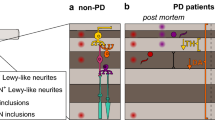
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is caused due to degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) which leads to the depletion of dopamine in the body. The lack of dopamine is mainly due to aggregation of misfolded α-synuclein which causes motor impairment in PD. Dopamine is also required for normal retinal function and the light–dark vision cycle. Misfolded α-synuclein present in inner retinal layers causes vision-associated problems in PD patients. Hence, individuals with PD also experience structural and functional changes in the retina. Mutation in LRRK2, PARK2, PARK7, PINK1, or SNCA genes and mitochondria dysfunction also play a role in the pathophysiology of PD. In this review, we discussed the different etiologies which lead to PD and future prospects of employing non-invasive techniques and retinal changes to diagnose the onset of PD earlier.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Alves JN, Westner BU, Højlund A, Weil RS, Dalal SS (2023) Structural and functional changes in the retina in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 94:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2022-329342
Archibald NK, Clarke MP, Mosimann UP, Burn DJ (2009) The retina in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 132:1128–1145. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp068
Balestrino R, Schapira AHV (2020) Parkinson disease. Eur J Neurol 27:27–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14108
Bantle CM, Hirst WD, Weihofen A, Shlevkov E (2021) Mitochondrial dysfunction in astrocytes: a role in Parkinson’s disease? Front Cell Dev Biol 8:608026. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.608026
Beach TG, Carew J, Serrano G, Adler CH, Shill HA, Sue LI, Sabbagh MN, Akiyama H, Cuenca N (2014) Phosphorylated α-synuclein-immunoreactive retinal neuronal elements in Parkinson’s disease subjects. Neurosci Lett 571:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2014.04.027
Bender A, Krishnan KJ, Morris CM, Taylor GA, Reeve AK, Perry RH, Jaros E, Hersheson JS, Betts J, Klopstock T, Taylor RW, Turnbull DM (2006) High levels of mitochondrial DNA deletions in substantia nigra neurons in aging and Parkinson disease. Nat Genet 38:515–517. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1769
Bidwell LC, McClernon FJ, Kollins SH (2011) Cognitive enhancers for the treatment of ADHD. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99:262–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2011.05.002
Bodis-Wollner I, Kozlowski PB, Glazman S, Miri S (2014) α-synuclein in the inner retina in parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 75:964–966. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24182
Bose A, Beal MF (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 139:216–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13731
Brozoski TJ, Brown RM, Rosvold HE, Goldman PS (1979) Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey. Science 205:929–932. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.112679
Camilleri A, Vassallo N (2014) The centrality of mitochondria in the pathogenesis and treatment of Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci Ther 20:591–602. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12264
Cerri S, Mus L, Blandini F (2019) Parkinson’s disease in women and men: what’s the difference? J Parkinsons Dis 9:501–515. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-191683
Chade AR, Kasten M, Tanner CM (2006) Nongenetic causes of Parkinson’s disease. In: Riederer P, Reichmann H, Youdim MBF, Gerlach M (eds) Parkinson’s disease and related disorders. Springer, Vienna, pp 147–151
Chan NC, Salazar AM, Pham AH, Sweredoski MJ, Kolawa NJ, Graham RLJ, Hess S, Chan DC (2011) Broad activation of the ubiquitin–proteasome system by Parkin is critical for mitophagy. Hum Mol Genet 20:1726–1737. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr048
Chang Z, **e F, Li H, Yuan F, Zeng L, Shi L, Zhu S, Lu X, Wei X, Wang Q (2022) Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and associations with cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 14:832768. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.832768
Chen PC, Chung CC, Cheng YY, Chen WT, Hong CT, Chan L, Chien LN (2021) Retinal diseases and Parkinson disease: a population-based study. Front Neurosci 15:679092. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.679092
Cordeiro MF (2007) DARC: a new method for detecting progressive neuronal death. Eye 21:S15–S17. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.eye.6702881
Cuenca N, Fernández-Sánchez L, Campello L, Maneu V, De la Villa P, Lax P, Pinilla I (2014) Cellular responses following retinal injuries and therapeutic approaches for neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res 43:17–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2014.07.001
Da Cunha C, Wietzikoski S, Wietzikoski EC, Miyoshi E, Ferro MM, Anselmo-Franci JA, Canteras NS (2003) Evidence for the substantia nigra pars compacta as an essential component of a memory system independent of the hippocampal memory system. Neurobiol Learn Mem 79:236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-7427(03)00008-X
Damier P, Hirsch EC, Agid Y, Graybiel AM (1999) The substantia nigra of the human brain: I. Nigrosomes and the nigral matrix, a compartmental organization based on calbindin D28K immunohistochemistry. Brain 122:1421–1436. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/122.8.1421
