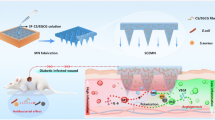
Abstract
In the current study, cupric oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) are chemically synthesized and blended with polyvinyl alcohol and chitosan (PVA-CS) solution to produce nanofibrous wound dressing material using an electrospinning technique. The fibrous morphology of CuO-blended nanofibers was studied by SEM, showing smooth beads and uniform nanofibers with an average diameter of around 86.4 nm. The nanofibers are further characterized using XRD to confirm the presence of CuO NPs. The incorporation of CuO NPs with polymer is evident from the peaks obtained from infrared spectrum. The addition of CuO NPs retained the hydrophilic nature of scaffold, as evident from the contact angle measurement. Further, the wound healing properties of scaffold are apparent from the studies such as antioxidant activity, MTT assay, wound scratch assay, and antibacterial studies. These results indicate the greater efficacy of CuO NPs incorporated in PVA/CS for wound healing applications.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is available upon reasonable request and express third-party consent.
References
Abd El-aziz AM, El-Maghraby A, Taha NA (2017) Comparison between polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofiber and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofiber/hydroxyapatite (HA) for removal of Zn2+ ions from wastewater. Arab J Chem 10:1052–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.09.025
Ahmad N (2023) In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization Methods for Evaluation of Modern Wound Dressings. Pharmaceutics 15:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010042
Alavarse AC, de Oliveira Silva FW, Colque JT, da Silva VM, Prieto T, Venancio EC, Bonvent JJ (2017) Tetracycline hydrochloride-loaded electrospun nanofibers mats based on PVA and chitosan for wound dressing. Mater Sci Eng C 77:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.199
Ambekar RS, Kandasubramanian B (2019) Advancements in nanofibers for wound dressing: A review. Eur Polym J 117:304–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.05.020
Bhardwaj N, Kundu SC (2010) Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol Adv 28:325–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.01.004
Cai N, Li C, Han C, Luo X, Shen L, Xue Y, Yu F (2016) Tailoring mechanical and antibacterial properties of chitosan/gelatin nanofiber membranes with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for potential wound dressing application. Appl Surf Sci 369:492–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.053
Chandrasekaran R, Yadav SA, Sivaperumal S (2020) Phytosynthesis and Characterization of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles using the Aqueous Extract of Beta vulgaris L and Evaluation of their Antibacterial and Anticancer Activities. J Clust Sci 31:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-016406
Chen Z, Meng H, **ng G, Chen C, Zhao Y, Jia G, Wang T, Yuan H, Ye C, Zhao F, Chai Z, Zhu C, Fang X, Ma B, Wan L (2006) Acute toxicological effects of copper nanoparticles in vivo. Toxicol Lett 163:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2005.10.003
Chethana DM, Thanuja TC, Mahesh HM, Kiruba MS, Jose AS, Barshilia HC, Manjanna J (2021) Synthesis, structural, magnetic and NO2 gas sensing property of CuO nanoparticles. Ceram Int 47:10381–10387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.06.129
Cui Z, Zheng Z, Lin L, Si J, Wang Q, Peng X, Chen W (2018) Electrospinning and crosslinking of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite nanofiber for transdermal drug delivery. Adv Polym Technol 37:1917–1928. https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21850
Das D, Nath BC, Phukon P, Dolui SK (2013) Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial behavior of CuO nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B 101:430–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.07.002
Dong R, Guo B (2021) Smart wound dressings for wound healing. Nano Today 41:101290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101290
Duru Kamaci U, Peksel A (2020) Fabrication of PVA-chitosan-based nanofibers for phytase immobilization to enhance enzymatic activity. Int J Biol Macromol 164:3315–3322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.226
Elkady M, Salama E, Amer WA, Ebeid EZ, Ayad MM, Shokry H (2020) Novel eco-friendly electrospun nanomagnetic zinc oxide hybridized PVA/alginate/chitosan nanofibers for enhanced phenol decontamination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:43077–43092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10247-8
Esmaeili A, Beni AA (2014) A novel fixed-bed reactor design incorporating an electrospun PVA/chitosan nanofiber membrane. J Hazard Mater 280:788–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.048
Filiz BC, Elalmis YB, Bektaş İS, Figen AK (2021) Fabrication of stable electrospun blended chitosan-poly (vinyl alcohol) nanofibers for designing naked-eye colorimetric glucose biosensor based on GOx/HRP. Int J Biol Macromol 192:999–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.048
Ghomi ER, Khalili S, Khorasani SN, Ramakrishna NRES (2019) Wound dressings: Current advances and future directions. J Appl Polym Sci 136:47738. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47738
