Abstract
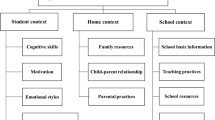
Psychoemotional well-being factors have been recognized to have a significant impact on students’ reading literacy. However, identifying which key psychoemotional well-being factors most significantly influence students’ reading performance is still not fully explored. This research examines the psychoemotional well-being factors that distinguish the reading literacy of high-level students from low-level ones using machine learning methods in four regions of China, including Bei**g, Shanghai, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang. In total, 3497 samples were drawn from the public database of the PISA 2018, including 2935 high-level students (with proficiency level at or above Level 5) and 562 low-achieving students (at Level 2 or below). By applying Recursive Feature Elimination with Cross-Validation feature selection and Support Vector Machine classifiers approach, this study successfully identifies 15 key factors (e.g., students’ socioeconomic status and learning goals) from the total 25 psychoemotional well-being factors that synergistically distinguish high-level students from low-level students with a high accuracy score (0.905). Further, using the Shapley Additive exPlanations method, the feature importance of the features set is shown, and 10 factors relevant to the psychoemotional well-being show the feature importance of reading literacy of high-level students. This study provides important insights into the factors of psychoemotional well-being that influence students’ reading literacy development.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. The data that support the findings of this study are openly available at https://webfs.oecd.org/pisa2018/SPSS_STU_QQQ.zip.
Materials and/or code availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aldridge, J., McChesney, K., & Afari, E. (2018). Relationships between school climate, bullying and delinquent behaviours. Learning Environments Research, 21, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-017-9249-6
Alivernini, F., & Manganelli, S. (2015). Country, school and students factors associated with extreme levels of science literacy across 25 countries. International Journal of Science Education, 37(12), 1992–2012. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2015.1060648
Alivernini, F., Cavicchiolo, E., Manganelli, S., Chirico, A., & Lucidi, F. (2020). Students’ psychological well-being and its multilevel relationship with immigrant background, gender, socioeconomic status, achievement, and class size. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 31(2), 172–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243453.2019.1642214
Antaramian, S. (2017). The importance of very high life satisfaction for students’ academic success. Cogent Education, 4(1), 1307622. https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2017.1307622
Apley, D. W., & Zhu, J. (2020). Visualizing the effects of predictor variables in black box supervised learning models. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodology, 82(4), 1059–1086. https://doi.org/10.1111/rssb.12377
Atasoy, R., Çoban, Ö., & Yatağan, M. (2022). Effect of ICT use, parental support and student hindering on science achievement: Evidence from PISA 2018. Journal of Learning and Teaching in Digital Age, 7, 127–140. https://doi.org/10.53850/joltida.945869
Attiat, M. (2023). Psycholsocial and social components predicting student self-efficacy: A study 2018. Jordan participation in the international student assessment program PISA 2018. Jordan Journal of Educational Sciences, 18, 203–216. https://doi.org/10.47015/18.4.1
Babu, V. D., & Malathi, K. (2022). Dynamic deep learning algorithm (DDLA) for processing of complex and large datasets. 2022 Second International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Energy (ICAIS) (pp. 336–342). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICAIS53314.2022.9743013
Badal, Y. T., & Sungkur, R. K. (2023). Predictive modelling and analytics of students’ grades using machine learning algorithms. Education and Information Technologies, 28(3), 3027–3057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11299-8
Baumann, C., & Harvey, M. (2021). What is unique about high performing students? Exploring personality, motivation and competitiveness. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 46, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2020.1870930
Benner, G. J., Filderman, M. J., Barnard-Brak, L., Pennefather, J., Smith, J. L. M., & Strycker, L. A. (2023). Evidence of efficacy of the integrated literacy study group professional learning program to enhance reading instruction for students with emotional and behavioral disorders. Psychology in the Schools, 60(1), 182–198. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22773
Blank, C., & Shavit, Y. (2016). The association between student reports of classmates’ disruptive behavior and student achievement. AERA Open, 2(3), 233285841665392. https://doi.org/10.1177/2332858416653921
