Abstract
The application of nisin is growing due to the demand of consumers for safe and healthy food. New delivery systems of nisin are being developed and based on its encapsulation. Biopolymers having high stability and low toxicity are largely used for that purpose. The study is aimed to fabricate nisin-loaded nanoparticles with different surface charges, i.e. positive and negative. First, nisin-loaded pectin nanoparticles were prepared by the complexation method, and subsequently, they were coated with chitooligosaccharides in the concentration range of 0.025–0.5 mg/mL. The interaction of components was demonstrated by FT-IR spectroscopy. For further analysis, nisin-loaded pectin nanoparticles coated with chitooligosaccharides at a concentration of 0.025 and 0.3 mg/mL were chosen. They were soluble complexes with negative and positive surface charge, respectively. Nanoparticles were characterized in terms of size, dispersity, zeta-potential, radical scavenging activity, and proteolytic stability. The nanoparticles demonstrated long-term stability at 4 °C. Encapsulation increased the proteolytic stability of nisin. High methoxyl, low methoxyl pectin, and pectic acid were used for nanoparticle preparation. Only high methoxyl pectin and low methoxyl pectin, but not pectic acid, allow the fabrication of nanoparticles having positive and negative surface charge and the same amount of encapsulated nisin. Those nanoparticles could be useful for the investigation of the effect of their surface charge on the interaction with microorganisms and the release of antimicrobial peptides.
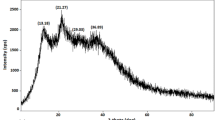
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials will be made available on request.
References
Asker D, Weiss J, McClements DJ (2011) Formation and stabilization of antimicrobial delivery systems based on electrostatic complexes of cationic-non-ionic mixed micelles and anionic polysaccharides. J Agric Food Chem 59:1041–1049
Bahrami A, Delshadi R, Jarafi SM, Williams L (2019) Nanoencapsulated nisin: an engineered natural antimicrobial system for the food industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 94:20–31
Balciunas EM, Martinez FAC, Todorov SD, de Melo Franco BDG, Converti A, de Souza Oliveira RP (2013) Novel biotechnological applications of bacteriocins: a review. Food Control 32:134–142
Bhattacharjee S (2016) DLS and zeta potential: What they are and what tHEY ARE NOT? J Control Release 235(2016):337–351
Bockuviene A, Sereikaite J (2019) Preparation and characterization of novel water-soluble β-carotene-chitooligosaccharides complexes. Carbohydr Polym 225:115226
Dawidowicz AL, Wianowska D, Olszowy M (2012) On practical problems in estimation of antioxidant activity of compounds by DPPH· method (problems in estimation of antioxidant activity). Food Chem 131:1037–1043
Eghbal N, Viton Ch, Gharsallaoui A (2022) Nano and microencapsulation of bacteriocins for food applications: a review. Food Biosci 50(Part B):102173
El-Jastimi R, Lafleur M (1997) Structural characterization of free and membrane-bound nisin by infrared spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1324:151–158
Gharsallaoui A, Oulahal N, Joly C, Degraeve P (2016) Nisin as a food preservative: part 1: physicochemical properties, antimicrobial activity, and main uses. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 56:1262–1274
Gruskiene R, Krivorotova T, Sereikaite J (2017) Nisin-loaded pectin and nisin-loaded pectin-inulin particles: comparison of their proteolytic stability with free nisin. LWT – Food Sci Technol Lettrs 82:283–286
Hu Y, Wu T, Wu C, Fu S, Yuan C, Chen S (2017) Formation and optimization of chitosan-nisin microcapsules and its characterization for antibacterial activity. Food Control 72:43–52
Huang P-H, Lu H-T, Wang Y-T, Wu M-C (2011) Antioxidant activity and emulsion-stabilizing effect of pectic enzyme treated pectin in soy protein isolate-stabilized oil/water emulsion. J Agric Food Chem 59:9623–9628
Jiang S, Ma Y, Wang Y, Wang R, Zeng M (2022) Effect of κ-carrageenan on the gelation of oyster protein. Food Chem 382:132329
Kacurakova M, Capek P, Sasinkova V, Wellner N, Ebringerova A (2000) FT-IR study of plant cell wall model compounds: pectic polysaccharides and hemicelluloses. Carbohydr Polym 43:195–203
Khan I, Tango CN, Miskeen S, Oh D-H (2018) Evaluation of nisin-loaded chitosan-monomethyl fumaric acid nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 184:100–107
Koziol A, Sroda-Pomianek K, Gorniak A, Wikiera A, Cyprych K (2022) Structural determination of pectins by spectroscopy methods. Coatings 12:546
Krivorotova T, Cirkovas A, Maciulyte S, Staneviciene R, Budriene S, Serviene E, Sereikaite J (2016) Nisin-loaded nanoparticles for food preservation. Food Hydrocoll 54:49–56
Krivorotova T, Staneviciene R, Luksa J, Serviene E, Sereikaite J (2017) Impact of pectin esterification on the antimicrobial activity of nisin-loaded pectin particles. Biotechnol Prog 33:245–251
