Abstract
Objective
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) has been demonstrated to exert a pro-carcinogenic effect in solid tissues. However, the precise biological function and underlying mechanisms in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains elucidated.
Aims
To investigate whether KLF4 participates in the proliferation and invasion of CRC.
Methods
The expression of KLF4 was investigated using immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting. The clinical significance of KLF4 was evaluated. Furthermore, the effect of inhibiting or overexpressing KLF4 on tumor was examined. Immunoblotting and qPCR were used to detect Epithelial–mesenchymal transition-related proteins levels. Additionally, the molecular function of KLF4 is related to the STAT3 signaling pathway and was determined through JASPAR, GSEA analysis, and in vitro experiments.
Results
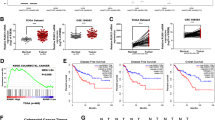
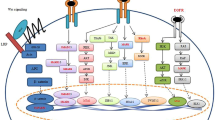
KLF4 exhibits down-regulated expression in CRC and is part of the vessel invasion, TNM stage, and worse prognosis. In vitro studies have shown that KLF4 promotes cellular proliferation and invasion, as well as EMT processes. Xenograft tumor models confirmed the oncogenic role of KLF4 in nude mice. Furthermore, GSEA and JASPAR databases analysis reveal that the binding of KLF4 to the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) promoter site induces activation of p-STAT3 signaling. Subsequent targeting of STAT3 confirmed its pivotal role in mediating the oncogenic effects exerted by KLF4.
Conclusion
The study suggests that KLF4 activates STAT3 signaling, inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition, thereby promoting CRC progression.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The information examined in this study is obtainable in the TCGA (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/), GSEA (https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/index.jsp), and JASPAR (https://jaspar.genereg.net/) databases.
Abbreviations
- KLF4:
-
Kruppel-like factor 4
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- p-STAT3:
-
Phosphorylation of STAT3
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- CHIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- GSEA:
-
Gene set enrichment analysis
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Hashemi M, Abbaszadeh S, Rashidi M et al. STAT3 as a newly emerging target in colorectal cancer therapy: Tumorigenesis, therapy response, and pharmacological/nanoplatform strategies. Environ Res. 2023;233:116458.
Feng RM, Zong YN, Cao SM, Xu RH. Current cancer situation in China: good or bad news from the 2018 Global Cancer Statistics? Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019;39:22.
Kawata M, Teramura T, Ordoukhanian P et al. Krüppel-like factor-4 and Krüppel-like factor-2 are important regulators of joint tissue cells and protect against tissue destruction and inflammation in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-221867.
Rowland BD, Peeper DS. KLF4, p21 and context-dependent opposing forces in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:11–23.
Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676.
Moad M, Pal D, Hepburn AC et al. A novel model of urinary tract differentiation, tissue regeneration, and disease: reprogramming human prostate and bladder cells into induced pluripotent stem cells. Eur Urol. 2013;64:753–761.
Shaverdashvili K, Padlo J, Weinblatt D et al. KLF4 activates NFκB signaling and esophageal epithelial inflammation via the Rho-related GTP-binding protein RHOF. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0215746.
Wang X, **a S, Li H et al. The deubiquitinase USP10 regulates KLF4 stability and suppresses lung tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:1747–1764.
Zhang L, Zhou Q, Qiu Q et al. CircPLEKHM3 acts as a tumor suppressor through regulation of the miR-9/BRCA1/DNAJB6/KLF4/AKT1 axis in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:144.
Zou H, Chen H, Zhou Z, Wan Y, Liu Z. ATXN3 promotes breast cancer metastasis by deubiquitinating KLF4. Cancer Lett. 2019;467:19–28.
Ganguly K, Krishn SR, Rachagani S et al. Secretory Mucin 5AC Promotes Neoplastic Progression by Augmenting KLF4-Mediated Pancreatic Cancer Cell Stemness. Cancer Res. 2021;81:91–102.
Ingruber J, Savic D, Steinbichler TB et al. KLF4, Slug and EMT in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells. 2021;10:539.
Subbalakshmi AR, Sahoo S, McMullen I et al. KLF4 Induces Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition (MET) by Suppressing Multiple EMT-Inducing Transcription Factors. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:5135.
**esh GG, Brohl AS. Classical epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and alternative cell death process-driven blebbishield metastatic-witch (BMW) pathways to cancer metastasis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7:296.
Yeung KT, Yang J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Mol Oncol. 2017;11:28–39.
Wong GL, Manore SG, Doheny DL, Lo HW. STAT family of transcription factors in breast cancer: Pathogenesis and therapeutic opportunities and challenges. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;86:84–106.
Yang J, Wang L, Guan X, Qin JJ. Inhibiting STAT3 signaling pathway by natural products for cancer prevention and therapy: In vitro and in vivo activity and mechanisms of action. Pharmacol Res. 2022;182:106357.
Ouyang S, Li H, Lou L et al. Inhibition of STAT3-ferroptosis negative regulatory axis suppresses tumor growth and alleviates chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Redox Biol. 2022;52:102317.
Liu Y, Gong W, Yang ZY et al. Quercetin induces protective autophagy and apoptosis through ER stress via the p-STAT3/Bcl-2 axis in ovarian cancer. Apoptosis. 2017;22:544–557.
Gong K, Jiao J, Xu C et al. The targetable nanoparticle BAF312@cRGD-CaP-NP represses tumor growth and angiogenesis by downregulating the S1PR1/P-STAT3/VEGFA axis in triple-negative breast cancer. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19:165.
Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H et al. IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:1853–1867.
Zhou Z, Wang P, Sun R et al. Tumor-associated neutrophils and macrophages interaction contributes to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression by activating STAT3. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9:e001946.