Brassai, L., Piko, B. F., & Steger, M. F. (2011). Meaning in life: Is it a protective factor for adolescents’ psychological health? International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 18(1), 44–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12529-010-9089-6
Cervantes, J., Garcia-Lamont, F., Rodríguez-Mazahua, L., & Lopez, A. (2020). A comprehensive survey on support vector machine classification: Applications, challenges and trends. Neurocomputing, 408, 189–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.118
Chapman, S. J. (2018). Review of discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics, 4th edition. Journal of Political Science Education, 14(1), 145–147. https://doi.org/10.1080/15512169.2017.1366328
Chen, J., Zhang, Y., Wei, Y., & Hu, J. (2019). Discrimination of the contextual features of top performers in scientific literacy using a machine learning approach. Research in Science Education, 51(S1), 129–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-019-9835-y
Costa, H., Ripoll, P., Sanchez, M., & Carvalho, C. (2013). Emotional intelligence and self-efficacy: Effects on psychological well-being in college students. Spanish Journal of Psychology, 16, e50. https://doi.org/10.1017/sjp.2013.39
Coulangeon, P. (2018). The impact of participation in extracurricular activities on school achievement of French middle school students: Human capital and cultural capital revisited. Social Forces, 97(1), 55–90. https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/soy016
Creemers, B., Kyriakides, L. (2007). The dynamics of educational effectiveness: A contribution to policy, practice and theory in contemporary schools. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203939185
Davidovitch, N. (2023). Social factors influencing students’ reading habits. African Educational Research Journal, 11, 351–359. https://doi.org/10.30918/AERJ.113.23.057
Demirtas-Zorbaz, S., Akin-Arikan, C., & Terzi, R. (2021). Does school climate that includes students’ views deliver academic achievement? A multilevel meta-analysis. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 32(4), 543–563. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243453.2021.1920432
Ding, Y., & Wilkins, D. (2006). Improving the performance of SVM-RFE to select genes in microarray data. BMC Bioinformatics, 7(S2), S12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-7-S2-S12
Fauzan, F., Eriyanti, R., & Asih, R. (2023). Misconception of reading literacy and its impacts on literacy acculturation in school. Jurnal Cakrawala Pendidikan, 42, 208–219. https://doi.org/10.21831/cp.v42i1.53041
Fredrickson, B. L., Tugade, M. M., Waugh, C. E., & Larkin, G. R. (2003). What good are positive emotions in crisis? A prospective study of resilience and emotions following the terrorist attacks on the United States on September 11th, 2001. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(2), 365–376. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.84.2.365
Friedman, J. H. (2001). Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. The Annals of Statistics, 29(5), 1189–1232. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1013203451
Gustafsson, H., Sagar, S. S., & Stenling, A. (2017). Fear of failure, psychological stress, and burnout among adolescent athletes competing in high level sport. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, 27(12), 2091–2102. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12797
Hanushek, E. A. (2011). The economic value of higher teacher quality. Economics of Education Review, 30(3), 466–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econedurev.2010.12.006
Hattie, J., & Timperley, H. (2007). The power of feedback. Review of Educational Research, 77(1), 81–112. https://doi.org/10.3102/003465430298487
Hu, J., & Dong, X. (2019). An exploration of impact factors influencing students’ reading literacy in Singapore with machine learning approaches. International Journal of English Linguistics, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijel.v9n5p52
Hu, J., & **e, Q. (2022). Assessing students’ digital reading performance: An educational data mining approach. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003351108
Hu, J., Dong, X., & Peng, Y. (2022). Discovery of the key contextual factors relevant to the reading performance of elementary school students from 61 countries/regions: Insight from a machine learning-based approach. Reading and Writing, 35(1), 93–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10176-z
Hu, J., Peng, Y., & Chen, X. (2023). Decoding contextual factors differentiating adolescents’ high, average and low digital reading performance through machine learning methods. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/TLT.2023.3281056
Huebner, E. S. (1991). Initial development of the student’s life satisfaction scale. School Psychology International, 12, 231–240. https://doi.org/10.1177/0143034391123010
James, G., Witten, D., Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2013). An introduction to statistical learning. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7138-7_2
