Abstract
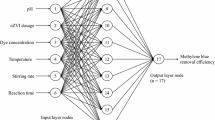
This study explores nitrate reduction in aqueous solutions using carboxymethyl cellulose loaded with zero-valent iron nanoparticles (Fe0-CMC). The structures of this nano-composite were characterized using various techniques. Based on the characterization results, the specific surface area of Fe0-CMC measured by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis were 39.6 m2/g. In addition, Scanning Electron Microscopy images displayed that spherical nano zero-valent iron particles (nZVI) with an average particle diameter of 80 nm are surrounded by carboxymethyl cellulose and no noticeable aggregates were detected. Batch experiments assessed Fe0-CMC’s effectiveness in nitrate removal under diverse conditions including different adsorbent dosages (Cs, 2–10 mg/L), contact time (t, 10–1440 min), initial pH (pHi, 2–10), temperature (T, 10–55 °C), and initial concentration of nitrate (C0, 10–500 mg/L). Results indicated decreased removal with higher initial pHi and C0, while increased Cs and T enhanced removal. The study of nitrate removal mechanism by Fe0-CMC revealed that the redox reaction between immobilized nZVI on the CMC surface and nitrate ions was responsible for nitrate removal, and the main product of this reaction was ammonium, which was subsequently completely removed by the synthesized nanocomposite. In addition, a stable deviation quantum particle swarm optimization algorithm (SD-QPSO) and a least square error method were employed to train the ANFIS parameters. To demonstrate model performance, a quadratic polynomial function was proposed to display the performance of the SD-QPSO algorithm in which the constant parameters were optimized through the SD-QPSO algorithm. Sensitivity analysis was conducted on the proposed quadratic polynomial function by adding a constant deviation and removing each input using two different strategies. According to the sensitivity analysis, the predicted removal efficiency was most sensitive to changes in pHi, followed by Cs, T, C0, and t. The obtained results underscore the potential of the ANFIS model (R2 = 0.99803, RMSE = 0.9888), and polynomial function (R2 = 0.998256, RMSE = 1.7532) as accurate and efficient alternatives to time-consuming laboratory measurements for assessing nitrate removal efficiency. These models can offer rapid insights and predictions regarding the impact of various factors on the process, saving both time and resources.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Agbaogun, B. K., Olu-Owolabi, B. I., Buddenbaum, H., & Fischer, K. (2023). Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and multiple linear regression (MLR) modelling of Cu, Cd, and Pb adsorption onto tropical soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30, 31085–31101.
Ahmed, S. M., Rind, S., & Rani, K. (2023). Systematic review: External carbon source for biological denitrification for wastewater. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 120, 642–658.
Alavijeh, H. N., Sadeghi, M., & Ghahremanfard, A. (2023). Experimental and economic evaluation of nitrate removal by a nanofiltration membrane. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30, 40783–40798.
Amini, P., Bagheri, A., & Moshfegh, S. (2019). Interval search with quadratic interpolation and stable deviation quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization (IQS-QPSO). The International Journal of Multiphysics, 13(2), 113–130.
Awwa, W. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). American Public Health Association.
Bagheri, A., Peyhani, H. M., & Akbari, M. (2014). Financial forecasting using ANFIS networks with quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. Expert Systems with Applications, 41, 6235–6250.
Banerjee, M., Bar, N., & Das, S. K. (2021). Cu (II) removal from aqueous solution using the walnut shell: Adsorption study, regeneration study, plant scale-up design, economic feasibility, statistical, and GA-ANN modeling. International Journal of Environmental Research, 15(5), 875–891.
Batool, F., Kurniawan, T. A., Mohyuddin, A., Othman, M. H. D., Ali, I., AbdulKareem-Alsultan, G., Anouzla, A., Goh, H. H., Zhang, D., Aziz, F., & Chew, K. W. (2024). Rosa damascena waste as biosorbent for co-existing pollutants removal: Fixed-bed column study and ANN modeling. Chemical Engineering Science, 293, 120057.