Ghorbani HR, Alizadeh V, Mehr FP, Jafarpourgolroudbary H, Erfan K, Yeganeh SS (2018) Preparation of polyurethane/CuO coating film and the study of antifungal activity. Prog Org Coat 123:322–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2018.05.021
Gopal A, Kant V, Gopalakrishnan A, Tandan SK, Kumar D (2014) Chitosan-based copper nanocomposite accelerates healing in excision wound model in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 731:8–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.02.033
Gu BK, Park SJ, Kim MS, Kang CM, Kim JI, Kim CH (2013) Fabrication of sonicated chitosan nanofiber mat with enlarged porosity for use as hemostatic materials. Carbohydr Polym 97:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.04.060
Guo Y, Wang X, Shen Y, Dong K, Shen L, Alzalab AA (2022) Research progress, models and simulation of electrospinning technology: a review. J Mater Sci 57:58–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06575-w
Hadidi M, Bigham A, Saebnoori E, Hassanzadeh-Tabrizi SA, Rahmati S, Alizadeh ZM, Nasirian V, Rafienia M (2017) Electrophoretic deposited hydroxyapatite copper nanocomposite as an antibacterial coating for biomedical applications. Surf Coat Technol 321:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.04.055
Haider A, Kwak S, Gupta KC, Kang IK (2015) Antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility of PLGA/CuO hybrid nanofiber scaffolds prepared by electrospinning. J Manometer 16:107–107. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/832762
Hong Thien DV (2016) Electrospun chitosan/PVA nanofibers for drug delivery. Vietnam J Sci Technol 54:185. https://doi.org/10.15625/2525-2518/54/4b/12040
Jadhav S, Gaikwad S, Nimse M, Rajbhoj A (2011) Copper Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Antibacterial Activity. J Clusty Sci 22:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-011-0349-7
Jayakumar R, Chennazhi KP, Muzzarelli RAA, Tamura H, Nair SV, Selvamurugan N (2010) Chitosan conjugated DNA nanoparticles in gene therapy. Carbohydr Polym 79:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.07.032
Jayakumar R, Menon D, Manzoor K, Nair SV, Tamura H (2010) Biomedical applications of chitin and chitosan based nanomaterials - A short review. Carbohydr Polym 82:227–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.04.074
Jayakumar R, Prabaharan M, Nair SV, Tamura H (2010) Novel chitin and chitosan nanofibers in biomedical applications. Biotechnol Adv 28:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.11.001
Jayaramudu T, Varaprasad K, Pyarasani RD, Reddy KK, Kumar KD, Akbari-Fakhrabadi A, Mangalaraja RV, Amalraj J (2019) Chitosan capped copper oxide/copper nanoparticles encapsulated microbial resistant nanocomposite films. Int J Biol Macromol 128:499–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.145
Jeyaraj M, Sathishkumar G, Sivanandhan G, MubarakAli D, Rajesh M, Arun R, Kapildev G, Manickavasagam M, Thajuddin N, Premkumar K, Ganapathi A (2013) Biogenic silver nanoparticles for cancer treatment: An experimental report. Colloids Surf B 106:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.01.027
Kamble P, Sadarani B, Majumdar A, Bhullar S (2017) Nanofiber based drug delivery systems for skin: A promising therapeutic approach. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 41:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2017.07.003
Karthega M, Pranesh M, Poongothai C, Srinivasan N (2021) Poly caprolactone/titanium dioxide nanofiber coating on AM50 alloy for biomedical application. J Magnes Alloy 9:532–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2020.07.003
Kong M, Chen XG, **ng K, Park HJ (2010) Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review. Int J Food Microbiol 144:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.09.012
Lei J, Sun L, Li P, Zhu C, Lin Z, Mackey V, Coy DH, He Q (2019) The Wound Dressings and Their Applications in Wound Healing and Management. Health Sci J 13:1–8 http://www.imedpub.com/
Li L, Qian Y, Lin C, Li H, Jiang C, Lv Y, Liu W, Cai K, Germershaus O, Yang L (2015) The effect of silk gland sericin protein incorporation into electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers on in vitro and in vivo characteristics. J Mater Chem B 3:859–870. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tb00653d
Mayandi V, Wen Choong AC, Dhand C, Lim FP, Aung TT, Sriram H, Dwivedi N, Periayah MH, Sridhar S, Fazil MH, Goh ET (2020) Multifunctional Antimicrobial Nanofiber Dressings Containing ϵ-Polylysine for the Eradication of Bacterial Bioburden and Promotion of Wound Healing in Critically Colonized Wounds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:15989–16005. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b21683
Nandhini G, Nivedha B, Pranesh M, Karthega M (2019) Study of polycaprolactone/curcumin loaded electrospun nanofibers on AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater Today: Proc 33:2170–2173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.327
Nasir A, Razak SIA, Adrus N, Suan CL, Rahmat Z, Bohari SPM (2023) Fabrication and characterization of electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers derived from rice husk for potential wound healing application. Cellulose 30:3153–3164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05083-1