Kalaiselvi, K., & Thirumurthi, R. A. (2020). Big data analytics and intelligence: A perspective for health care (pp. 1–16). Emerald Publishing Limited. https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-83909-099-820201005
Kalonia, N., Garhwal, K., & Singh, V. (2023). Life satisfaction and resilience as a predictor of psychological well-being among youth. The International Journal of Indian Psychology, 10, 1004–1010. https://doi.org/10.25215/1004.098
Kamboj, K. P., & Garg, P. (2021). Teachers’ psychological well-being role of emotional intelligence and resilient character traits in determining the psychological well-being of Indian school teachers. International Journal of Educational Management, 35(4), 768–788. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEM-08-2019-0278
Kamiri, J., & Mariga, G. (2021). Research methods in machine learning: A content analysis. International Journal of Computer and Information Technology, 10, 2279–0764. https://doi.org/10.24203/ijcit.v10i2.79
Kang, N., Wang, E., Yu, Y., & Duan, Z. (2021). Valuing recreational services of the national forest parks using a tourist satisfaction method. Forests, 12(1688), 1688. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12121688
Khan, A., & Husain, A. (2010). Social Support as a moderator of positive psychological strengths and subjective well-being. Psychological Reports, 106, 534–538. https://doi.org/10.2466/PR0.106.2.534-538
Klem, A. M., & Connell, J. P. (2004). Relationships matter: Linking teacher support to student engagement and achievement. Journal of School Health, 74(7), 262–273. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1746-1561.2004.tb08283.x
Kovess-Masfety, V., Ester, W. A., Wild, K., Bitfoi, A., Goelitz, D., Lesinskiene, S., Mihova, Z., Otten, R., & Husky, M. M. (2022). Mental health problems, low birthweight and academic achievement in mathematics and reading. Current Psychology, 41(5), 2810–2820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-00674-8
Kyriakides, L., Creemers, B. P. M., & Charalambous, E. (2019). Searching for differential teacher and school effectiveness in terms of student socioeconomic status and gender: Implications for promoting equity. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 30(3), 286–308. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243453.2018.1511603
Lazarus, R. S. (1970). Cognitive and personality factors underlying threat and co**. Social Stress, 10(3), 143–164. Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315129808-8
Leseman, P. P. M., & De Jong, P. F. (1998). Home literacy: Opportunity, instruction, cooperation and social-emotional quality predicting early reading achievement. Reading Research Quarterly, 33(3), 294–318. https://doi.org/10.1598/RRQ.33.3.3
Lezhnina, O., & Kismihók, G. (2022). Combining statistical and machine learning methods to explore German students’ attitudes towards ICT in PISA. International Journal of Research & Method in Education, 45(2), 180–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/1743727X.2021.1963226
Li, Q., Salman, R., Test, E., Strack, R., & Kecman, V. (2013). Parallel multitask cross validation for support vector machine using GPU. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 73, 293–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2012.02.011
Lippman, L., Moore, K., & Mcintosh, H. (2009). Positive indicators of child well-being: A conceptual framework, measures, and methodological issues. UNICEF Innocenti Research Centre, Innocenti Working Papers, 6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-011-9138-6
Litvinova, A. (2022). Goal-setting among students with different levels of academic achievement. Integration of Education, 26, 708–721. https://doi.org/10.15507/1991-9468.109.026.202204.708-721
Liu, J., Peng, P., & Luo, L. (2020). The relation between family socioeconomic status and academic achievement in China: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review, 32(1), 49–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-019-09494-0
Liu, Y. B., Hou, X. Y., & Chen, B. B. (2022). Links between Chinese vocational school students’ perception of parents’ emotional support and school cooperation climate and their academic performance: The mediating role of school belonging. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 952001. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.952001
Liu, D., Wang, L., Xu, Z., Li, M., Joshi, R. M., Li, N., & Zhang, X. (2023). Understanding Chinese children’s word reading by considering the factors from cognitive, psychological and ecological factors. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 73, 102163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2023.102163
Malakouti, S., Menhaj, M., & Suratgar, A. (2023). The usage of 10-fold cross-validation and grid search to enhance ML methods performance in solar farm power generation prediction. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 15, 100664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2023.100664