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:819–822. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1087753
Dexter DT, Jenner P (2013) Parkinson disease: from pathology to molecular disease mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med 62:132–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.018
Dorsey ER, Sherer T, Okun MS, Bloem BR (2018) The emerging evidence of the Parkinson pandemic. J Parkinsons Dis 8:S3–S8. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-181474
Emamzadeh FN, Surguchov A (2018) Parkinson’s disease: biomarkers, treatment, and risk factors. Front Neurosci 12:612. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00612
Flood MD, Eggers ED (2021) Dopamine D1 and D4 receptors contribute to light adaptation in ON-sustained retinal ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol 126:2039–2052. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00218.2021
Giugni JC, Okun MS (2014) Treatment of advanced Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol 27:450–460. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000118
Gonzalez-Iglesias AE, Murano T, Li S, Tomić M, Stojilkovic SS (2008) Dopamine inhibits basal prolactin release in pituitary lactotrophs through pertussis toxin-sensitive and -insensitive signaling pathways. Endocrinology 149:1470–1479. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2007-0980
Hajee ME, March WF, Lazzaro DR, Wolintz AH, Shrier EM, Glazman S, Bodis-Wollner IG (2009) Inner retinal layer thinning in Parkinson disease. Arch Ophthalmol 127:737–741. https://doi.org/10.1001/archophthalmol.2009.106
Harnois C, Di Paolo T (1990) Decreased dopamine in the retinas of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Investig Ophthalmol vis Sci 31:2473–2475
Huang M, Chen S (2021) DJ-1 in neurodegenerative diseases: pathogenesis and clinical application. Prog Neurobiol 204:102114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2021.102114
Ikemoto S (2010) Brain reward circuitry beyond the mesolimbic dopamine system: a neurobiological theory. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:129–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.02.001
Indrieri A, Pizzarelli R, Franco B, De Leonibus E (2020) Dopamine, alpha-synuclein, and mitochondrial dysfunctions in parkinsonian eyes. Front Neurosci 14:567129. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.567129
Jellinger KA (2010) Basic mechanisms of neurodegeneration: a critical update. J Cell Mol Med 14:457–487. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01010.x
Juárez Olguín H, Calderón Guzmán D, Hernández García E, Barragán Mejía G (2016) The role of dopamine and its dysfunction as a consequence of oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:9730467. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9730467
Kalinderi K, Bostantjopoulou S, Fidani L (2016) The genetic background of Parkinson’s disease: current progress and future prospects. Acta Neurol Scand 134:314–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12563
Karunanithi S, Brown IR (2015) Heat shock response and homeostatic plasticity. Front Cell Neurosci 9:68. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00068
Kirbas S, Turkyilmaz K, Tufekci A, Durmus M (2013) Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in Parkinson disease. J Neuro-Ophthalmol 33:62–65. https://journals.lww.com/jneuro-ophthalmology/Fulltext/2013/03000/Retinal_Nerve_Fiber_Layer_Thickness_in_Parkinson.16.aspx
Klein C, Westenberger A (2012) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a008888. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a008888
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, Murata S, Iwata J, Tanida I, Ueno T, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Kominami E, Tanaka K (2006) Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature 441:880–884. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04723
Krüger R, Kuhn W, Müller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, Kösel S, Przuntek H, Epplen JT, Schols L, Riess O (1998) AlaSOPro mutation in the gene encoding α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet 18:106–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0298-106
Lax NZ, Turnbull DM, Reeve AK (2011) Mitochondrial mutations: newly discovered players in neuronal degeneration. Neuroscientist 17:645–658. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858411385469
Li JQ, Tan L, Yu JT (2014) The role of the LRRK2 gene in parkinsonism. Mol Neurodegener 9:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1326-9-47
Liddle RA (2018) Parkinson’s disease from the gut. Brain Res 1693:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.01.010
Lotankar S, Prabhavalkar KS, Bhatt LK (2017) Biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease: recent advancement. Neurosci Bull 33:585–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-017-0183-5
Magistrelli L, Contaldi E, Comi C (2021) The impact of SNCA variations and its product alpha-synuclein on non-motor features of Parkinson’s disease. Life (basel) 11:804
Maiti P, Manna J, Dunbar GL (2017) Current understanding of the molecular mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease: targets for potential treatments. Transl Neurodegener 6:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-017-0099-z