Birks, L., & Friedman, H. (1946). Particle size determination from X-ray line broadening. Journal of Applied Physics, 17, 687–692.
Cerdà, V., Cerdà, J. L., & Idris, A. M. (2016). Optimization using the gradient and simplex methods. Talanta, 148, 641–648.
Curcio, G. M., Limonti, C., Siciliano, A., & Kabdaşlı, I. (2022). Nitrate removal by zero-valent metals: A comprehensive review. Sustainability, 14(8), 4500.
Deng, Y., Wang, X., Lynch, I., Guo, Z., Zhang, P., Wu, L., Wu, X., & Li, T. (2024). Homogeneous dispersion of amorphous nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on chlorella-derived biochar: In-situ synthesis and application mechanism for Cr (VI) removal over a wide pH range. Separation and Purification Technology, 330, 125207.
Dey, S., Basha, S. R., Babu, G. V., & Nagendra, T. (2021). Characteristic and biosorption capacities of orange peels biosorbents for removal of ammonia and nitrate from contaminated water. Cleaner Materials, 1, 100001.
Dong, H., Zhao, F., He, Q., **e, Y., Zeng, Y., Zhang, L., Tang, L., & Zeng, G. (2017). Physicochemical transformation of carboxymethyl cellulose-coated zero-valent iron nanoparticles (nZVI) in simulated groundwater under anaerobic conditions. Separation and Purification Technology, 175, 376–383.
El-Lateef, H. M. A., Khalaf, M. M., Al-Fengary, A. E. D., & Elrouby, M. (2022). Removal of the harmful nitrate anions from potable water using different methods and materials, including zero-valent iron. Molecules, 27(8), 2552.
Fang, S., Zhang, J., Niu, Y., Ju, S., Gu, Y., Han, K., Wan, X., Li, N., & Zhou, Y. (2023). Removal of nitrate nitrogen from wastewater by green synthetic hydrophilic activated carbon supported sulfide modified nanoscale zerovalent Iron: Characterization, performance and mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal, 461, 141990.
Fiyadha, S. S., Alardhi, S. M., Al Omar, M., Aljumaily, M. M., Al Saadic, M. A., Fayaedd, S. S., Ahmede, S. N., Salman, A. D., Abdalsalmb, A. H., & Jabbarh, N. M. (2023). A comprehensive review on modelling the adsorption process for heavy metal removal from water using artificial neural network technique. Heliyon, 9, e15455.
Han, M., Wei, X., Wang, R., Li, J., Sun, W., & Zhang, C. (2024). Recycling Cu (II) from complexing copper wastewater using ferrous sulfide stabilized by carboxymethyl cellulose: Efficiency and mechanism insights. Separation and Purification Technology, 330, 125209.
Hao, S., & Zhang, H. (2017). High catalytic performance of nitrate reduction by synergistic effect of zero-valent iron (Fe0) and bimetallic composite carrier catalyst. Journal of Cleaner Production, 167, 192–200.
Javadi Moghaddam, J., Momeni, D., & Zarei, G. (2022). Thermal, ANFIS, and polynomial neural network models for predicting environmental variables in an arch greenhouse. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 24(3), 617–633.
Jiao, W., Song, Y., Zhang, D., Chang, G., Fan, H., & Liu, Y. (2019). Nanoscale zero-valent iron modified with carboxymethyl cellulose in an im**ing stream-rotating packed bed for the removal of lead (II). Advanced Powder Technology, 30, 2251–2261.
Joshi, V. C., Gupta, A. R., Karthik, M., & Sharma, S. (2024). Emerging iron based porous metallopolymeric material with cross-linked networks for the separation of ultra-trace arsenic from aqueous environment and simulation with artificial neural network. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 14, 100417.
