Abstract
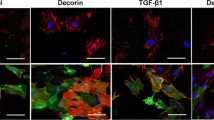
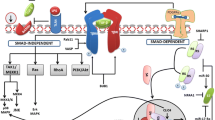
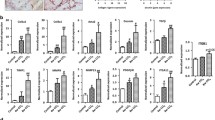
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are key players in liver fibrosis and regeneration via collagen degradation and synthesis. These phenomena involve inflammatory cytokines released from non-parenchymal liver cells such as Kupffer cells. Although the effects of individual cytokines on many cell types have been investigated in various conditions, such as inflammation and tissue fibrosis, investigating the effect of combined cytokines would further our understanding of the regulatory mechanisms in tissue fibrosis. Here, we report the effect of multiple cytokine combinations on primary HSCs. We first examined the effect of individual cytokines and then the simultaneous exposure of different cytokines, including interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1 alpha (IL-1α), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), on matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP1) gene expression in primary HSCs. We observed that the combination of all five cytokines induced higher levels of MMP1 gene expression. Of these cytokines, TNF-α and IL-1α were found to be the key cytokines for not only inducing MMP1 expression, but also increasing α-smooth muscle actin gene expression. In conclusion, the combined treatment of TNF-α and IL-1α on HSCs had an enhanced effect on the expression of the fibrotic genes, MMP1 and α-smooth muscle actin, so appears to be an important regulator for tissue regeneration. This finding suggests that stimulation with combined anti-fibrotic cytokines is a potential approach in the development of a novel therapy for the recovery of liver fibrosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angulo P, Keach JC, Batts KP, Lindor KD (1999) Independent predictors of liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 30:61356–61362
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115:209
Benyon RC, Iredale JP (2000) Is liver fibrosis reversible? Gut 46:443–446
Borthwick LA, Wynn TA, Fisher AJ (2013) Cytokine mediated tissue fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:1049–1060
Brenner DA, Kisseleva T, Scholten D, Paik YH, Iwaisako K, Inokuchi S, Taura K (2012) Origin of myofibroblasts in liver fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 5(Suppl 1):S17
Chambers M, Kirkpatrick G, Evans M, Gorski G, Foster S, Borghaei RC (2013) IL-4 inhibition of IL-1 induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) expression in human fibroblasts involves decreased AP-1 activation via negative crosstalk involving of Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK). Exp Cell Res 319:1398–1408
Cheng G, Wei L, **urong W, **angzhen L, Shiguang Z, Songbin F (2009) IL-17 stimulates migration of carotid artery vascular smooth muscle cells in an MMP-9 dependent manner via p38 MAPK and ERK1/2-dependent NF-kB and AP-1 activation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:1161–1168
Chensue SW, Terebuh PD, Remick DG, Scales WE, Kunkel SL (1991) In vivo biologic and immunohistochemical analysis of interleukin-1 alpha, beta and tumor necrosis factor during experimental endotoxemia. Kinetics, Kupffer cell expression, and glucocorticoid effects. Am J Pathol 138:395–402
Choy EH, Panayi GS (2001) Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 344:907–916
Coker RK, Laurent GJ (1998) Pulmonary fibrosis: cytokines in the balance. Eur Respir J 11:1218–1221
Fausto N, Campbell JS, Riehle KJ (2012) Liver regeneration. J Hepatol 57:692–694
Firestein GS, Alvaro-Gracia JM, Maki R, Alvaro-Garcia JM (1990) Quantitative analysis of cytokine gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 144:3347–3353
Foey AD, Parry SL, Williams LM, Feldmann M, Foxwell BM, Brennan FM (1998) Regulation of monocyte IL-10 synthesis by endogenous IL-1 and TNF-α: role of the p38 and p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Immunol 160:920–928
Friedman SL (2008) Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 88:125–172
Gabay C, McInnes IB (2009) The biological and clinical importance of the ‘new generation’cytokines in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 11:230
Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R (2006) Modern pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and TGF-beta as major players and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med 10:76–99