Marcílio, W. E., & Eler, D. M. (2020). From explanations to feature selection: Assessing SHAP values as feature selection mechanism. 2020 33rd SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI) (pp. 340–347). https://doi.org/10.1109/SIBGRAPI51738.2020.00053
Maxwell, S., Reynolds, K. J., Lee, E., Subasic, E., & Bromhead, D. (2017). The impact of school climate and school identification on academic achievement: Multilevel modeling with student and teacher data. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 2069. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02069
Mayer, J. D., & Salovey, P. (1993). The intelligence of emotional intelligence. Intelligence, 17(4), 433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/0160-2896(93)90010-3
Memisevic, H., & Biscevic, I. (2022). Mathematics, gender and the meaning in life: The results of PISA testing in Bosnia and Herzegovina. European Journal of Mathematics and Science Education, 3(2), 171–179. https://doi.org/10.12973/ejmse.3.2.171
Meng, L., Qiu, C., Liu, X., & Kong, M. (2023). The structural relations among learning environment, achievement goals and reading achievement in China: Evidence from PISA 2018. Asia Pacific Journal of Education. https://doi.org/10.1080/02188791.2023.2233704
Michelucci, U. (2019). Advanced applied deep learning: Convolutional neural networks and object detection. Apress L. P. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4842-4976-5
Miguel, H., Vasconcelos-Raposo, J., & Brust, R. (2012). Factors associated with positive mental health in a Portuguese community sample: A look through the lens of Ryff’s psychological well-being model (V. Olisah). InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/36907
Mishra, P., & Close, K. (2020). The value of school. ECNU Review of Education, 3(3), 576–583. https://doi.org/10.1177/2096531120926687
Molina-Muñoz, D., Contreras-García, J., & Molina-Portillo, E. (2023). Does the psychoemotional well-being of Spanish students influence their mathematical literacy? Evidence from PISA 2018. Frontiers in Psychology, 14, 1196529. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1196529
Noble, W. S. (2006). What is a support vector machine? Nature Biotechnology, 24(12), 1565–1567. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1206-1565
Nyorere, O. I., James, I. O., & Patricia, Y. I. (2022). Social activities and academic self-concept of secondary school students in Uyo local education committee. International Journal of Interdisciplinary Research Methods, 9(1), 27–37. https://doi.org/10.37745/ijirm.14/vol9n1pp2737
OECD. (2009). PISA data analysis manual: SPSS (2nd ed.). OECD. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264056275-en
OECD. (2013). OECD guidelines on measuring subjective well-being. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: OECD. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264191655-en
OECD. (2018). PISA for development assessment and analytical framework: Reading, mathematics and science. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264305274-en
OECD. (2019a). PISA 2018 Results (Volume I): What students know and can do. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. https://doi.org/10.1787/5f07c754-en
OECD. (2019b). PISA 2018 Results (Volume III): What school life means for students’ lives. OECD. https://doi.org/10.1787/acd78851-en
OECD. (2019c). PISA 2018 Well-being framework (pp. 257–298). OECD. https://doi.org/10.1787/38a34353-en
Oluchi Anyanwu, G., Nwakanma, C. I., Lee, J.-M., & Kim, D.-S. (2023). Optimization of RBF-SVM kernel using grid search algorithm for DDoS attack detection in SDN-based VANET. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 10(10), 8477–8490. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2022.3199712
Pečjak, S. (2021). Reading culture from the psychological and educational perspectives. Revija Za Elementarno Izobraževanje, 4, 461–483. https://doi.org/10.18690/rei.14.4.461-483.2021
Pehlivan, O., & Aslan, G. (2023). Investigation of sociocultural and socioeconomic factors affecting the academic achievement: PISA 2018 Turkey sample. Kastamonu Eğitim Dergisi, 31, 367–377. https://doi.org/10.24106/2021-0041
Pertegal, M., & Oliva, A. (2017). A model on the contribution of school assets to the achievement of adolescents’ well-being and academic performance. The Spanish Journal of Psychology, 20, E44. https://doi.org/10.1017/sjp.2017.47
Pettersson, C. (2018). Psychological well-being, improved self-confidence, and social capacity: Bibliotherapy from a user perspective. Journal of Poetry Therapy, 31(2), 124–134. https://doi.org/10.1080/08893675.2018.1448955
Philippe, F. L., Gingras, M. P., Ghassemi-Bakhtiari, N., Poulin, F., Robitaille, J., Denault, A. S., Dandeneau, S., & Geoffroy, M. C. (2023). Organized Civic and non-civic activities as predictors of academic GPA in high school students. Applied Developmental Science, 27(2), 189–204. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888691.2022.2053127
Pimple, J. (2023). Correlational analysis of emotional intelligence and psychological well-being. Indian Journal of Positive Psychology, 14, 39–42.