Kalani, H., Sardarabadi, M., & Passandideh-Fard, M. (2017). Using artificial neural network models and particle swarm optimization for manner prediction of a photovoltaic thermal nanofluid based collector. Applied Thermal Engineering, 113, 1170–1177.
Karaboga, D., & Kaya, E. (2016). An adaptive and hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm (aABC) for ANFIS training. Applied Soft Computing, 49, 423–436.
Keeney, D. R., Nelson, D. W. (1983). Nitrogen—inorganic forms. Methods of soil analysis: Part 2 chemical and microbiological properties 9, 643–698.
Kodikara, J., Gunawardana, B., Jayaweera, M., Sudasinghe, M., & Manatunge, J. (2020). Nitrate removal in potable groundwater by nano zerovalent iron under oxic conditions. Water Practice & Technology, 15(4), 1126–1143.
Kumar, G. P., Pydiraju, Y. B., Lokesh, G. V., & Likith, U. S. (2023a). Removal of rhodamine B using three adsorbents: Isothermal, kinetic, and ANN modeling studies. Water Conservation Science and Engineering, 8(1), 17.
Kumar, V., Singh, E., Singh, S., Pandey, A., & Bhargava, P. C. (2023b). Micro-and nano-plastics (MNPs) as emerging pollutant in ground water: Environmental impact, potential risks, limitations and way forward towards sustainable management. Chemical Engineering Journal, 459, 141568.
Liu, T., Wang, Z.-L., Zhao, L., & Yang, X. (2012). Enhanced chitosan/Fe0-nanoparticles beads for hexavalent chromium removal from wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 189, 196–202.
Liu, X., Wei, J., Hou, L., Zhu, Y., Wu, Y., **ng, L., Zhang, Y., & Li, J. (2021). Feasibility of nanoscale zerovalent iron-loaded sediment-based biochar (nZVI-SBC) for simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate: High selectivity toward dinitrogen and synergistic mechanism. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 37448–37458.
Liu, Y., Zhang, X., & Wang, J. (2022). A critical review of various adsorbents for selective removal of nitrate from water: Structure, performance and mechanism. Chemosphere, 291, 132728.
Ma, X., He, D., Jones, A. M., Collins, R. N., & Waite, T. D. (2016). Reductive reactivity of borohydride-and dithionite-synthesized iron-based nanoparticles: A comparative study. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 303, 101–110.
Marini, F., & Walczak, B. (2015). Particle swarm optimization (PSO). A tutorial. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 149, 153–165.
Mendy, A., & Thorne, P. S. (2024). Long-term cancer and overall mortality associated with drinking water nitrate in the United States. Public Health, 228, 82–84.
Meng, F., Yang, Y., Li, M., Zhu, Q., Qin, B., & Yang, C. (2024). Nano Zero-valent iron (nZVI) encapsulated with ABS (nZVI/(ABS+ EC)) for sustainable denitrification performance and anti-aggregation. Processes, 12(4), 697.
Menke, J.-H., Hegemann, J., Gehler, S., & Braun, M. (2018). Heuristic monitoring method for sparsely measured distribution grids. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 95, 146–155.
Moghaddam, J. J., & Bagheri, A. (2015). A novel stable deviation quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization to optimal piezoelectric actuator and sensor location for active vibration control. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part i: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 229, 485–494.
Nighojkar, A., Plappally, A., & Soboyejo, W. (2023). Neural network models for simulating adsorptive eviction of metal contaminants from effluent streams using natural materials (NMs). Neural Computing and Applications, 35, 5751–5767.
Pan, Z., Li, Z., Zeng, B., Shen, L., & Lin, H. (2023). Enhanced denitrification performance of granular sludge for the treatment of waste brine from ion exchange resin process. Journal of Environmental Management, 344, 118473.
Pandey, K., Sharma, S., & Saha, S. (2022). Advances in design and synthesis of stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles for groundwater remediation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(3), 107993.