Mariottoni EB, Jammal AA, Urata CN, Berchuck SI, Thompson AC, Estrela T, Medeiros FA (2020) Quantification of retinal nerve fibre layer thickness on optical coherence tomography with a deep learning segmentation-free approach. Sci Rep 10:402. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57196-y
McNaught KSP, Olanow CW, Halliwell B, Isacson O, Jenner P (2001) Failure of the ubiquitin–proteasome system in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:589–594. https://doi.org/10.1038/35086067
Mei J, Desrosiers C, Frasnelli J (2021) Machine learning for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: a review of literature. Front Aging Neurosci 13:633752. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.633752
Mishra A, Singh S, Shukla S (2018) Physiological and functional basis of dopamine receptors and their role in neurogenesis: possible implication for Parkinson’s disease. J Exp Neurosci 12:1179069518779829. https://doi.org/10.1177/1179069518779829
Mohana Devi S, Mahalaxmi I, Aswathy NP, Dhivya V, Balachandar V (2020) Does retina play a role in Parkinson’s disease? Acta Neurol Belg 120:257–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-020-01274-w
Moon HE, Paek SH (2015) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurobiol 24:103–116. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2015.24.2.103
Morais VA, Verstreken P, Roethig A, Smet J, Snellinx A, Vanbrabant M, Haddad D, Frezza C, Mandemakers W, Vogt-Weisenhorn D, Van Coster R, Wurst W, Scorrano L, De Strooper B (2009) Parkinson’s disease mutations in PINK1 result in decreased Complex I activity and deficient synaptic function. EMBO Mol Med 1:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.200900006
Narendra DP, Youle RJ (2011) Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction: role for PINK1 and Parkin in mitochondrial quality control. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:1929–1938. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3799
Neve KA, Seamans JK, Trantham-Davidson H (2004) Dopamine receptor signaling. J Recept Signal Transduct 24:165–205. https://doi.org/10.1081/RRS-200029981
Nicola SM, Surmeier DJ, Malenka RC (2000) Dopaminergic modulation of neuronal excitability in the striatum and nucleus accumbens. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:185–215. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.23.1.185
Nightingale S, Mitchell KW, Howe JW (1986) Visual evoked cortical potentials and pattern electroretinograms in Parkinson’s disease and control subjects. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49:1280–1287. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.49.11.1280
Normando EM, Davis BM, De Groef L, Nizari S, Turner LA, Ravindran N, Pahlitzsch M, Brenton J, Malaguarnera G, Guo L, Somavarapu S, Cordeiro MF (2016) The retina as an early biomarker of neurodegeneration in a rotenone-induced model of Parkinson’s disease: evidence for a neuroprotective effect of rosiglitazone in the eye and brain. Acta Neuropathol Commun 4:86. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-016-0346-z
Oczkowska A, Kozubski W, Lianeri M, Dorszewska J (2013) Mutations in PRKN and SNCA genes important for the progress of Parkinson’s disease. Curr Genom 14:502–517. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202914666131210205839
Poewe W, Seppi K, Tanner CM, Halliday GM, Brundin P, Volkmann J, Schrag AE, Lang AE (2017) Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17013. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.13
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E et al (1997) Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 76:2045–2047. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5321.2045
Popova E (2020) Role of dopamine in retinal function. In: Kolb H, Fernandez E, Nelson R (eds) Organ Retin Vis Syst. University of Utah, Salt Lake City
Pramanik M, Pradhan R, Nandy P, Qaisar SM, Bhoi AK (2021) Assessment of acoustic features and machine learning for Parkinson’s detection. J Healthc Eng 2021:9957132. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9957132
Prasuhn J, Davis RL, Kumar KR (2021) Targeting mitochondrial impairment in Parkinson’s disease: challenges and opportunities. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:615461. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.615461
Pukaß B, Richter-Landsberg C (2015) Inhibition of UCH-L1 in oligodendroglial cells results in microtubule stabilization and prevents α-synuclein aggregate formation by activating the autophagic pathway: implications for multiple system atrophy. Front Cell Neurosci 9:163. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00163
Quinn PMJ, Moreira PI, Ambrósio AF, Alves HC (2020) PINK1/PARKIN signalling in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathol Commun 8:189. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-020-01062-w
Ramalingam M, Huh YJ, Lee YI (2019) The impairments of α-synuclein and mechanistic target of rapamycin in rotenone-induced SH-SY5Y cells and mice model of Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurosci 13:1028. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01028
Ringel MJ, Tang EM, Tao YK (2021) Advances in multimodal imaging in ophthalmology. Ther Adv Ophthalmol 13:25158414211002400. https://doi.org/10.1177/25158414211002400
Robbins CB, Thompson AC, Bhullar PK, Koo HY, Agrawal R, Soundararajan S, Yoon SP, Polascik BW, Scott BL, Grewal DS, Fekrat S (2021) Characterization of retinal microvascular and choroidal structural changes in Parkinson disease. JAMA Ophthalmol 139:82–188. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2020.5730
