Abstract
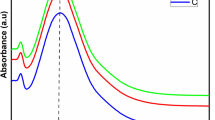
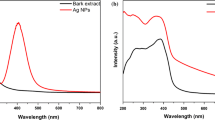
Plant extracts are a great alternative to synthesizing nanoparticles of different metals and metal oxides. This green synthesis method has opened up numerous possibilities in various scientific domains. In present study, Leaf extract from Vitex negundo is a non-deciduous, long-lasting shrub from the Verbenaceae family is used as cap** and reducing agents for the synthesis of silver and palladium nanoparticles. The characterization study UV–vis spectrophotometer analysis showed absorbance value around 320 nm which confirming that Ag–Pd nanoparticles have been successfully obtained. Further, SEM is used to investigate the morphology of Ag–Pd NPs, which revealing their spherical and rod-like configuration, aggregation, and the size of the particles are obtained between 50 and 100 nm. The successful synthesis of Ag–Pd NPs was further confirmed by the EDAX chart, which displayed the peak of Ag and Pd at bending energies between 0.5 and 1.5 keV. According to the quantitative study, Ag and Pd ions found about 5.24 and 13.28%, respectively. In addition, surface studies with TEM confirming that synthesized Ag–Pd NPs are predominates with spheres structure morphologies, with sizes averaging 11.20 nm and ranging from 10 to 20 nm. Further, Ag–Pd nanoparticles was applied as potential photocatalyst materials to degrade methylene blue dye and found about 85% of the degradation efficiency within 150 min of the sunlight exposure thus could be used as catalyst to removal of hazardous organic dye molecules.
Graphical abstract
Photo catalytic degradation through VNLE Ag–Pd NPs synthesis





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Tohamy, R., Ali, S. S., Li, F., Okasha, K. M., Mahmoud, Y. A. G., Elsamahy, T., et al. (2022). A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 231, 113160. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2021.113160
Al-Zaban, M. I., Mahmoud, M. A., & AlHarbi, M. A. (2021). Catalytic degradation of methylene blue using silver nanoparticles synthesized by honey. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 28(3), 2007–2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.01.003
Beyene, H. D., Werkneh, A. A., Bezabh, H. K., & Ambaye, T. G. (2017). Synthesis paradigm and applications of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), a review. Sustainable Materials and Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2017.08.001
Chen, Y., Tang, J., Liu, X., Ren, X., Zhen, M., & Wang, L. (2019). Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Eriobotrya japonica (Thunb.) leaf extract for reductive catalysis. Materials, 12(1), 189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010189
Devaraj, P., Kumari, P., Aarti, C., & Renganathan, A. (2013). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using cannonball leaves and their cytotoxic activity against MCF-7 cell line. Journal of Nanotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/598328
Długosz, O., Szostak, K., Staroń, A., Pulit-Prociak, J., & Banach, M. (2020). Methods for reducing the toxicity of metal and metal oxide NPs as biomedicine. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13020279
Gulbagça, F., Aygun, A., Altuner, E. E., Bekmezci, M., Gur, T., Sen, F., et al. (2022). Facile bio-fabrication of Pd-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles and its performance in catalytic and pharmaceutical applications: Hydrogen production and in-vitro antibacterial, anticancer activities, and model development. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 180, 254–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2022.02.024
Katheresan, V., Kansedo, J., & Lau, S. Y. (2018). Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6(4), 4676–4697. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JECE.2018.06.060
Khademi, M., Nasiri, S., Tabatabaei, F. S., Karmakar, N., Chakraborty, A., Nanjundiah, R. S., et al. (2017). A review on the classification, characterisation, synthesis of nanoparticles and their application. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 263(3), 032019. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/263/3/032019
Khan, A., Naz, S., Farooq, U., Shahid, M., Ullah, I., Ali, I., et al. (2018). Bioactive chromone constituents from Vitex negundo alleviate pain and inflammation. Journal of Pain Research, 11, 95–102. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S145551
Krishna, P. G., Chandra Mishra, P., Naika, M. M., Gadewar, M., Ananthaswamy, P. P., Rao, S., et al. (2022). Photocatalytic activity induced by metal nanoparticles synthesized by sustainable approaches: A comprehensive review. Frontiers in Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2022.917831
Kulkarni, R. R., Virkar, A. D., & Dmello, P. (2008). Antioxidant and antiinflammatory activity of Vitex negundo. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 70(6), 838–840. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474X.49140
Lee, K. C., Lin, S. J., Lin, C. H., Tsai, C. S., & Lu, Y. J. (2008). Size effect of Ag nanoparticles on surface plasmon resonance. Surface and Coatings Technology, 202(22–23), 5339–5342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.06.080
Lellis, B., Fávaro-Polonio, C. Z., Pamphile, J. A., & Polonio, J. C. (2019). Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnology Research and Innovation, 3(2), 275–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biori.2019.09.001
Lin, M., Dong, L., Chen, Q., Xu, H., Han, X., Luo, R., et al. (2021). Lentinan-based oral nanoparticle loaded budesonide with macrophage-targeting ability for treatment of ulcerative colitis. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.702173
Link, S., & El-Sayed, M. A. (1999). Spectral properties and relaxation dynamics of surface plasmon electronic oscillations in gold and silver nanodots and nanorods. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 103(40), 8410–8426. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9917648
Maciej Serda, M., Becker, F. G., Cleary, M., Team, R. M., Holtermann, H., The, D., et al. (2013). Synteza i aktywność biologiczna nowych analogów tiosemikarbazonowych chelatorów żelaza. Uniwersytet śląski, 7(1), 343–354.
