Abstract
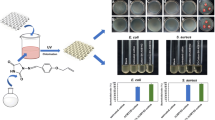
The incorporation of a single antimicrobial agent on textiles has been proven to be effective to enhance the antibacterial efficacy against single bacteria family. However, the daily usage of textile products face challenges from multiple microbes, i.e., bacterial, fungal, or/and viral, which threaten human’s safety and health. A “combination” of antimicrobial agents could be efficient and accessible to against several microbes at one time. In this study, a Schiff base-pyridinium quaternary ammonium salt-halamine precursor compound (E)-3-(((2,4-dioxoimidazolidin-1-yl)imino)methyl)pyridin-1-ium (4-DMPY) was synthesized and grafted onto MPTES-treated cotton fabric by thiol-ene click chemistry. The results of NRM, FTIR, Raman, EDX, XPS and SEM tests showed that 4-DMPY was synthesized and grafted onto cotton fabrics. The antibacterial test results showed that 4-DMPY had antibacterial activity against both Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. The antibacterial activity of 4-DMPY-finished cotton fabric was significantly enhanced after chlorination treatment, which could kill 98% of S. aureus and 98.9% of E. coli at a concentration of 5 g/L, confirming the enhanced synergistic effect between 4-DMPY and N-chloramine. The antimicrobial substance on the cotton fabric is non-soluble, which kills 98.4% E. coli and 98.3% S. aureus within 1 min by a direct contact. In addition, the produced fabric retained 81% and 63% of active chlorine content after 30 washes and 30 days of storage, indicating a good antimicrobial durability. Herein, we anticipate the technology can be used to enhance antibacterial function of cellulose products and thus resist the potential threats from microbes to ensure human’s health.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y, Wang Y, Wang Z, Wang Y, Han Y, Zhang Q, Han Q (2021) Engineering of super bactericidal cotton using pyridinium/di-N-chloramine siloxane with intensified synergism. Cellulose 28(10):6713–6725
Correia VG, Ferraria AM, Pinho MG, Aguiar-Ricardo A (2015) Antimicrobial contact-active oligo(2-oxazoline)s-grafted surfaces for fast water disinfection at the point-of-use. Biomacromolecules 16(12):3904–3915
Dai L, Lou JF, Baek NW, Zhang X, Yuan JG, Xu J, Fan XR (2022) A rapid way of preparing switchable bacteria-killing and bacteria-releasing cellulosic material with anti-bacteria adhesion capability. Cellulose 29(9):5305–5323
DeForest CA, Anseth KS (2011) Cytocompatible click-based hydrogels with dynamically tunable properties through orthogonal photoconjugation and photocleavage reactions. Nat Chem 3(12):925–931
Demir B, Cerkez I, Worley SD, Broughton RM, Huang TS (2015) N-Halamine-modified antimicrobial polypropylene nonwoven fabrics for use against airborne bacteria. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(3):1752–1757
Dong A, Wang YJ, Gao Y, Gao T, Gao G (2017) Chemical Insights into Antibacterial N-Halamines. Chem Rev 117(6):4806–4862
Fahs S, Rowther FB, Dennison SR, Patil-Sen Y, Warr T, Snape TJ (2014) Development of a novel, multifunctional, membrane-interactive pyridinium salt with potent anticancer activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24(15):3430–3433
Frolov N, Detusheva E, Fursova N, Ostashevskaya I, Vereshchagin A (2022) Microbiological evaluation of novel bis-quaternary ammonium compounds: clinical strains, biofilms, and resistance study. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 15(5):1–12
Fu XR, Shen Y, Jiang X, Huang D, Yan YQ (2011) Chitosan derivatives with dual-antibacterial functional groups for antimicrobial finishing of cotton fabrics. Carbohydr Polym 85(1):221–227
Gutman O, Natan M, Banin E, Margel S (2014) Characterization and antibacterial properties of N-halamine-derivatized cross-linked polymethacrylamide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 35(19):5079–5087
Hasan CM, Dutta D, Nguyen ANT (2022) Revisiting antibiotic resistance: mechanistic foundations to evolutionary outlook. Antibiotics-Basel 11(1):1–23
Jiang QY, Jiang ZM, Ma KK, Li R, Du JM, **e ZW, Ren XH, Huang TS (2014) Development of cytocompatible antibacterial electro-spun nanofibrous composites. J Mater Sci 49(19):6734–6741
Kaur R, Liu S (2016) Antibacterial surface design-Contact kill. Prog Surf Sci 91(3):136–153
Kocer HB, Akdag A, Worley SD, Acevedo O, Broughton RM, Wu YN (2010) Mechanism of photolytic decomposition of N-Halamine antimicrobial siloxane coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2(8):2456–2464
Kocer HB, Cerkez I, Worley SD, Broughton RM, Huang TS (2011) Polymeric antimicrobial N-halamine epoxides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(8):2845–2850
