Abstract
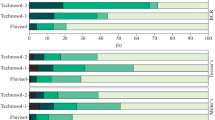
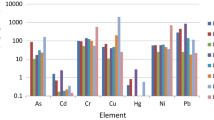
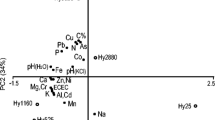
Metal speciation, linked directly to bioaccessibility and lability, is a key to be considered when assessing associated human and environmental health risks originated from anthropogenic activities. To identify the Zn and Cu speciation in the highly contaminated, technogenically transformed soils (Technosol) from the impact zone near the industrial sludge reservoirs of chemical plant (Siverskyi Donets River floodplain, southern Russia), the validity of the BCR sequential extraction procedure using the X-ray absorption fine-structure and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) analyses was examined after each of the three stages. After the removal of exchange and carbonate-bonded Zn and Cu compounds from Technosol (first stage of extraction), the resulting residual soil showed enrichment in a great diversity of metal compounds, primarily with Me–S and Me–O bonds. The number of compounds with a higher solubility decreased at the subsequent stages of extraction. In the residual soil left over after extracting the first and second fractions, the dominant Zn–S bond appeared as würtzite (hexagonal ZnS) that made up more than 50%, while the Cu–S bond was almost completely represented only by chalcocite (Cu2S). The XRD analysis revealed the authigenic minerals of metals with S: sphalerite (cubic ZnS), würtzite (hexagonal ZnS), covellite (CuS) and bornite (Cu5FeS4). The scanning electron microscopy data confirmed that würtzite was the dominant form of Me with sulfur-containing and carbonate-containing minerals. The Zn–S bond was the main component (57%), whereas the Cu–O bond was dominant in the residual fraction (the fraction after the third-stage extraction). The results revealed that the composition of the residual fractions might include some of the most stable and hard-to-recover metal compounds of technogenic origin. Thus, the application of the novel instrumental methods, coupled with the chemical fractionation, revealed the incomplete selectivity of the extractants in the extraction of Zn and Cu in long-term highly contaminated soils.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta, J. A., Gabarrón, M., Faz, A., Martínez-Martínez, S., Zornoza, R., & Arocena, J. M. (2015). Influence of population density on the concentration and speciation of metals in the soil and street dust from urban areas. Chemosphere, 134, 328–337.
Akcay, H., Oguz, A., & Karapire, C. (2003). Study of heavy metal pollution and speciation in Buyak Menderes and Gediz river sediments. Water Research, 37(4), 813–822.
Albertsson, J., Abrahams, S. C., & Kvick, A. (1989). Atomic displacement, anharmonic thermal vibration, expansivity, and pyroelectric coefficient thermal dependences in ZnO. Acta Crystallographica, 45, 34–40.
Al-Hwaiti, M. S., Brumsack, H. J., & Schnetger, B. (2015). Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in waste clay sediment discharged through the phosphate beneficiation process in Jordan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(7), 401.
Bauer, T. V., Linnik, V. G., Minkina, T. M., Mandzhieva, S. S., & Nevidomskaya, D. G. (2018). Ecological-geochemical studies of technogenic soils in the flood plain landscapes of the Seversky Donets, Lower Don basin. Geochemistry International, 56(10), 992–1002.
Burachevskaya, M., Minkina, T., Mandzhieva, S., Bauer, T., Chaplygin, V., Zamulina, I., et al. (2019). Study of copper, lead, and zinc speciation in the Haplic Chernozem surrounding coal-fired power plant. Applied Geochemistry, 104, 102–108.
Chernyshov, A. A., Veligzhanin, A. A., & Zubavichus, Y. V. (2009). Structural materials science end-station at the Kurchatov synchrotron radiation source: Recent instrumentation upgrades and experimental results. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors, and Associated Equipment, 603(1–2), 95–98.
Covelo, E. F., Matías, J. M., Vega, F. A., Reigosa, M. J., & Andrade, M. L. (2008). A tree regression analysis of factors determining the sorption and retention of heavy metals by soil. Geoderma, 147, 75–85.
Cuong, D. T., & Obbard, J. P. (2006). Metal speciation in coastal marine sediments from Singapore using a modified BCR-sequential extraction procedure. Applied Geochemistry, 21(8), 1335–1346.
Favorito, J. E., Luxton, T. P., Eick, M. J., & Grossl, P. R. (2017). Selenium speciation in phosphate mine soils and evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure using XAFS. Environmental Pollution, 229, 911–921.
Fernández-Ondoño, E., Bacchetta, G., Lallena, A. M., Navarro, F. B., Ortiz, I., & Jiménez, M. N. (2017). Use of BCR sequential extraction procedures for soils and plant metal transfer predictions in contaminated mine tailings in Sardinia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 172, 133–141.