Neto CD, Giacometti JA, Job AE, Ferreira FC, Fonseca JL, Pereira MR (2005) Thermal analysis of chitosan-based networks. Carbohydr Polym 62:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.02.022
Otsuka I, N**ang CN, Borsali R (2017) Simple fabrication of cellulose nanofibers via electrospinning of dissolving pulp and tunicate. Cellulose 24:3281–3288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1360-4
Pervez MN, Stylios GK (2018) Investigating the synthesis and characterization of a novel “green” H2O2-assisted, water-soluble chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol nanofiber for environmental end uses. Manometer 8:395. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060395
Rajeeve AD, Yamuna R, Vinoba M, Bhagiyalakshmi M (2023) β-Cyclodextrin-Stabilized CuO/MXene Nanocomposite as an Electrode Material for High-Performance Supercapacitors. Langmuir 39:17688–17699. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c02140
Rehana D, Mahendiran D, Kumar RS, Rahiman AK (2017) Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using medicinally important plant extracts. Biomed Pharmacother 89:1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.101
Rodríguez K, Gatenholm P, Renneckar S (2012) Electrospinning cellulosic nanofibers for biomedical applications: Structure and in vitro biocompatibility. Cellulose 19:1583–1598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9734-0
Sagadevan S, Vennila S, Marlinda AR, Al-Douri Y, Rafie Johan M, Anita Lett J (2019) Synthesis and evaluation of the structural, optical, and antibacterial properties of copper oxide nanoparticles. Appl Phys a: Mater Sci Process 125:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2785-4
Sarwar MN, Ali HG, Ullah S, Yamashita K, Shahbaz A, Nisar U, Hashmi M, Kim IS (2022) Electrospun PVA/CuONPs/Bitter Gourd Nanofibers with Improved Cytocompatibility and Antibacterial Properties: Application as Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Polym 14:1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071361
Sheikh FA, Barakat NA, Kanjwal MA, Chaudhari AA, Jung IH, Lee JH, Kim HY (2009) Electrospun Antimicrobial Polyurethane Nanofibers Containing Silver Nanoparticles for Biotechnological Applications. Macromol Res 17:688–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218929
Su P, Wang C, Yang X, Chen X, Gao C, Feng XX, Chen JY, Ye J, Gou Z (2011) Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: The favorable effect of metal ions. Carbohydr Polym 84:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.11.031
Thakar MA, Jha SS, Phasinam K, Manne R, Qureshi Y, Babu VH (2021) X ray diffraction (XRD) analysis and evaluation of antioxidant activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized from leaf extract of Cissus vitiginea. Mater Today: Proc 51:319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.05.410
Tiwari M, Narayanan K, Thakar MB, Jagani HV, Venkata Rao J (2014) Biosynthesis and wound healing activity of copper nanoparticles. IET Nanobiotechnol 8:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2013.0052
Veetil VT, Rajeeve AD, Saran GP, Kumar KM, Bhagiyalakshmi M, Vinoba M, Yamuna R (2023) β-Cyclodextrin capped ZnS nanoparticles for CER-assisted colorimetric and spectrophotometric detection of Pb2+, Cu2+, and Hg2+ in an aqueous solution. Heliyon 9:e21850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21850
Wali A, Zhang Y, Sengupta P, Higaki Y, Takahara A, Badiger MV (2018) Electrospinning of non-ionic cellulose ethers/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers: Characterization and applications. Carbohydr Polym 181:175–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.070
Zarrintaj P, Saeb MR, Jafari SH, Mozafari M (2020) Application of compatibilized polymer blends in biomedical fields. In: Compatibilization of polymer blends, pp 511–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816006-0.00018-9
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the CoE-AMGT center (MHRD, New Delhi) for providing instrumental facilities. Thanks to BioMe Live Analytical Center for providing the antibacterial study, antioxidant study, MTT assay, and wound scratch assay.
Funding
This research was not supported by any public, private, or non – profit funding organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS and ADR contributed to the material preparation, Investigation, formal analysis, data analysis, wrote the original manuscript. SC contributed to the material preparation and data analysis. VTV contributed to the data collection. MB contributed to the formal analysis. RY and MK contributed to the design of experiments, visualization, supervision, conceptualization, validation, reviewing and editing. The final manuscript was revised and approved by all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
No humans or animals’ subjects used for this study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sandra, S., Anakha, D.R., Silpa, C. et al. Synthesis of electrospun PVA/chitosan nanofibrous scaffold impregnated with CuO nanoparticles for wound healing. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05960-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05960-3