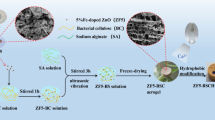
Abstract
Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants is an effective, energy-saving and renewable technique. In this study, functional oil/water (O/W) Pickering emulsions with excellent photocatalytic activity were prepared by the adsorption of nano-titanium oxide (TiO2) into bacterial cellulose (BC). The results indicate that the novel hybrid structure enhanced the interfacial diffusion rate of BC-TiO2 and further improved the mechanical strength of the obtained interfacial layer. Stable medium internal phase emulsions (MIPEs) and high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) were also obtained by using low-loading hybrid particles. The investigation of morphology and rheological properties indicated that the shear-thinning and solid-like behaviors of the obtained emulsion systems. The photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B was much faster in the emulsion system than p-TiO2 suspension, which was stabilized by BC-TiO2 (45 min, 90%) with respect to the case of TiO2 (90 min, 90%) and an aqueous system containing TiO2 (120 min, 53%). Therefore, this paper gives new insights to the application of BC as an efficient scaffold for loading TiO2 coupling at the oil–water interface, thus paving the way for the development of sustainable catalyst.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashby NP, Binks BP (2000) Pickering emulsions stabilised by Laponite clay particles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 24:5640–5646. https://doi.org/10.1039/B007098J
Bai L, Greca LG, **ang W, Lehtonen J, Huan S, Nugroho RWN et al (2019) Adsorption and assembly of cellulosic and lignin colloids at oil/water interfaces. Langmuir 35:571–588. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01288
Chen H, McClements DJ, Chen E, Liu S, Li B, Li Y (2017a) In situ interfacial conjugation of chitosan with cinnamaldehyde during homogenization improves the formation and stability of chitosan-stabilized emulsion. Langmuir 33:14608–14617. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b03852
Chen K, Yu G, He F, Zhou Q, **ao D, Li J, Feng Y (2017b) A pH-responsive emulsion stabilized by alginate-grafted anisotropic silica and its application in the controlled release of lambdacyhalothrin. Carbohydr Polym 176:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017b.07.046
Chen L, **ong Z, **ong H, Wang Z, Din ZU, Nawaz A, Wang P, Hu C (2018) Effects of nano-TiO2 on bonding performance, structure stability and film-forming properties of starch-g-VAc based wood adhesive. Carbohydr Polym 200:477–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.023
Chen T, Colver PJ, Bon SAF (2007) Organic–inorganic hybrid hollow spheres prepared from TiO2-stabilized Pickering emulsion polymerization. Adv Mater 19:2286–2289. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200602447
Chen X, Mao SS (2007) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev 107:2891–2959. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr0500535
Dickinson E (2010) Food emulsions and foams: stabilization by particles. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 15:40–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2009.11.001
Dickinson E (2012) Use of nanoparticles and microparticles in the formation and stabilization of food emulsions. Trends Food Sci Technol 24:4–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2011.09.006
Dickinson E (2015) Microgels: an alternative colloidal ingredient for stabilization of food emulsions. Trends Food Sci Technol 43:178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2015.02.006
Feng M, Gu C, Bao C, Chen X, Yan H, Shi Z, Liu XH, Lin Q (2018) Synthesis of a benzyl-grafted alginate derivative and its effect on the colloidal stability of nanosized titanium dioxide aqueous suspensions for Pickering emulsions. RSC Adv 8:34397–34407. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA04300K
Fessi N, Nsib MF, Chevalier Y, Guillard C, Dappozze F, Houas A, Palmisano L, Parrino F (2019) Photocatalytic degradation enhancement in Pickering emulsions stabilized by solid particles of bare TiO2. Langmuir 35: 2129–2136 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b03806
Li Q, Chen P, Li Y, Li B, Liu S (2020) Construction of cellulose-based Pickering stabilizer as a novel interfacial antioxidant: a bioinspired oxygen protection strategy. Carbohydr Polym 229:115395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115395
Li Q, Wang Y, Wu Y, He K, Li Y, Luo X, Li B, Wang C, Liu S (2019a) Flexible cellulose nanofibrils as novel pickering stabilizers: The emulsifying property and packing behavior. Food Hydrocolloids 88:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.09.039
Li Q, **e B, Wang Y, Wang Y, Peng L, Li Y, Li B, Liu S (2019b) Cellulose nanofibrils from Miscanthus floridulus straw as green particle emulsifier for O/W Pickering emulsion. Food Hydrocolloids 97:105214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105214
Li Q, Zhao T, Li M, Li W, Yang B, Qin D, Lv K, Wang X, Wu L, Wu X, Sun J (2019c) One-step construction of Pickering emulsion via commercial TiO2 nanoparticles for photocatalytic dye degradation. Appl Catal B 249:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019c.02.057
Li X, Sun G, Li Y, Yu JC, Wu J, Ma GH, Ngai T (2014) Porous TiO2 materials through Pickering high-internal phase emulsion templating. Langmuir 30:2676–2683. https://doi.org/10.1021/la404930h
Lin C, Song Y, Cao L, Chen S (2013) Effective photocatalysis of functional nanocomposites based on carbon and TiO2 nanoparticles. Nanoscale 5:4986–4992. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr01033c
Lu S, Yang D, Li Y, Li Z, Qiu X (2019) Double pH-responsive pickering emulsions stabilized by quaternized lignin combination with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Acta Polym Sin 50:160–169