Chen C, Gupta P, Parashar D et al. ERBB3-induced furin promotes the progression and metastasis of ovarian cancer via the IGF1R/STAT3 signaling axis. Oncogene 2020;39:2921–2933.
Zhang X, Sai B, Wang F et al. Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:40.
Castro-Mondragon JA, Riudavets-Puig R, Rauluseviciute I et al. JASPAR 2022: the 9th release of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D165-d173.
Sandelin A, Alkema W, Engström P, Wasserman WW, Lenhard B. JASPAR: an open-access database for eukaryotic transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:D91-94.
Menon SS, Guruvayoorappan C, Sakthivel KM, Rasmi RR. Ki-67 protein as a tumour proliferation marker. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;491:39–45.
Zhang J, Zhu Z, Wu H et al. PODXL, negatively regulated by KLF4, promotes the EMT and metastasis and serves as a novel prognostic indicator of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2019;22:48–59.
Zhou H, Guan Q, Hou X et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal reprogramming by KLF4-regulated Rictor expression contributes to metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18:4869–4883.
Li H, Wang J, **ao W et al. Epigenetic inactivation of KLF4 is associated with urothelial cancer progression and early recurrence. J Urol. 2014;191:493–501.
Orzechowska-Licari EJ, LaComb JF, Mojumdar A, Bialkowska AB. SP and KLF Transcription Factors in Cancer Metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:9956.
Yan Y, Li Z, Kong X et al. KLF4-Mediated Suppression of CD44 Signaling Negatively Impacts Pancreatic Cancer Stemness and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2016;76:2419–2431.
He H, Li S, Chen H et al. 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate promotes breast cancer cell motility by increasing S100A14 level in a Kruppel-like transcription factor 4 (KLF4)-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:9089–9099.
Yori JL, Seachrist DD, Johnson E et al. Krüppel-like factor 4 inhibits tumorigenic progression and metastasis in a mouse model of breast cancer. Neoplasia 2011;13:601–610.
Yang X, Li G, Tian Y et al. Identifying the E2F3-MEX3A-KLF4 signaling axis that sustains cancer cells in undifferentiated and proliferative state. Theranostics. 2022;12:6865–6882.
Pastushenko I, Blanpain C. EMT Transition States during Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019;29:212–226.
**ong X, Schober M, Tassone E et al. KLF4, A Gene Regulating Prostate Stem Cell Homeostasis, Is a Barrier to Malignant Progression and Predictor of Good Prognosis in Prostate Cancer. Cell Rep. 2018;25:3006-3020.e3007.
Schulz-Heddergott R, Stark N, Edmunds SJ et al. Therapeutic Ablation of Gain-of-Function Mutant p53 in Colorectal Cancer Inhibits Stat3-Mediated Tumor Growth and Invasion. Cancer Cell. 2018;34:298-314.e297.
Sun Q, Zhao X, Li R et al. STAT3 regulates CD8+ T cell differentiation and functions in cancer and acute infection. J Exp Med. 2023;220:e20220686.
Liu S, Liu S, Yu Z et al. STAT3 regulates antiviral immunity by suppressing excessive interferon signalling. Cell Rep. 2023;42:112806.
Balic JJ, Albargy H, Luu K et al. STAT3 serine phosphorylation is required for TLR4 metabolic reprogramming and IL-1β expression. Nat Commun. 2020;11:3816.
Balanis N, Wendt MK, Schiemann BJ, Wang Z, Schiemann WP, Carlin CR. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition promotes breast cancer progression via a fibronectin-dependent STAT3 signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:17954–17967.
Zhang C, Guo F, Xu G, Ma J, Shao F. STAT3 cooperates with Twist to mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2015;33:1872–1882.
Ka-Yue Chow L, Lai-Shun Chung D, Tao L et al. Epigenomic landscape study reveals molecular subtypes and EBV-associated regulatory epigenome reprogramming in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. EBioMedicine. 2022;86:104357.
Ou DL, Chen CW, Hsu CL et al. Regorafenib enhances antitumor immunity via inhibition of p38 kinase/Creb1/Klf4 axis in tumor-associated macrophages. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9:e001657.
You W, Ouyang J, Cai Z, Chen Y, Wu X. Comprehensive Analyses of Immune Subtypes of Stomach Adenocarcinoma for mRNA Vaccination. Front Immunol. 2022;13:827506.
Zhao W, Hisamuddin IM, Nandan MO, Babbin BA, Lamb NE, Yang VW. Identification of Krüppel-like factor 4 as a potential tumor suppressor gene in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23:395–402.
Ma Y, Wu L, Liu X et al. KLF4 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation dependent on NDRG2 signaling. Oncol Rep. 2017;38:975–984.
Zou S, Tong Q, Liu B, Huang W, Tian Y, Fu X. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:145.
Acknowledgment
Thanks to my colleagues for their contributions.
Funding
This work was funded by Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Province (GJJ2200241).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.Y. and Y.M. carried out the formal analysis and drafted the initial manuscript; J.X. oversaw the project administration; L.Y. conducted the experiments. Y.M. participated in software analysis; L.Y. and J.X. conducted data curation; L.Y., Y.M., and J.X. were instrumental in authoring, critically revising, and editing the manuscript; all contributors thoroughly reviewed and endorsed the final version submitted for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors affirm that there exists no competing interest in relation to the publication of this manuscript.
Ethical approval
In compliance with local laws and institutional guidelines, ethical review and approval were waived for this research involving human participants. Similarly, in adherence to national regulations and institutional standards, written informed consent from participants was not necessary for this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, L., Meng, Y. & **ang, J. KLF4 Induces Colorectal Cancer by Promoting EMT via STAT3 Activation. Dig Dis Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-024-08473-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-024-08473-y