Han YP, Zhou L, Wang J, **ong S, Garner WL, French SW, Tsukamoto H (2004) Essential role of matrix metalloproteinases in interleukin-1-induced myofibroblastic activation of hepatic stellate cell in collagen. J Biol Chem 279:4820–4828
Hemmann S, Graf J, Roderfeld M, Roeb E (2007) Expression of MMPs and TIMPs in liver fibrosis–a systematic review with special emphasis on anti-fibrotic strategies. J Hepatol 46:955–975
Johnson GL, Lapadat R (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 298:1911–1912
Kleiner DE, Stetler-Stevenson WG (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases and metastasis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 43:S42–S51
Kolios G, Valatas V, Kouroumalis E (2006) Role of Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 12:7413–7420
Lee KS, Buck M, Houglum K, Chojkier M (1995) Activation of hepatic stellate cells by TGF alpha and collagen type I is mediated by oxidative stress through c-myb expression. J Clin Invest 96:2461–2468
Mak KM, Chu E, Lau KH, Kwong AJ (2012) Liver fibrosis in elderly cadavers: localization of collagen types I, III, and IV, α-smooth muscle actin, and elastic fibers. Anat Rec 295:1159–1167
McInnes IB, Schett G (2007) Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol 7:429–442
Mengshol JA, Vincenti MP, Brinckerhoff CE (2001) IL-1 induces collagenase-3 (MMP-13) promoter activity in stably transfected chondrocytic cells: requirement for Runx-2 and activation by p38 MAPK and JNK pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4361–4372
Nakamura A, Ueno T, Yagi Y, Okuda K, Ogata T, Nakamura T, Torimura T, Iwamoto H, Ramadoss S, Sata M, Tsutsumi V, Yasuda K, Tomiyasu Y, Obayashi K, Tashiro K, Kuhara S (2010) Human primary cultured hepatic stellate cells can be cryopreserved. Med Mol Morphol 43:107–115
Poynard T, Bedossa P, Opolon P (1997) Natural history of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Lancet 349:825–832
Reunanen N, Li SP, Ahonen M, Foschi M, Han J, Kähäri VM (2002) Activation of p38α MAPK enhances collagenase-1 (matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1) and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) expression by mRNA stabilization. J Biol Chem 277:32360–32368
Rockey DC, Weymouth N, Shi Z (2013) Smooth muscle α actin (Acta 2) and myofibroblast function during hepatic wound healing. PLoS ONE 29:e77166
Sasaki M, Kashima M, Ito T, Watanabe A, Izumiyama N, Sano M, Miura M (2000) Differential regulation of metalloproteinase production, proliferation and chemotaxis of human lung fibroblasts by PDGF, interleukin-1Β and TNF-α. Mediators Inflamm 9:155–160
Seger R, Krebs EG (1995) The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J 9:726–735
Seki E, De Minicis S, Österreicher CH, Kluwe J, Osawa Y, Brenner DA, Schwabe RF (2007) TLR4 enhances TGF-Β signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med 13:1324–1332
Tarrats N, Moles A, Morales A, García-Ruiz C, Fernández-Checa JC, Marí M (2011) Critical role of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1, but not 2, in hepatic stellate cell proliferation, extracellular matrix remodeling, and liver fibrogenesis. Hepatology 54:319–327
Thurman RG (1998) II. Alcoholic liver injury involves activation of Kupffer cells by endotoxin. Am J Physiol 275:G605–G611
Tran SE, Holmström TH, Ahonen M, Kähäri VM, Eriksson JE (2001) MAPK/ERK overrides the apoptotic signaling from Fas, TNF, and TRAIL receptors. J Biol Chem 276:16484–16490
Wells RG (2005) The role of matrix stiffness in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. J Clin Gastroenterol 39:S158–S161
Xu L, Hui AY, Albanis E, Arthur MJ, O’Byrne SM, Blaner WS, Mukherjee P, Friedman SL, Eng FJ (2005) Human hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: new tools for analysis of hepatic fibrosis. Gut 54:142–151
Xu J, Itoh Y, Hayashi H, Takii T, Miyazawa K, Onozaki K (2011) Dihydrotestosterone inhibits interleukin-1α or tumor necrosis factor α induced proinflammatory cytokine production via androgen receptor-dependent inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activation in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synovial cell line. Biol Pharm Bull 34:1724–1730
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, A., Obayashi, K., Sonoda, Y. et al. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and alpha-smooth muscle actin expression by interleukin-1 alpha and tumour necrosis factor alpha in hepatic stellate cells. Cytotechnology 69, 461–468 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-9948-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-016-9948-3