Pons, A., & Houldsworth, L. (2020). Insights and interpretations. OECD. https://doi.org/10.1787/d0f4a644-en
Porter-Owens, N. (2022). How do psychological factors interact with reading performance? Order No. 30246030 dissertation. Concordia University Chicago, United States. https://doi.org/10.2316/Journal.201.2018.3.201-2979. Accessed 23 Aug 2023.
Rance, G., Dowell, R. C., & Tomlin, D. (2023). The effect of classroom environment on literacy development. Npj Science of Learning, 8(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41539-023-00157-y
Reis, S., Mccoach, D. B., Little, C., Muller, L., & Kaniskan, R. (2011). The effects of differentiated instruction and enrichment pedagogy on reading achievement in five elementary schools. American Educational Research Journal, 48, 462–501. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831210382891
Rizzotto, J. S., & França, M. T. A. (2022). Indiscipline: The school climate of Brazilian schools and the impact on student performance. International Journal of Educational Development, 94, 102657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedudev.2022.102657
Roderick, M., & Engel, M. (2001). The Grasshopper and the Ant: Motivational responses of low-achieving students to high-stakes testing. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 23(3), 197–227. https://doi.org/10.3102/01623737023003197
Roeser, R. W., Midgley, C., & Urdan, T. C. (1996). Perceptions of the school psychological environment and early adolescents’ psychological and behavioral functioning in school: The mediating role of goals and belonging. Journal of Educational Psychology, 88(3), 408–422. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.88.3.40
Rustamov, E., Aliyeva, M., Rustamova, N., & Zalova-Nuriyeva, U. (2023). Adaptation of the school climate questionnaire: Its association with psychological distress, academic self-efficacy, and mental wellbeing in Azerbaijan. Problems of Education in the 21st Century, 81, 517–530. https://doi.org/10.33225/pec/23.81.517
Ryff, C. D. (1995). Psychological well-being in adult life. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 4(4), 99–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8721.ep10772395
Salle, T. P. L., Meyers, J., Varjas, K., & Roach, A. (2015). A cultural-ecological model of school climate. International Journal of School & Educational Psychology, 3(3), 157–166. https://doi.org/10.1080/21683603.2015.1047550
Sammons, P., Hall, J., Sylva, K., Melhuish, E., Siraj-Blatchford, I., & Taggart, B. (2013). Protecting the development of 5–11-year-olds from the impacts of early disadvantage: The role of primary school academic effectiveness. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 24(2), 251–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243453.2012.749797
Seijo, D., Vazquez, M., Novo, M., & Fariña, F. (2023). Studying the effects of sense of belonging to virtual communities in psychological well-being and adjustment to academic setting. Educación XX1, 26, 229–247. https://doi.org/10.5944/educxx1.31818
Sejuti, Z., & Islam, M. (2023). A hybrid CNN–KNN approach for identification of COVID-19 with 5-fold cross validation. Sensors International, 4, 100229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sintl.2023.100229
Senaviratna, N., & Cooray, T. (2019). Diagnosing multicollinearity of logistic regression model. Asian Journal of Probability and Statistics, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajpas/2019/v5i230132
Senko, C. (2019). When do mastery and performance goals facilitate academic achievement? Contemporary Educational Psychology, 59, 101795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.101795
Siouli, S., Makris, S., Romanopoulou, E., & Bamidis, P. P. D. (2020). Living with learning difficulties: Two case studies exploring the relationship between emotion and performance in students with learning difficulties (pp. 131–143). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57717-9_10
Sparks, T. A., Hunter, S. K., Backman, T. L., Morgan, G. A., & Ross, R. G. (2012). Maternal parenting stress and mothers’ reports of their infants’ mastery motivation. Infant Behavior and Development, 35(1), 167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infbeh.2011.07.002
Stepanyan, L. S., Yu, S. A., & Grigoryan, V. H. (2010). Psychophysiological correlates of influence of different gameplay on teenagers’ psychoemotional state. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 77(3), 278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2010.06.132
Strobl, C., Malley, J., & Tutz, G. (2009). An introduction to recursive partitioning: Rationale, application, and characteristics of classification and regression trees, bagging, and random forests. Psychological Methods, 14(4), 323–348. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016973
Suldo, S., Frank, M., Chappel, A., Albers, M., & Bateman, L. (2014). American high school students’ perceptions of determinants of life satisfaction. Social Indicators Research, 118, 485–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0436-2
Tabri, N., & Elliott, C. M. (2012). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. Canadian Graduate Journal of Sociology and Criminology, 1(1), 59–60. https://doi.org/10.15353/cgjsc.v1i1.3787