Marto J, Gouveia LF, Goncalves L, Chiari-Andreo BG, Isaac V, Pinto P, Oliveira E, Almeida AJ, Ribeiro HM (2016) Design of novel starch-based Pickering emulsions as platforms for skin photoprotection. J Photochem Photobiol, B 162:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.06.026
Mccullagh C, Skillen N, Adams M, Robertson PKJ (2011) Photocatalytic reactors for environmental remediation: a review. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 86:1002–1017. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2650
Nikiforidis CV, Biliaderis CG, Kiosseoglou V (2012) Rheological characteristics and physicochemical stability of dressing-type emulsions made of oil bodies–egg yolk blends. Food Chem 134:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.058
Nsib MF, Maayoufi A, Moussa N, Tarhouni N, Massouri A, Houas A, Chevalier Y (2013) TiO2 modified by salicylic acid as a photocatalyst for the degradation of monochlorobenzene via Pickering emulsion way. J Photochem Photobiol, A 251:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.10.007
Nsib MF, Maayoufi A, Moussa N, Tarhouni N, Massouri A, Houas A, Chevalier Y (2013) TiO2 modified by salicylic acid as a photocatalyst for the degradation of monochlorobenzene via Pickering emulsion way. J Photochem Photobiol A 251:10-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.10.007
Pang K, Ding B, Liu X, Wu H, Duan Y, Zhang J (2017) High-yield preparation of a zwitterionically charged chitin nanofiber and its application in a doubly pH-responsive Pickering emulsion. Green Chem 19:3665–3670. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7GC01592E
Peddireddy KR, NicolaiT BL, Capron I (2016) Stabilization of Water-in-Water Emulsions by Nanorods. ACS Macro Lett 5:283–286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmacrolett.5b00953
Qiu XZ, Tao Y, Xu XQ, He XH, Fu XY (2018) Synthesis and characterization of paraffin/TiO2-P(MMA-co-BA) phase change material microcapsules for thermal energy storage. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46447. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46447
Shandilya N, Capron I (2017) Safer-by-design hybrid nanostructures: an alternative to conventional titanium dioxide UV filters in skin care products. RSC Adv 7:20430–20439. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA02506H
Tavernier I, Wijaya W, Van der Meeren P, Dewettinck K, Patel AR (2016) Food-grade particles for emulsion stabilization. Trends Food Sci Technol 50:159–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2016.01.023
Tenorio AT, Gieteling J, Nikiforidis CV, Boom RM, Aj VDG (2017) Interfacial properties of green leaf cellulosic particles. Food Hydrocolloids 71:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.04.030
Wang J, Yu M, Yang C (2019) Colloidal TiO2 nanoparticles with near-neutral wettability: An efficient Pickering emulsifier. Colloids Surf A 570:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.03.035
Ward AFH, Tordai L (1946) Time-dependence of boundary tensions of solutions I. the role of diffusion in time-effects. J Chem Phys 14:453–461. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1724167
Wu J, Ma GH (2016) Recent studies of pickering emulsions: particles make the difference. Small 12:4633–4648. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201600877
Wu W, Gao S, Tu W, Chen J, Zhang P (2010) Intensified photocatalytic degradation of nitrobenzene by Pickering emulsion of ZnO nanoparticles. Particuology 8:453–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2010.05.006
**ao J, Li Y, Huang Q (2016) Recent advances on food-grade particles stabilized Pickering emulsions: fabrication, characterization and research trends. Trends Food Sci Technol 55:48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2016.05.010
Xu M, Jiang J, Pei X, Song B, Cui Z, Binks BP (2018) Novel oil-in-water emulsions stabilised by ionic surfactant and similarly charged nanoparticles at very low concentrations. Angew Chem 130:7864–7868. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201802266
Yang Y, Fang Z, Chen X, Zhang W, **e Y, Chen Y et al (2017) An overview of Pickering emulsions: solid-particle materials, classification, morphology, and applications. Front Pharmacol 8:287. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00287
Zhang RY, Elzatahryb AA, Al-Deyabb SS, Zhao DY (2012) Mesoporous titania: from synthesis to application. Nano Today 7:344–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2012.06.012
Zhang S, Xu J, Hu J, Cui C, Liu H (2017) Interfacial growth of TiO2-rGO composite by pickering emulsion for photocatalytic degradation. Langmuir 33:5015–5024. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b00719
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972038), the Applied Basic Frontiers Program of Wuhan City (2019020701011474) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-2013-OCRI).
Funding
Funding was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972038), the Applied Basic Frontiers Program of Wuhan City (2019020701011474) and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-2013-OCRI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QL Conducted experiments and analytical characterization methodology, Investigation, Writing-original draft. YZ Follow-up experiments; Data curation; Formal analysis; Writing-review & editing. SL Visualization. ZL Visualization, Writing-review & editing. FH Project administration. MZ Conceptualization, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Zhang, Y., Liu, Z. et al. Novel bacterial cellulose-TiO2 stabilized Pickering emulsion for photocatalytic degradation. Cellulose 29, 5223–5234 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04604-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04604-8