Laokuldilok T, Potivas T, Kanha N, Surawang S, Seesuriyachan P, Wangtueai S, Phimolsiripol Y, Regenstein JM (2017) Physicochemical, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties of chitooligosaccharides produced using three different enzyme treatments. Food Biosci 18:28–33
Lee EH, Khan I, Oh DH (2018) Evaluation of the efficacy of nisin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles against foodborne pathogens in orange juice. J Food Sci Technol 55:1127–1133
Liaqat F, Eltem R (2018) Chitooligosaccharides and their biological activities: a comprehensive review. Carbohydr Polym 184:243–259
Liu N, Yang W, Li X, Zhao P, Liu Y, Guo L, Huang L, Gao W (2022) Comparison of characterization and antioxidant activity of different citrus peel pectins. Food Chem 386:132683
Maquelin K, Kirschner C, Choo-Smith LP, van den Braak N, Endtz HP, Naumann D, Puppels GJ (2002) Identification of medically relevant microorganisms by vibrational spectroscopy. J Microbiol Methods 51:255–271
Nilsen-Nygaard J, Strand SP, Varum KM, Draget KI, Nordgard CT (2015) Chitosan: gels and interfacial properties. Polymers 7:552–579
Novickij V, Staneviciene R, Grainys A, Luksa J, Badokas K, Krivorotova T, Sereikaite J, Novickij J, Serviene E (2016) Electroporation-assisted inactivation of Escherichia coli using nisin-loaded pectin nanoparticles. Innov Food Sci Technol 38:98–104
O’Connor PM, Kuniyoshi TM, Oliveira RPS, Hill C, Ross RP, Cotter PD (2020) Antimicrobials for food and feed; a bacteriocin perspective. Curr Opin Biotechnol 61:160–167
Pajerski W, Ochonska D, Brzychczy-Wloch M, Indyka P, Jarosz M, Golda-Cepa M, Sojka Z, Kotarba A (2019) Attachment efficiency of gold nanoparticles by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains governed by surface charge. J Nanopart Res 21:186
Rehman A, Ahmad T, Aadil RM, Spotti MJ, Bakry AM, Khan IM, Zhao L, Riaz T, Tong Q (2019) Pectin polymers as wall materials for the nano-encapsulation of bioactive compounds. Trends Food Sci Technol 90:35–46
Ricci A, Parpinello GP, Teslic N, Kilmartin PA, Versari A (2019) Suitability of the cyclic voltammetry measurements and DPPH· spectrophotometric assay to determine the antioxidant capacity of food-grade oenological tannins. Molecules 24:2925
Siddiqui AA, Feroz A, Khaki PSS, Bano B (2017) Binding of λ-carrageenan (a food additive) to almond cystatin: an insight involving spectroscopic and thermodynamic approach. Int J Biol Macromol 98:684–690
Staroszczyk H, Sztuka K, Wolska J, Wojtasz-Pajak A, Kolodziejska I (2014) Interactions of fish gelatin and chitosan in uncrosslinked and crosslinked with EDC films: FT-IR study. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 117:707–712
Synytsya A, Copikova J, Matejka P, Machovic V (2003) Fourier transform Raman and infrared spectroscopy of pectins. Carbohydr Polym 54:97–106
Tanaka N, Takeuchi M, Ichishima E (1977) Purification of an acid proteinase from aspergillus saitoi and determination of peptide bond specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta 485:406–416
Tello-sois SR (2001) Effect of the pH in the conformation and activity of the acid protease from Aspergillus saitoi. Protein Pept Lett 8:101–108
Tomida H, Fujii T, Furutani N, Michihara A, Yasufuku T, Akasaki K, Maruyama T, Otagiri M, Gebicki JM, Anraku M (2009) Antioxidant properties of some different molecular weight chitosans. Carbohydr Res 344:1690–1696
Wang X, Chen Q, Lu X (2014) Pectin extracted from apple pomace and citrus peel by subcritical water. Food Hydrocoll 38:129–137
Wilson WW, Wade MM, Holman SC, Champlin FR (2001) Status of methods for assessing bacterial cell surface charge properties based on zeta potential measurements. J Microbiol Methods 43:153–164
**ao D, Gommel C, Davidson PM, Zhong Q (2011) Intrinsic tween 20 improves release and antilisterial properties of co-encapsulated nisin and thymol. J Agric Food Chem 59:9572–9580
**ao F, Xu T, Lu B, Liu R (2020) Guidelines for antioxidant assays for food components. Food Front 1:60–69
**e W, Xu P, Liu Q (2001) Antioxidant activity of water-soluble chitosan derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11:1699–1701
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Tatjana Kavleiskaja for a fruitful discussion on the manuscript.
Funding
The study did not receive external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JP and AB performed the experiments. RG wrote the draft of the manuscript. JS edited the manuscripts and supervised the research. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have approved the manuscript and agreed with the publication in Cellulose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pachaleva, J., Gruskiene, R., Bockuviene, A. et al. The application of pectin and chitooligosaccharides for the preparation of nisin-loaded nanoparticles with different surface charges. Cellulose 30, 8985–8996 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05380-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05380-9