Pei, Y., Cheng, W., Liu, R., Di, H., Jiang, Y., Zheng, C., & Jiang, Z. (2024). Synergistic effect and mechanism of nZVI/LDH composites adsorption coupled reduction of nitrate in micro-polluted water. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 464, 133023.
Picetti, R., Deeney, M., Pastorino, S., Miller, M. R., Shah, A., Leon, D. A., Dangour, A. D., & Green, R. (2022). Nitrate and nitrite contamination in drinking water and cancer risk: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Environmental Research, 210, 112988.
Plessl, K., Russ, A., & Vollprecht, D. (2023). Application and development of zero-valent iron (ZVI) for groundwater and wastewater treatment. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 20(6), 6913–6928.
Prabhakar, R., & Samadder, S. R. (2020). Use of adsorption-influencing parameters for designing the batch adsorber and neural network–based prediction modelling for the aqueous arsenate removal using combustion synthesised nano-alumina. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(21), 26367–26384.
Pu, S., Deng, D., Wang, K., Wang, M., Zhang, Y., Shangguan, L., & Chu, W. (2019). Optimizing the removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions via reduced graphite oxide–supported nZVI: Synthesis, characterization, kinetics, and reduction mechanism. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 3932–3945.
Roy, D., Roy, B., & Manna, A. K. (2023). Pyrolyzed mesoporous activated carbon preparation from natural rubber common effluent biosludge: Characterization, isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics, and ANN modeling during phenol adsorption. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 23, 101020.
Sahinkaya, E., Muhsin, N., & Ozkaya, B. (2008). Neural network prediction of nitrate in groundwater of Harran plain, Turkey M Irfan Yesilnacar. Journal of Environmental Geology, 56, 19–25.
Savasari, M., Emadi, M., Bahmanyar, M. A., & Biparva, P. (2015). Optimization of Cd (II) removal from aqueous solution by ascorbic acid-stabilized zero valent iron nanoparticles using response surface methodology. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 21, 1403–1409.
Selvaraj, R., Jogi, S., Murugesan, G., Srinivasan, N. R., Goveas, L. C., Varadavenkatesan, T., Samanth, A., Vinayagam, R., Alshehri, M. A., & Pugazhendhi, A. (2024). Machine learning and statistical physics modeling of tetracycline adsorption using activated carbon derived from Cynometra ramiflora fruit biomass. Environmental Research, 252, 118816.
Sepehri, S., Heidarpour, M., & Abedi-Koupai, J. (2014). Nitrate removal from aqueous solution using natural zeolite-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Soil and Water Research, 9, 224–232.
Sepehri, S., Kanani, E., Abdoli, S., Rajput, V. D., Minkina, T., & Asgari Lajayer, B. (2023). Pb (II) Removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption on stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles—a green approach. Water, 15, 222.
Sepehri, S., & Nakhjavanimoghaddam, M. (2019). Batch removal of aqueous nitrate ions using an effective nano-biocomposite. Global Nest Journal, 21, 265–275.
Sergeyev, Y. D., Kvasov, D. E., & Mukhametzhanov, M. S. (2017). Operational zones for comparing metaheuristic and deterministic one-dimensional global optimization algorithms. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 141, 96–109.
Shakil, M. H., Trisha, A. T., Rahman, M., Talukdar, S., Kobun, R., Huda, N., & Zzaman, W. (2022). Nitrites in cured meats, health risk issues, alternatives to nitrites: A review. Foods, 11, 3355.
Song, N., Xu, J., Cao, Y., **a, F., Zhai, J., Ai, H., Shi, D., Gu, L., & He, Q. (2020). Chemical removal and selectivity reduction of nitrate from water by (nano) zero-valent iron/activated carbon micro-electrolysis. Chemosphere, 248, 125986.
Tan, M. H. Y., & Geubelle, P. H. (2017). 3D dimensionally reduced modeling and gradient-based optimization of microchannel cooling networks. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 323, 230–249.
