Abstract
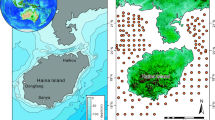
Surface sediment samples were collected at 27 stations of Bohai Bay, North China. Sequential extractions were carried out in this study. REE were leached out from four labile fractions: Exchangeable (L1), bound to carbonates (L2), bound to Fe–Mn oxides (L3), bound to organic matter (L4), and the remainder was residual (R5). The total contents of REE fluctuate slightly in Bohai Bay, and are mainly concentrated in the middle region, showing relatively higher levels in the north than that in the south of Bohai Bay. Percentages of L1, L2, L3, L4, and R5 for REE suggest that the residual fraction accounts for the major component of REE, whereas Fe–Mn oxides also play important roles in combining labile REE. As the REE complex is not stabilized, the competition of complex could induce dissociation of the complex and redistribution of the REE in various environments. According to REE patterns and Y/Ho ratios of samples, REE are not anthropogenic or oceanic sources but riverine input, whereas suitable environment varieties can slightly affect the patterns and fractionations of REE. As powerful tracers for the variable of environment, higher anomaly of Eu and Ce in southern regions indicates a greater reduction in the condition of surface sediment in the south than that in the north of Bohai Bay.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubert, D., Probst, A., & Stille, P. (2004). Distribution and origin of major and trace elements (particularly REE, U and Th) into labile and residual phases in an acid soil profile (Vosges Mountains, France). Applied Geochemistry, 19(6), 899–916.
Bulnaev, K. B. (2004). Behavior of Sr, Ba, and REE in carbonatites of western Transbaikalia. Geochemistry International, 42(3), 285–292.
Busa, T., Clochiatti, R., & Cristofolini, R. (2002). The role of apatite fractionation and REE distribution in alkaline rocks from Mt. Etna, Sicily. Mineralogy and Petrology, 74(1), 95–114.
Chavagnac, V., et al. (2008). Tracing dust input to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between 14 degrees 45′ N and 36 degrees 14′ N: Geochemical and Sr isotope study. Marine Geology, 247, 208–225.
Class, C., & le Roex, A. P. (2008). Ce anomalies in Gough Island lavas—Trace element characteristics of a recycled sediment component. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 265(3–4), 475–486.
Cullers, R. L. (2002). Implications of elemental concentrations for provenance, redox conditions, and metamorphic studies of shales and limestones near Pueblo, CO, USA. Chemical Geology, 191(4), 305–327.
Davranche, M., et al. (2008). Competitive binding of REE to humic acid and manganese oxide: Impact of reaction kinetics on development of cerium anomaly and REE adsorption. Chemical Geology, 247(1–2), 154–170.
de Oliveira, S. M. B., da Silva, P. S. C., Mazzilli, B. P., Favaro, D. I. T., & Saueia, C. H. (2007). Rare earth elements as tracers of sediment contamination by phosphogypsum in the Santos estuary, southern Brazil. Applied Geochemistry, 22(4), 837–850.
Gaudette, H. E., Flight, W. R., Toner, L., & Folger, D. W. (1974). An inexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediment. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 44(1), 249–253.
Gu, X. Y., Wang, X. R., Gu, Z. M., Dai, L. M., & Chen, Y. J. (2001). Effects of humic acid on speciation and bioavailability to wheat of rare earth elements in soil. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability, 13(3), 83–88.
He, J., et al. (2004). Speciation and distribution characters of rare earth elements in the Baotou section of the Yellow River. Environmental Science, 25(2), 61–66 (in Chinese).
Janssen, R. P. T., & Verweij, W. (2003). Geochemistry of some rare earth elements in groundwater, Vierlingsbeek, The Netherlands. Water Research, 37(6), 1320–1350.
Kimoto, A., Nearing, M. A., Zhang, X. C., & Powell, D. M. (2006). Applicability of rare earth element oxides as a sediment tracer for coarse-textured soils. Catena, 65(3), 214–221.
Koc, S., & Recber, A. (2001). Rare earth element geochemistry and fluid inclusion study of Akcakent fluorite veins in central Anatolian Massif of Turkey. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 26(2A), 97–107.
Land, M., Ohlander, B., Ingri, J., & Thunberg, J. (1999). Solid speciation and fractionation of rare earth elements in a spodosol profile from northern Sweden as revealed by sequential extraction. Chemical Geology, 160(1–2), 121–138.
Leleyter, L., et al. (1999). REE distribution pattern in river sediments: Partitioning into residual and labile fractions. Comptes Rendus De L Academie Des Sciences Serie Ii Fascicule a-Sciences De La Terre Et Des Planetes, 329(1), 45–52.
Leybourne, M. I., Goodfellow, W. D., Boyle, D. R., & Hall, G. M. (2000). Rapid development of negative Ce anomalies in surface waters and contrasting REE patterns in groundwaters associated with Zn-Pb massive sulphide deposits. Applied Geochemistry, 15(6), 695–723.
Li, F. L., Shan, X. Q., Zhang, T. H., & Zhang, S. Z. (1998). Evaluation of plant availability of rare earth elements in soils by chemical fractionation and multiple regression analysis. Environmental Pollution, 102(2–3), 269–277.