Tang, X., & Dai, T. (2021). How do classroom behaviors predict longitudinal reading achievement? A conditional autoregressive latent growth analysis. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 54, 239–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecresq.2020.09.007
Telef, B. B., & Furlong, M. J. (2017). Social and emotional psychological factors associated with subjective well-being: A comparison of Turkish and California adolescents. Cross-Cultural Research, 51(5), 491–520. https://doi.org/10.1177/1069397117694815
Torppa, M., Eklund, K., Sulkunen, S., Niemi, P., & Ahonen, T. (2018). Why do boys and girls perform differently on PISA Reading in Finland? The effects of reading fluency, achievement behaviour, leisure reading and homework activity. Journal of Research in Reading, 41(1), 122–139. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9817.12103
Wang, T., & Wen, J. (2023). Experiential teaching is more conducive to student learning than traditional teaching. Journal of Education and Culture Studies, 7(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.22158/jecs.v7n1p100
Wei, Y., Yang, Q., Chen, J., & Hu, J. (2018). The exploration of a machine learning approach for the assessment of learning styles changes. Mechatronic Systems and Control, 46(1), 121–126. https://doi.org/10.2316/Journal.201.2018.3.201-2979
Werang, B. R., Jampel, I. N., Agung, A. A. G., Putri, H. W. S., & Asaloei, S. I. (2022). Teacher teaching performance, students’ learning motivation and academic achievement. Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences, 17(12), 4672–4682. https://doi.org/10.18844/cjes.v17i12.7586
Wu, Y. (2023). The mediating effect of emotional self-regulation on the relationship of perceived benefits of dance exercises/physical activity and psychological well -being. International Journal of Education and Humanities, 8, 103–108. https://doi.org/10.54097/ijeh.v8i3.8395
**ao, Y., & Hew, K. F. (2022). The relationships among ICT-Related psychological factors, school contextual factors and secondary students’ reading performance: A multilevel analysis across 47 economies. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 60(5), 1166–1196. https://doi.org/10.1177/07356331211070975
**ao, Y., & Hu, J. (2019). Assessment of optimal pedagogical factors for Canadian ESL learners’ reading literacy through artificial intelligence algorithms. International Journal of English Linguistics, 9, 1. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijel.v9n4p1
**ao, Y., Liu, Y., & Hu, J. (2019). Regression analysis of ICT impact factors on early adolescents’ reading proficiency in five high-performing countries. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 457763. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01646
**ao, Z., **ng, H., Zhao, B., Qu, R., Luo, S., Dai, P., Li, K., & Zhu, Z. (2023). Deep contrastive representation learning with self-distillation. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1109/TETCI.2023.3304948
**ng, H., **ao, Z., Qu, R., Zhu, Z., & Zhao, B. (2022a). An efficient federated distillation learning system for multitask time series classification. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 71, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2022.3201203
**ng, H., **ao, Z., Zhan, D., Luo, S., Dai, P., & Li, K. (2022b). SelfMatch: Robust semisupervised time-series classification with self-distillation. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 37(11), 8583–8610. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22957
Yalcin, S., & Tavsancil, E. (2014). The comparison of Turkish students’ PISA achievement levels by year via data envelopment analysis. Educational Sciences Theory & Practice, 14(3), 961–968.
Zheng, J. Q., Cheung, K., & Sit, P. S. (2023). Identifying key features of resilient students in digital reading: Insights from a machine learning approach. Education and Information Technologies. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11908-0
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the 2023 priority research topic for Bei**g Education Science Planning, focused on the “Current Status and Comparative Study of Science Education in Bei**g’s Primary and Secondary Schools” (Grant number: 3059-0012). I would like to declare on behalf of my co-authors that the work described was original research that has not been published previously, and not under consideration for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part. We are grateful to the editors and reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Our study utilizes publicly available survey data. Ethics approval is not applicable in this case.
Consent
Our study utilized publicly available survey data. Consent is not applicable in this case.
Competing interests
No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript, and the manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, X., Yuan, W., Liu, T. et al. Machine learning investigation of optimal psychoemotional well-being factors for students’ reading literacy. Educ Inf Technol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12580-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12580-8