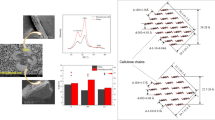
Abstract
The mechanical and physical properties of lignocellulosic materials are closely related to the orientation and interaction of the polymers within cell walls. In this work, Imaging Polarized FTIR, combined with directional chemical removal, was applied to characterize the spatial orientation and interaction of cell wall polymers in bamboo fibers and parenchyma cells from two bamboo species. The results demonstrate the cellulose in bamboo fibers is nearly axially oriented whereas it is almost transversely arranged in parenchyma cells. Xylan and lignin are both preferentially oriented alongside cellulose, but with less orientation degree in the parenchyma cells. After lignin removal, the average orientation of xylan and cellulose is little affected, suggesting a strong interaction between cellulose and xylan. However, the alkaline treatment significantly weakens the orientation of lignin in both fibers and parenchyma cells, and more significant for the latter, indicating the easy-degradable nature of lignin in parenchyma cells. Additionally, it seemed the lignin and xylan in fibers were more difficult to remove as compared to parenchyma cells, supporting the assumption that stronger interaction exists between lignin and xylan in the fibers. In a word, it is believed parenchyma cells are more suitable for biorefinery owing to their less ordered and relatively loose molecular assembly, as compared to fibers.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Yano H (2010) Comparison of the characteristics of cellulose microfibril aggregates isolated from fiber and parenchyma cells of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens). Cellulose 17(2):271–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9382-1
Ahvenainen P, Dixon PG, Kallonen A, Suhonen H, Gibson LJ, Svedstr MK (2017) Spatially-localized bench-top X-ray scattering reveals tissue-specific microfibril orientation in moso bamboo. Plant Methods 13(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-016-0155-1
Akerholm M, Salmén L (2001) Interactions between wood polymers studied by dynamic FT-IR spectroscopy. Polymer 42:963–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00434-1
Akerholm M, Salmén L (2003) The oriented structure of lignin and its viscoelastic properties studied by static and dynamic FT-IR spectroscopy. Holzforschung 57:459–465. https://doi.org/10.1515/HF.2003.069
Atalla RH, Agarwal UP (1985) Raman microprobe evidence for lignin orientation in the cell walls of native woody tissue. Science 227:636–638. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.227.4687.636
Chang SS, Salmén L, Olsson AM, Clair B (2014) Deposition and organisation of cell wall polymers during maturation of poplar tension wood by ftir microspectroscopy. Planta 239(1):243–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1980-3
Dick M, Zhang Y, Hayes J, Salazar A, Zabotina OA, Hong M (2011) Structure and interactions of plant cell-wall polysaccharides by two- and three-dimensional magic-angle-spinning solid-state NMR. Biochemistry 50(6):989–1000. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi101795q
Fackler K, Thygesen LG (2013) Microspectroscopy as applied to the study of wood molecular structure. Wood Sci Technol 47(1):203–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-012-0516-5
Faix O (1991) Classification of lignins from different botanical origins by FTIR spectroscopy. Holzforschung 45:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1515/hfsg.1991.45.s1.21
Fengel D, Wegener, G (1984) Chemical composition and analysis of wood. Wood
Grabber JH, Hatfield RD, Ralph J, Amrhein N (1995) Ferulate cross-linking in cell walls isolated from maize cell suspensions. Phytochemistry 40:1077–1082. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(95)00413-2
Hinterstoisser B, Åkerholm M, Salmén L (2001) Effect of fiber orientation in dynamic FTIR study on native cellulose. Carbohydr Res 334:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6215(01)00167-7
Ji G, Han L, Gao C, **ao W, Zhang Y, Cao Y (2017) Quantitative approaches for illustrating correlations among the mechanical fragmentation scales, crystallinity ad enzymatic hydrolysis glucose yield of rice straw. Bioresour Technol 241:262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.062
** K, Kong L, Liu X, Jiang Z, Tian G, Yang S (2019) Understanding the xylan content for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of individual bamboo fiber and parenchyma cells. Acs Sustain Chem Eng 7(22):18603–18611. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b04934
Jung HG, Mertens DR, Phillips RL (2011) Effect of reduced ferulate mediated lignin/arabinoxylan cross-linking in corn silage on feed intake, digestibility, and milk production1. J Dairy Sci 94:5124–5137. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2011-4495
Kang X, Kirui A, Widanage MD, Mentink F, Cosgrove DJ, Wang T (2019) Lignin-polysaccharide interactions in plant secondary cell walls revealed by solid-state nmr. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-08252-0
Knox JP (2008) Revealing the structural and functional diversity of plant cell walls. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:308–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2008.03.001
Liang CY, Basset KH, McGinnes EA, Marchessault RH (1960) Infrared spectra of crystalline polysaccharides; VII. Thin Wood Sect Tappi 43:232–235
Liese W (1980) The anatomy of bamboo culms. Inbar Technical Report
Loque D, Scheller HV, Pauly M (2015) Engineering of plant cell walls for enhanced biofuel production. Curr Opin Plant Biol 25:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2015.05.018