Ghayoraneh, M., & Qishlaqi, A. (2017). Concentration, distribution and speciation of toxic metals in soils along a transect around a Zn/Pb smelter in the northwest of Iran. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 180, 1–14.
ISO 14235. (1998). Soil quality – Determination of organic carbon by sulfochromic oxidation.
ISO 10381-1. (2002). Soil quality. Sampling. Part 1. Guidance on the Design of Sampling Programmes.
ISO 10390. (2005). Soil quality: Determination of pH.
ISO 10693. (1995). Soil quality: Determination of carbonate content—Volumetric method.
IUSS Working Group WRB. (2015). World reference base for soil resources 2014, update 2015. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps. World soil resources reports, FAO, Rome, issue 106.
Jacquat, O., Voegelin, A., & Kretzschmar, R. (2009). Soil properties controlling Zn speciation and fractionation in contaminated soils. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(18), 5256–5272.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soil and plants. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Kirpichtchikova, T. A., Manceau, A., Spadini, L., Panfili, F., Marcus, M. A., & Jacquet, T. (2006). Speciation and solubility of heavy metals in contaminated soil using X-ray microfluorescence, EXAFS spectroscopy, chemical extraction, and thermodynamic modeling. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(9), 2163–2190.
Klementev, K. V. (2001). Extraction of the fine structure from x-ray absorption spectra. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 34(2), 209.
Ladonin, D. V. (2016). Forms of compounds of heavy metals in technogenically contaminated soils. Dissertation for the degree of Doctor of Biological Sciences, Moscow. (in Russian).
Lee, Y. J., Elzinga, E. J., & Reeder, R. J. (2005). Cu (II) adsorption at the calcite–water interface in the presence of natural organic matter: Kinetic studies and molecular-scale characterization. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(1), 49–61.
Leermakers, M., Mbachou, B. E., Husson, A., Lagneau, V., & Descostes, M. (2019). An alternative sequential extraction scheme for the determination of trace elements in ferrihydrite rich sediments. Talanta, 199, 80–88.
Mahanta, M. J., & Bhattacharyya, K. G. (2011). Total concentrations, fractionation and mobility of heavy metals in soils of urban area of Guwahati, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173(1–4), 221–240.
Manceau, A., Marcus, M. A., & Tamura, N. (2002). Quantitative speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments by synchrotron X-ray techniques. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 49(1), 341–428.
Marguí, E., Queralt, I., Carvalho, M. L., & Hidalgo, M. (2007). Assessment of metal availability to vegetation (Betula pendula) in Pb-Zn ore concentrate residues with different features. Environmental Pollution, 145(1), 179–184.
Mclean, J. E., & Bledsoe, B. E. (1992). Behaviour of metals in soils. EPA ground water issue. Washington: Environmental Protection Agency, EPA.
Minkina, T., Nevidomskaya, D., Bauer, T., Shuvaeva, V., Soldatov, A., Mandzhieva, S., et al. (2018). Determining the speciation of Zn in soils around the sediment ponds of chemical plants by XRD and XAFS spectroscopy and sequential extraction. Science of the Total Environment, 634, 1165–1173.
Minkina, T., Nevidomskaya, D., Burachevskaya, M., Bauer, T., Shuvaeva, V., Soldatov, A., et al. (2019). Possibilities of chemical fractionation and X-ray spectral analysis in estimating the speciation of Cu2+ with soil solid-phase components. Applied Geochemistry, 102, 55–63.
Minkina, T. M., Soldatov, A. V., Motuzova, G. V., Podkovyrina, Y. S., & Nevidomskaya, D. G. (2013). Molecular-structural analysis of the Cu (II) ion in ordinary chernozem: evidence from XANES spectroscopy and methods of molecular dynamics. Doklady Earth Sciences, 449(2), 418–421.
Nannoni, F., Protano, G., & Riccobono, F. (2011). Fractionation and geochemical mobility of heavy elements in soils of a mining area in northern Kosovo. Geoderma, 16, 63–73.
Nevidomskaya, D. G., Minkina, T. M., Soldatov, A. V., Shuvaeva, V. A., Zubavichus, Y. V., & Podkovyrina, Y. S. (2016). Comprehensive study of Pb(II) speciation in soil by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XANES and EXAFS) and sequential fractionation. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(4), 1183–1192.
Newville, M. (2001). IFEFFIT: Interactive XAFS analysis and FEFF fitting. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 8(2), 322–324.
Nielsen, M. T., Scott-Fordsmand, J. J., Murphy, M. W., & Kristiansen, S. M. (2015). Speciation and solubility of copper along a soil contamination gradient. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 15, 1558–1570.
Panfili, F., Manceau, A., Sarret, G., Spadini, L., Kirpichtchikova, T., Bert, V., et al. (2005). The effect of phytostabilization on Zn speciation in a dredged contaminated sediment using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray fluorescence, EXAFS spectroscopy, and principal components analysis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(9), 2265–2284.
