Abstract
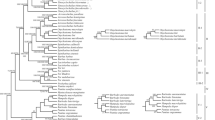
The northwestern part of Guangxi is a typical karst landform. There are about ten species of the genus Sinocyclocheilus distributed in the region. To investigate the phylogenetic relationships and resolve the taxonomic status of these species, we determined nucleotide sequences of complete mitochondrial cytochrome b gene of 11 ingroup species and one outgroup species Barbodes laticeps. Phylogenetic trees were reconstructed using maximum parsimony and maximum likelihood analyses. Phylogenetic results showed that these species cluster as one clade with strong support. The 95% credibility interval (CI) of the divergence time between the species in the northwest part of Guangxi and other species in the genus Sinocyclocheilus is 8.28–12.40Mya. For the karst environment, these species show marked, recent genetic differentiation. From the overall consideration of morphology and molecular data Sinocyclocheilus tianeensis should be a valid species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Yang J, Lan J (1997) One new species of blind cavefish from Guangxi with comments on its phylogenetic status (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae: Barbinae). Acta Zootax Sin 22:219–223
Felsenstein J (1985) ConWdence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Hillis DM, Bull JJ (1993) An empirical test of bootstrap** as a method for assessing conWdence in phylogenetic analysis. Syst Biol 42:182–192
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA 2: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Li G (1989) On a new fish of the genus Sinocyclocheilus from Guangxi China. Acta Zootax Sin 14:123–126
Li W, Lan J (1992) A new genus and three new species of Cyprinidae from Guangxi, China. J Zhanjiang Fish Coll 12:46–51
Li W, **ao H, Zan R, Luo Z, Li H (2000) A new species of Sinocyclocheilus from Guangxi, China. Zool Res 21:155–157
Li W, Lan J, Chen S (2003a) A new species of cave Sinocyclocheilus from Guangxi—Sinocyclocheilus Jiuxuensis Li et Lan, sp. nov. J Guangxi Norm Univ 21:83–85
Li W, **ao H, Zan R, Luo Z, Ban C, Fen J (2003b) A new species of Sinocyclocheilus from caves in Guangxi. J Guangxi Norm Univ 21:80–81
Li Z, Guo B, Li J, He S, Chen Y (2008) Bayesian model and divergence time of cave fishes in China. Sci China Press 53(13):1560–1569
Lin R, Luo Z (1986) A new blind barbid fish (Pisces, Cyprinidae) from subterranean water in Guangxi, China. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 10:380–382
Romero A, Zhao Y, Chen X (2009) The Hypogean fishes of China. Environ Biol Fish 86(1):211–278
Rutschmann F (2005) Bayesian molecular dating using PAML/multidivtime. A step–by–step manual. University of Zurich, Switzerland. Available at http://www.plant.ch.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Shan XH, Yue PQ (1994) The study on phylogeny of the Sinocyclocheilus fishes (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae: Barbinae). Zool Res 15(supp):36–44
Shan X, Lin R, Yue P, Chu X (2000) Barbinae. In: Yue P (ed) Fauna Sinica, Osteichthyes, Cypriniformes III. Science, Bei**g, pp 3–170
Swovord, DL (2003) PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and Other Methods).Version 4.0b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA.
Tamura K, Nei M, Kumar S (2004) Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11030–11035
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Wang DZ, Chen YY, Li XY (1999) An analysis on the phylogeny of the genus Sinocyclocheilus. Acta Acad Med Zunyi 22:1–6
**ao H, Chen SY, Liu ZM, Zhang RD, Li WX, Zan RG, Zhang YP (2005) Molecular phylogeny of Sinocyclocheilus (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 36(1):67–77
Yang Z, Yoder AD (2003) Comparison of likelihood and Bayesian methods for estimating divergence times using multiple gene loci and calibration points, with application to a radiation of cute–looking mouse lemur species. Syst Biol 52:705–716
Zhang C, Zhao Y (2001) A new fish of Sinocyclocheilus from Guangxi, China with a comment on its some biological adaptation. Acta Zootax Sin 26:102–107
Zhao Y, Zhang C (2009) An endemic cavefish genus Sinocyclocheilus in China—species diversity, systematics and zoogeography (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae). Science press, Bei**g
Zhao Y, Watanabe K, Zhang C (2006) Sinocyclocheilus donglanensis, a new cavefish (Teleostei: Cypriniformes) from Guangxi, China. Ichthyol Res 53:121–128
Zhao Y, Lan J, Zhang C (2009) A new cavefish species, Sinocyclocheilus brevibarbatus (Teleostei: Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae), from Guangxi, China. Environ Biol Fish 86(1):203–209
Zhou J, Zhang C, He A (2004) A new species of the genus Sinocyclocheilus from Guangxi, China (Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae). Acta Zootax Sin 29:591–594
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, XF., Cao, L. & Zhang, Cg. Molecular phylogeny of the Sinocyclocheilus (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae) fishes in northwest part of Guangxi, China. Environ Biol Fish 92, 371–379 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-011-9847-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-011-9847-6