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192, 439.
Yadav, R. K., Kumar, A., Lal, D., & Batra, L. (2004). Yield responses of winter (Rabi) forage crops to irrigation with saline drainage water. Experimental Agriculture, 40, 65–75.
Yang, J., Zhou, J., Liu, L., & Li, Y. (2009a). A novel strategy of pareto-optimal solution searching in multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO). Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 57, 1995–2000.
Yang, C. C., Chang, L. C., Chen, C. S., & Yeh, M. S. (2009b). Multi-objective planning for conjunctive use of surface and subsurface water using genetic algorithm and dynamics programming. Water Resour Manage, 23, 417–437.
Yang, S., Li, M., Liu, X., & Zheng, J. (2013). A grid-based evolutionary algorithm for many-objective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 17, 721–736.
Yekom Consulting Engineers (2013). Studies for updating Iran’s integrated water plan (Gavkhouni River Basin), Final report, Water and Wastewater section, Ministry of Energy (In Persian).
Yeom, J.-M., Lee, C.-S., Park, S.-J., Ryu, J.-H., Kim, J.-J., Kim, H.-C., & Han, K.-S. (2015). Evapotranspiration in Korea estimated by application of a neural network to satellite images. Remote Sensing Letters, 6(6), 429–438.
Yousefi, M., Banihabib, M. E., Soltani, J., & Roozbahani, A. (2018). Multi-objective particle swarm optimization model for conjuctive use of treated wastewater and groundwater. Agricultural Water Management, 208, 224–231.
Zayandab Consulting Engineers (2008). Studies of water supplies and demands in the Zayandeh-Rud River Basin, The Preliminary Studies, 5th Volume, Agricultural Studies (In Persian).
Zeinali, M., Azari, A., & Heidari, M. M. (2020). Multiobjective optimization for water resource management in low-flow areas based on a coupled surface water–groundwater model. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manage., 146(5), 04020020.
Zeleny, M. (1973). Compromise programming, multiple criteria decision-making. In J. L. Cochrane & M. Zeleny (Eds.), Multiple criteria decision making (pp. 263–301). Columbia: University of South Carolina Press.
Zhou, A., Zhao, S., Suganthan, P. N., Liu, W., & Tiwari, S. (2009). Multiobjective optimization test instances for the CEC 2009 special session and competition. In Proceedings of University of Essex, Colchester, UK and Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Special Session on Performance Assessment of Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithms, Technical Report (2008).
Funding
This work was supported by Iran’s National Science Foundation (INSF) with grant No. 97001722, which is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaei, F., Safavi, H.R. f-MOPSO/Div: an improved extreme-point-based multi-objective PSO algorithm applied to a socio-economic-environmental conjunctive water use problem. Environ Monit Assess 192, 767 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08727-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08727-y