Manuja, A., Kumar, B., Kumar, R., Chhabra, D., Ghosh, M., Manuja, M., et al. (2021). Metal/metal oxide nanoparticles: Toxicity concerns associated with their physical state and remediation for biomedical applications. Toxicology Reports, 8, 1970–1978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.11.020
Mariadoss, A. V. A., Ramachandran, V., Shalini, V., Agilan, B., Franklin, J. H., Sanjay, K., et al. (2019). Green synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles by Malus domestica and its cytotoxic effect on (MCF-7) cell line. Microbial Pathogenesis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103609
Muhammad, W., Ullah, N., Haroon, M., & Abbasi, B. H. (2019a). Optical, morphological and biological analysis of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using: Papaver somniferum L. RSC Advances, 9(51), 29541–29548. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra04424h
Mulvaney, P. (1996). Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nanosized metal particles. Langmuir, 12(3), 788–800. https://doi.org/10.1021/la9502711
Navaladian, S., Viswanathan, B., Varadarajan, T. K., & Viswanath, R. P. (2009). A rapid synthesis of oriented palladium nanoparticles by UV irradiation. Nanoscale Research Letters, 4(2), 181–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11671-008-9223-4/FIGURES/7
Pandit, C., Roy, A., Ghotekar, S., Khusro, A., Islam, M. N., Emran, T. B., et al. (2022). Biological agents for synthesis of nanoparticles and their applications. Journal of King Saud University - Science, 34(3), 101869. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JKSUS.2022.101869
Patil, S. P., & Kumbhar, S. T. (2020). Vitex negundo assisted green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles with different applications: A mini review. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 6(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00111-4
Pushankina, P., Baryshev, M., & Petriev, I. (2022). Synthesis and study of palladium mono- and bimetallic (with Ag and Pt) nanoparticles in catalytic and membrane hydrogen processes. Nanomaterials, 12(23), 4178. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234178
Rafiq, A., Ikram, M., Ali, S., Niaz, F., Khan, M., Khan, Q., & Maqbool, M. (2021). Photocatalytic degradation of dyes using semiconductor photocatalysts to clean industrial water pollution. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.02.017
Rajeshkumar, S., Vanaja, M., & Kalirajan, A. (2021). Degradation of toxic dye using phytomediated copper nanoparticles and its free-radical scavenging potential and antimicrobial activity against environmental pathogens. Bioinorganic Chemistry and Applications. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1222908
Rasmussen, J. W., Martinez, E., Louka, P., & Wingett, D. G. (2010). Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2010.502560
Sable, S. V., Kawade, S., Ranade, S., & Joshi, S. (2020). Bioreduction mechanism of silver nanoparticles. Materials Science and Engineering C, 107, 110299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110299
Saha, N., Trivedi, P., & Dutta Gupta, S. (2016). Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) based optimization of biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from rhizome extract of Curculigo orchioides Gaertn. and Its Antioxidant potential. Journal of Cluster Science, 27(6), 1893–1912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-016-1050-7
Sahayaraj, K., & Ravi, C. (2008). Preliminary phytochemistry of Ipomea carnea jacq. and Vitex negundo linn. leaves. International Journal of Chemical Science, 6(1), 1–6.
Sasireka, K. S., & Lalitha, P. (2021). Biogenic synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticles and their applications. Reviews in Inorganic Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1515/revic-2020-0024
Singh, K., Nancy Singh, G., & Singh, J. (2023). Sustainable synthesis of biogenic ZnO NPs for mitigation of emerging pollutants and pathogens. Environmental Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.114952
Sivamaruthi, B. S., Ramkumar, V. S., Archunan, G., Chaiyasut, C., & Suganthy, N. (2019). Biogenic synthesis of silver palladium bimetallic nanoparticles from fruit extract of Terminalia chebula—in vitro evaluation of anticancer and antimicrobial activity. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 51, 139–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.02.024
Thomas, R., Snigdha, S., Bhavitha, K. B., Babu, S., Ajith, A., & Radhakrishnan, E. K. (2018). Biofabricated silver nanoparticles incorporated polymethyl methacrylate as a dental adhesive material with antibacterial and antibiofilm activity against Streptococcus mutans. 3 Biotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205-018-1420-Y
Vinodhini, S., Vithiya, B. S. M., & Prasad, T. A. A. (2022). Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using aqueous plant extracts and its biomedical applications. Journal of King Saud University - Science, 34(4), 102017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102017
Acknowledgment
The authors express their sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSP2024R398) King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Authors also thank to Department of Science and Technology, Government of India for the award of National Postdoctoral Fellow (PDF/2022/001253).
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jayaraman Narenkumar: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Ajitha kannabiran: Methodology, Original draft preparation Shenbhagaraman ramalingam: Reviewing, Punniyakotti Parthipan:Validation, Bhaskar Das:Reviewing, Software, Mohamad S AlSalhi: Validation, funding. Sandhanasamy Devanesan: Validation, Seralathan Kamala-kannan: Validation. S. Thanigaivel: Validation, Aruliah Rajasekar: Validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Narenkumar, J., kannabiran, A., Ramalingam, S. et al. Photo-catalytic dye degradation potentials of Ag–Pd bimetallic nanoparticles synthesized from Vitex negundo. Environ Geochem Health 46, 200 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01978-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01978-5