Pinskii, D. L., & Minkina, T. M. (2013). Regularities of Cu, Pb and Zn adsorption by chernozems of the South of Russia. Eurasian Journal of Soil Science, 2(1), 59–68.
Pueyo, M., Rauret, G., Lück, D., Yli-Halla, M., Muntau, H., Quevauviller, P., et al. (2001). Certification of the extractable contents of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in a freshwater sediment following a collaboratively tested and optimised three-step sequential extraction procedure. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 3(2), 243–250.
Rajapaksha, A. U., Ahmad, M., Vithanage, M., Kim, K. R., Chang, J. Y., Lee, S. S., et al. (2015). The role of biochar, natural iron oxides, and nanomaterials as soil amendments for immobilizing metals in shooting range soil. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37(6), 931–942.
Ramos, L., Hernandez, L. M., & Gonzalez, M. J. (1994). Sequential fractionation of copper, lead, cadmium and zinc in soils from or near Donana National Park. Journal of Environmental Quality, 23(1), 50–57.
Scheinost, A. C., Kretzschmar, R., Pfister, S., & Roberts, D. R. (2002). Combining selective sequential extractions, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, and principal component analysis for quantitative zinc speciation in soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(23), 5021–5028.
Schlegel, M. L., Manceau, A., Charlet, L., Chateigner, D., & Hazemann, J. L. (2001). Sorption of metal ions on clay minerals. III. Nucleation and epitaxial growth of Zn phyllosilicate on the edges of hectorite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(22), 4155–4170.
Shein, E. V. (2009). The particle-size distribution in soils: problems of the methods of study, interpretation of the results, and classification. Eurasian Soil Science, 42(3), 284–291.
Strawn, D. G., & Baker, L. L. (2008). Speciation of Cu in a contaminated agricultural soil measured by XAFS, μ-XAFS, and μ-XRF. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(1), 37–42.
Sulkowski, M., & Hirner, A. V. (2006). Element fractionation by sequential extraction in a soil with high carbonate content. Applied Geochemistry, 21(1), 16–28.
Sutherland, R. A. (2010). BCR®-701: A review of 10-years of sequential extraction analyses. Analytica Chimica Acta, 680(1–2), 10–20.
Svetogorov, R. D., Dorovatovskii, P. V., & Lazarenko, V. A. (2020). Belok/XSA diffraction beamline for studying crystalline samples at Kurchatov Synchrotron Radiation Source. Crystal Research and Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.201900184.
Tack, F. M. G., & Verloo, M. G. (1995). Chemical speciation and fractionation in soil and sediment heavy metal analysis: A review. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 59(2–4), 225–238.
Ure, A. M., Quevauviller, P. H., Muntau, H., & Griepink, B. (1993). Speciation of heavy metals in soils and sediments. An account of the improvement and harmonization of extraction techniques undertaken under the auspices of the BCR of the Commission of the European Communities. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 51(1–4), 135–151.
Vieira, J. S., Botelho, C. M., & Boaventura, R. A. (2009). Trace metal fractionation by the sequential extraction method in sediments from the Lis River (Portugal). Soil and Sediment Contamination, 18(1), 102–119.
Vinogradov, F. P. (1957). Geochemistry of rare and dispersed elements in soils. Moscow, AN SSSR. (in Russian).
Vodyanitskii, Y. N., Minkina, T. M., Kubrin, S. P., Pankratov, D. A., & Fedorenko, A. G. (2019). Common and rare iron, sulfur, and zinc minerals in technogenically contaminated hydromorphic soil from Southern Russia. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(1), 95–108.
Voegelin, A., Pfister, S., Scheinost, A. C., Marcus, M. A., & Kretzshmar, R. (2005). Changes in zinc speciation in field soil after contamination with zinc oxide. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(17), 6616–6623.
Voegelin, A., Tokpa, G., Jacquat, O., Barmettler, K., & Kretzshmar, R. (2008). Zinc fractionation in contaminated soils by sequential and single extractions: Influence of soil properties and zinc content. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37, 1190–1200.
**a, K., Bleam, W., & Helmke, P. A. (1997). Studies of the nature of binding sites of first row transition elements bound to aquatic and soil humic substances using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(11), 2223–2235.
Yuan, C. G., Shi, J. B., He, B., Liu, J. F., Liang, L. N., & Jiang, G. B. (2004). Speciation of heavy metals in marine sediments from the East China Sea by ICP-MS with sequential extraction. Environment International, 30(6), 769–783.
Acknowledgements
The research was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (No. 0852-2020-0029) and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (No. 19-34-60041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nevidomskaya, D.G., Minkina, T.M., Soldatov, A.V. et al. Speciation of Zn and Cu in Technosol and evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure using XAS, XRD and SEM–EDX analyses. Environ Geochem Health 43, 2301–2315 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00693-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00693-1