Lin, C. Y., et al. (2008). Rare earth element content in the SPM of Daliao river system and its comparison with that in the sediments, loess and soils in China. Journal of Rare Earths, 26(3), 414–420.
Otosaka, S., Honda, M. C., & Noriki, S. (2004). La/Yb and Th/Sc in settling particles: Vertical and horizontal transport of lithogenic material in the western North Pacific. Geochemical Journal, 38(6), 515–525.
Polyakov, V. O., & Nearing, M. A. (2004). Rare earth element oxides for tracing sediment movement. Catena, 55(3), 255–276.
Pourret, O., Davranche, M., Gruau, G., & Dia, A. (2007). Competition between humic acid and carbonates for rare earth elements complexation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 305(1), 25–31.
Protano, G., & Riccobono, F. (2002). High contents of rare earth elements (REES) in stream waters of a Cu-Pb-Zn mining area. Environmental Pollution, 117(3), 499–514.
Rengarajan, R., & Sarin, M. M. (2004). Distribution of rare earth elements in the Yamuna and the Chambal rivers, India. Geochemical Journal, 38(6), 551–569.
Song, J. M. (1998). Vertical transformation processes of rare earth elements in the coral reef ecosystem of Nansha islands waters, South China Sea. Studia Marina Sinica, 40, 125–130.
Song, J. M., & Li, P. C. (1998). Vertical transferring process of rare elements in coral reef lagoons of Nansha Islands, South China Sea. Science in China Series D-Earth Sciences, 41(1), 42–48.
Sonke, J. E. (2006). Lanthanide-humic substances complexation. II. Calibration of humic ion-binding model V. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(24), 7481–7487.
Sonke, J. E., & Salters, V. J. M. (2006). Lanthanide-humic substances complexation. I. Experimental evidence for a lanthanide contraction effect. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(6), 1495–1506.
Sun, H., et al. (1998). The species of spiked rare earth elements in sediment and potential bioavailability to algae (Chlorella Vulgarize Beijerinck). Chemosphere, 36(2), 329–337.
Takahashi, Y., et al. (2000). A new method for the determination of Ce-III/Ce-IV ratios in geological materials; application for weathering, sedimentary and diagenetic processes. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 182(3–4), 201–207.
Tang, J. W., & Johannesson, K. H. (2006). Controls on the geochemistry of rare earth elements along a groundwater flow path in the Carrizo Sand aquifer, Texas, USA. Chemical Geology, 225(1–2), 156–171.
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. G. C., & Bisson, M. (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Analytical Chemistry, 51(7), 844–851.
Viscosi-Shirley, C., Mammone, K., Pisias, N., & Dymond, J. (2003). Clay mineralogy and multi-element chemistry of surface sediments on the Siberian-Arctic shelf: Implications for sediment provenance and grain size sorting. Continental Shelf Research, 23(11–13), 1175–1200.
Wang, J. T. (1991). REE geochemistry of surficial sediments from the Yellow sea of China. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 10(4), 88–98.
Wang, Z. L., & Liu, C. Q. (2008). Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the dissolved, acid-soluble and residual phases in surface waters of the Changjiang Estuary. Journal of Oceanography, 64(3), 407–416.
Wang, L. J., Zhang, C. S., Liang, T., & Li, G. S. (2001). Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in intertidalite of Tian**. Journal of the Chinese Rare Earth Society, 19(5), 456–460 (in Chinese).
Yan, X. P., Kerrich, R., & Hendry, M. J. (1999). Sequential leachates of multiple grain size fractions from a clay-rich till, Saskatchewan, Canada: Implications for controls on the rare earth element geochemistry of porewaters in an aquitard. Chemical Geology, 158(1–2), 53–79.
Yang, S. Y., Lim, D. I., Jung, H. S., & Oh, B. C. (2004). Geochemical composition and provenance discrimination of coastal sediments around Cheju Island in the southeastern Yellow Sea. Marine Geology, 206(1–4), 41–53.
Zhang, J., & Liu, C. Q. (2004). Major and rare earth elements in rainwaters from Japan and East China Sea: Natural and anthropogenic sources. Chemical Geology, 209(3–4), 315–326.
Zhang, C. S., Wang, L. J., Zhang, S., & Li, X. X. (1998). Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the mainstream of the Yangtze River, China. Applied Geochemistry, 13(4), 451–462.
Zhu, J. G., & **ng, G. X. (1992). Forms of rare earth elements in soils: Distribution. Pedosphere, 2(2), 125–134.
Zhu, L. M., Du, J. M., Zhang, Y. H., & Xu, J. (2006). Tracing the sediment source at E2 hole in the South Yellow Sea with rare earth element and trace element. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 26(3), 495–500 (in Chinese).
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by Fund for Creative Research Groups by NSFC (no. 40821004), the National Key Project for Basic Research of China (no. 2007CB407305), and the “100 Talents Project” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. We also show our sincere thanks to Mr. Patterson who has provided information about language editing on this paper. Project NO.2011T07 supported by special research fund for the national non-profit institutes (East China Sea Fisheries Research Institute).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Song, J., Duan, L. et al. Fraction characteristics of rare earth elements in the surface sediment of Bohai Bay, North China. Environ Monit Assess 184, 7275–7292 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2496-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2496-6