Tatar, A., Barati-Harooni, A., Najafi-Marghmaleki, A., Norouzi-Farimani, B., & Mohammadi, A. H. (2016). Predictive model based on ANFIS for estimation of thermal conductivity of carbon dioxide. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 224, 1266–1274.
Tee, G. T., Gok, X. Y., & Yong, W. F. (2022). Adsorption of pollutants in wastewater via biosorbents, nanoparticles and magnetic biosorbents: A review. Environmental Research, 212, 113248.
Wang, W., Zhou, M., Mao, Q., Yue, J., & Wang, X. (2010). Novel NaY zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron as an efficient heterogeneous Fenton catalyst. Catalysis Communications, 11, 937–941.
Wang, Z., Chen, G., Wang, X., Li, S., Liu, Y., & Yang, G. (2020). Removal of hexavalent chromium by bentonite supported organosolv lignin-stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles from wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 267, 122009.
Wong, K. I., & Wong, P. K. (2017). Optimal calibration of variable biofuel blend dual-injection engines using sparse Bayesian extreme learning machine and metaheuristic optimization. Energy Conversion and Management, 148, 1170–1178.
Xu, J., Pu, Y., Qi, W.-K., Yang, X. J., Tang, Y., Wan, P., & Fisher, A. (2017). Chemical removal of nitrate from water by aluminum-iron alloys. Chemosphere, 166, 197–202.
Xu, W., Yang, T., Liu, S., Du, L., Chen, Q., Li, X., Dong, J., Zhang, Z., Lu, S., Gong, Y., Zhou, L., Liu, Y., & Tan, X. (2022). Insights into the Synthesis, types and application of iron Nanoparticles: The overlooked significance of environmental effects. Environment International, 158, 106980.
Yang, S., Wang, M. (2004). A quantum particle swarm optimization, Proceedings of the 2004 congress on evolutionary computation (IEEE Cat. No. 04TH8753). IEEE, pp. 320–324.
Yaseen, Z. M. (2021). An insight into machine learning models era in simulating soil, water bodies and adsorption heavy metals: Review, challenges and solutions. Chemosphere, 277, 130126.
Yılmaz, T., & Sahinkaya, E. (2023). Performance of sulfur-based autotrophic denitrification process for nitrate removal from permeate of an MBR treating textile wastewater and concentrate of a real scale reverse osmosis process. Journal of Environmental Management, 326, 116827.
Zhang, S., Kong, Z., Wang, H., Yan, Q., Vayenas, D. V., & Zhang, G. (2022). Enhanced nitrate removal by biochar supported nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) at biocathode in bioelectrochemical system (BES). Chemical Engineering Journal, 433, 133535.
Zhang, W., Huang, W., Tan, J., Huang, D., Ma, J., & Wu, B. (2023). Modeling, optimization and understanding of adsorption process for pollutant removal via machine learning: Recent progress and future perspectives. Chemosphere, 311, 137044.
Zhou, Y., & Li, X. (2022). Green synthesis of modified polyethylene packing supported tea polyphenols-NZVI for nitrate removal from wastewater: Characterization and mechanisms. Science of the Total Environment, 806, 150596.
Zolgharnein, J., Shariatmanesh, T., & Farahani, S. D. (2023). Artificial neural network (ANN) modeling for simultaneous removal of a binary mixture of Pb (II) and Cu (II) by cobalt hydroxide nano-flakes. Journal of Chemometrics, 37(4), e3475.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.S., M.C., J.J.M., S.A., and B.A.L: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. W.S. and G.W.P.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sepehri, S., Javadi Moghaddam, J., Abdoli, S. et al. Application of artificial intelligence in modeling of nitrate removal process using zero-valent iron nanoparticles-loaded carboxymethyl cellulose. Environ Geochem Health 46, 262 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-02089-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-02089-x