Sajal MSR, Ehsan MT, Vaidyanathan R, Wang S, Aziz T, Al Mamun KA (2020) Telemonitoring Parkinson’s disease using machine learning by combining tremor and voice analysis. Brain Inform 7:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40708-020-00113-1
Sharma S, Moon CS, Khogali A, Haidous A, Chabenne A, Ojo C, Jelebinkov M, Kurdi Y, Ebadi M (2013) Biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease (recent update). Neurochem Int 63:201–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.06.005
Shinde S, Prasad S, Saboo Y, Kaushick R, Saini J, Pal PK, Ingalhalikar M (2019) Predictive markers for Parkinson’s disease using deep neural nets on neuromelanin sensitive MRI. NeuroImage Clin 22:101748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101748
Subramaniam MD, Kumar A, Chirayath RB, Nair AP, Iyer M, Vellingiri B (2021) Can deep learning revolutionize clinical understanding and diagnosis of optic neuropathy? Artif Intell Life Sci 1:100018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ailsci.2021.100018
Tabashum T, Zaffer A, Yousefzai R, Colletta K, Jost MB, Park Y, Chawla J, Gaynes B, Albert MV, **ao T (2021) Detection of Parkinson’s disease through automated pupil tracking of the post-illumination pupillary response. Front Med 8:645293. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.645293
Thakoor KA, Koorathota SC, Hood DC, Sajda P (2021) Robust and interpretable convolutional neural networks to detect glaucoma in optical coherence tomography images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 68:2456–2466. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2020.3043215
Tian T, Zhu XH, Liu YH (2011) Potential role of retina as a biomarker for progression of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Ophthalmol 4:433–438. https://doi.org/10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2011.04.21
Tritsch NX, Ding JB, Sabatini BL (2012) Dopaminergic neurons inhibit striatal output through non-canonical release of GABA. Nature 490:262–266. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11466
Tseng KY, Riquelme LA, Belforte JE, Pazo JH, Murer MG (2000) Substantia nigra pars reticulata units in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats: responses to striatal D2 dopamine receptor stimulation and subthalamic lesions. Eur J Neurosci 12:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00910.x
Ubuka T (2021) Subchapter 131A—dopamine. In: Ando H, Ukena K (eds) Handbook of hormones. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 1037–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820649-2.00289-8
Undieh AS (2010) Pharmacology of signaling induced by dopamine D(1)-like receptor activation. Pharmacol Ther 128:37–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.05.003
William LJ, Philip B, Tetrud JJ, Ian I (1983) Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219:979–980. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.6823561
Witkovsky P (2004) Dopamine and retinal function. Doc Ophthalmol 108:17–40. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:doop.0000019487.88486.0a
Wooten GF, Currie LJ, Bovbjerg VE, Lee JK, Patrie J (2004) Are men at greater risk for Parkinson’s disease than women? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:637–639. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2003.020982
Yu J, Feng Y, **ang Y, Huang J, Savini G, Parisi V, Yang W, Fu X (2014) Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness changes in Parkinson disease: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 9:e85718. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085718
Zecca L, Tampellini D, Gerlach M, Riederer P, Fariello RG, Sulzer D (2001) Substantia nigra neuromelanin: structure, synthesis, and molecular behaviour. Mol Pathol 54:414–418. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11724917.
Zhuang Y, Xu P, Mao C, Wang L, Krumm B, Zhou XE, Huang S et al (2021) Structural insights into the human D1 and D2 dopamine receptor signalling complexes. Cell 184:931-942.e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.027
Živković M, Dayanir V, Stamenović J, Ljubisavljević S, Pražić A, Zlatanović M, Zlatanović G, Jakšić V, Radenković M, Jovanović S (2017) Retinal ganglion cell/inner plexiform layer thickness in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Folia Neuropathol 55:168–173. https://doi.org/10.5114/fn.2017.68584
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) (ECR/2018/000718), India for providing the necessary funding to complete this research work successfully.
Funding
This study was funded by Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) (ECR/2018/000718).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SMD participated in the conceptualization and review and editing of the manuscript, AJ, AB, JG, and APN participated in the writing and editing of the manuscript; MI and BV participated in the review and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Subramaniam, M.D., Aishwarya Janaki, P., Abishek Kumar, B. et al. Retinal Changes in Parkinson’s Disease: A Non-invasive Biomarker for Early Diagnosis. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 3983–3996 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01419-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01419-4