Malanit P, Barbu MC, Frühwald A (2011) Physical and mechanical properties of oriented strand lumber made from an Asian bamboo (Dendrocalamus asper Backer). Eur J Wood Wood Prod 69:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-009-0394-1
Marchessault RH (1962) Application of infra-red spectroscopy to cellulose and wood polysaccharides. Pure Appl Chem 5:107–130. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac196205010107
Olsson AM, Bjurhager I, Gerber L, Sundberg B, Salmén L (2011) Ultra-structural organisation of cell wall polymers in normal and tension wood of aspen revealed by polarisation FTIR microspectroscopy. Planta 233:1277–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1384-1
Peng P, Peng F, Bian J, Xu F, Sun RC, Kennedy JF (2011) Isolation and structural characterization of hemicelluloses from the bamboo species phyllostachys incarnata wen. Carbohydr Polym 86(2):883–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.05.038
Peng H, Salmén L, Stevanic JS, Lu J (2019) Structural organization of the cell wall polymers in compression wood as revealed by ftir microspectroscopy. Planta 250:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-019-03158-7
Poovaiah CR, Nageswara M, Soneji JR, Baxter HL, Stewart CN (2014) Altered lignin biosynthesis using biotechnology to improve lignocellulosic biofuel feedstocks. Plant Biotechnol J 12:1163–1173. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12225
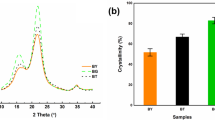
Ren W, Guo F, Zhu J, Cao M, Wang H, Yu Y (2021) A comparative study on the crystalline structure of cellulose isolated from bamboo fibers and parenchyma cells. Cellulose 28:5993–6005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03892-w
Rennie EA, Scheller HV (2014) Xylan biosynthesis. Curr Opin Biotechnol 26:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2013.11.013
Simmons TJ, Mortimer JC, Bernardinelli OD, Pppler AC, Brown SP, Deazevedo ER (2016) Folding of xylan onto cellulose fibrils in plant cell walls revealed by solid-state NMR. Nat Commun 7:13902. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13902
Slabaugh E (2014) Cellulose synthases: new insights from crystallography and modeling. Trends Plant Sci 19:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.09.009
Stevanic JS, Salmén L (2009) Orientation of the wood polymers in the cell wall of spruce wood fibres. Holzforschung 63(5):497–503. https://doi.org/10.1515/HF.2009.094
Stevanic J, Simonovic J, Djikanovic D, Salmén L, Radotic K (2011) Anisotropy of cell wall polymers in branches of hardwood and softwood: a polarized FTIR study. Cellulose 18:1433–1440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9584-1
Tatjana D, Sivakumar P, Markus G, Nicolai D, Malcolm O, Katharina SG, Philipp MG (2017) Insights into cell wall structure of Sida hermaphrodita and its influenceon recalcitrance. Carbohydr Polym 168:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.03.062
Terrett OM, Dupree P (2019) Covalent interactions between lignin and hemicelluloses in plant secondary cell walls. Curr Opin Biotechnol 56:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2018.10.010
Tsuboi K, Kondo T, Yokota S (2014) Difference between bamboo- and wood-derived cellulose nanofibers prepared by the aqueous counter collision method. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 29(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.3183/NPPRJ-2014-29-01-p069-076
Tsuji T, Tsuboi K, Yokota S, Tagawa S, Kondo T (2021) Characterization of an amphiphilic janus-type surface in the cellulose nanofibril prepared by aqueous counter collision. Biomacromol 22(2):620–628. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c01464
Vanholme R, Morreel K, Ralph J, Boerjan W (2008) Lignin engineering. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2008.03.005
Wen J, **ao L, Sun Y, Sun S, Xu F, Sun R (2011) Comparative study of alkali-soluble hemicelluloses isolated from bamboo (bambusa rigida). Carbohydr Res 346:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2010.10.006
Wen JL, Sun SL, Xue BL, Sun RC (2015) Structural elucidation of inhomogeneous lignins from bamboo. Int J Biol Macromol 77:250–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.03.044
Zhang N, **ong LM, Hong Y, Chen Y (2015) Cellulose-hemicellulose interaction in wood secondary cell-wall. Model Simul Mater Sc 23(8):085010. https://doi.org/10.1088/0965-0393/23/8/085010
Zhang X, Liu M, Wang HK, Yu Y (2018) Ultralight, hydrophobic, anisotropic bamboo-derived cellulose nanofibrils aerogels with excellent shape recovery via freeze-casting. Carbohydr Polym 208:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.073
Zhang B, Guo Y, Liu X, Chen H, Yang S, Wang Y (2020) Mechanical properties of the fiber cell wall in bambusa pervariabilis bamboo and analyses of their influencing factors. BioResources 15(3):5316–5327. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.15.3.5316-5327
Zhao Y, Man Y, Wen J, Guo Y, Lin J (2019) Advances in imaging plant cell walls. Trends Plant Sci 24(9):1819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2019.05.009
Zhu JW, Guo F, Ma CY, Wang HK, Wen JL, Yu Y (2022) The alkaline extraction efficiency of bamboo cell walls is related to their structural differences on both anatomical and molecular level. Ind Crop Prod 178:114628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114628
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31770600 and 32001255).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest and that the manuscript has been approved by all authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Ren, W., Guo, F. et al. The spatial orientation and interaction of cell wall polymers in bamboo revealed with a combination of imaging polarized FTIR and directional chemical removal. Cellulose 29, 3163–3176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04506-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04506-9