Li CH, Hou JJ, Huang Z, Zhao TY, **ao LH, Gao G, Harnoode C, Dong A (2015) Assessment of 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinol-based amine N-halamine-labeled silica nanoparticles as potent antibiotics for deactivating bacteria. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces 126:106–114
Liu Y, Liu Y, Ren X, Huang TS (2014) Antimicrobial cotton containing N-halamine and quaternary ammonium groups by grafting copolymerization. Appl Surf Sci 296:231–236
Liu Y, Li J, Li L, McFarland S, Ren X, Acevedo O, Huang TS (2016) Characterization and mechanism for the protection of photolytic decomposition of N-alamine siloxane coatings by titanium dioxide. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(5):3516–3523
Luo J, Chen ZB, Sun YY (2006) Controlling biofilm formation with an N-halamine-based polymeric additive. J Biomed Mater Res Part A 77a(4):823–831
Ma KK, **e ZW, Jiang QY, Li J, Li R, Ren XH, Huang TS, Zhang KQ (2014) Cytocompatible and regenerable antimicrobial cellulose modified by N-halamine triazine ring. J Appl Polym Sci 131(16):40627
Mi Y, Chen Y, Tan W, Zhang J, Li Q, Guo Z (2022) The influence of bioactive glyoxylate bearing Schiff base on antifungal and antioxidant activities to chitosan quaternary ammonium salts. Carbohydr Polym 278:118970
Morais DS, Guedes RM, Lopes MA (2016) Antimicrobial approaches for textiles: from research to market. Materials 9(6):498
Pernak J, Kalewska J, Ksycinska H, Cybulski J (2001) Synthesis and anti-microbial activities of some pyridinium salts with alkoxymethyl hydrophobic group. Eur J Med Chem 36(11–12):899–907
Ren X, Akdag A, Kocer HB, Worley SD, Broughton RM, Huang TS (2009) N-Halamine-coated cotton for antimicrobial and detoxification applications. Carbohydr Polym 78(2):220–226
Rong L, Liu H, Wang B, Mao Z, Xu H, Zhang L, Zhong Y, Feng X, Sui X (2019) Durable antibacterial and hydrophobic cotton fabrics utilizing enamine bonds. Carbohydr Polym 211:173–180
Sohrabi C, Alsafi Z, O’Neill N, Khan M, Kerwan A, Al-Jabir A, Iosifidis C, Agha R (2020) World health organization declares global emergency: a review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int J Surg 76:71–76
Tan K, Obendorf SK (2007) Fabrication and evaluation of electrospun nanofibrous antimicrobial nylon 6 membranes. J Membr Sci 305(1–2):287–298
Wang P, Zhang MY, Qu JH, Wang LJ, Geng JZ, Fu FY, Liu XD (2022) Antibacterial cotton fabric prepared by a grafting to strategy using a QAC copolymer. Cellulose 29(6):3569–3581
Wen W, Zhang Z, **g L, Zhang T (2020) Synthesis of a Hein–Schiff base compound and its antibacterial activity on cotton fabrics. Cellulose 27(12):7243–7254
Wen W, Zhang ZX, **g LX, Zhang TH (2021) Highly antibacterial efficacy of a cotton fabric treated with Piperazinyl Schiff Base. Fibers Polym 22(12):3298–3308
** WX, Scott TF, Kloxin CJ, Bowman CN (2014) Click chemistry in materials science. Adv Funct Mater 24(18):2572–2590
Xue Y, **ao H (2015) Antibacterial/Antiviral property and mechanism of dual-functional quaternized pyridinium-type copolymer. Polymers 7(11):2290–2303
Zeng MH, Xu JY, Luo Q, Hou CX, Qiao SP, Fu S, Fan XT, Liu JQ (2020) Constructing antibacterial polymer nanocapsules based on pyridine quaternary ammonium salt. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl 108:110383
Zhang B, Jiao Y, Kang Z, Ma K, Ren X, Liang J (2013) Durable antimicrobial cotton fabrics containing stable quaternarized N-halamine groups. Cellulose 20(6):3067–3077
Acknowledgments
Prof. Zaixing Zhang and Lingxiao **g contributed equally to this work as co-corresponding authors.
Funding
This work was supported by the Jiangsu Province Social development Projects (Key R & D Projects), (BE2022777). This research was also supported by Autonomous Region Science and Technology Support **njiang Project Plan (2022E02018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XT: Conceptualization, Writing—Original Draft; ZZ: Conceptualization, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision; LJ: Conceptualization, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision; KL: Writing—Review; SZ: Investigation; TZ: Conceptualization, Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. In this experiment, we did not collect any samples of humans and animals.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Zhang, Z., **g, L. et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of Schiff base-pyridine quaternary ammonium salt-halamine compounds on cotton fabrics. Cellulose 30, 10519–10531 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05510-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05510-3