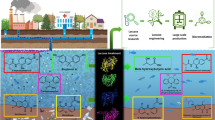
Abstract
In this paper, five recombinant strains: GS115-LacA, GS115-LacB, GS115-LacC, KM71H-Lcc1 and GS115-Lcc2 were selected to produce laccase isozymes with high activities, which reached 13,001 U/L, 10,254 U/L, 11,495 U/L, 9924 U/L and 10,031 U/L on 15th, respectively. Then, we investigated the specificity of several recombinant laccase isozymes for the degradation of endocrine disrupting chemicals (phenolic compounds). The results showed that LacB had the most efficient in degradation of bisphenol A and octyl phenol, while Lcc1 degraded 4-n-octylphenol, gossypol and hydroquinone better. Finally, the effects of degradation conditions were optimized, which shown that the degradation rates of phenolic compounds increased with the optimum temperature and pH by different laccases were different, which were closely related to their enzymatic properties. Under the optimum reaction conditions, the degradation rate of bisphenol A, gossypol, 4-n-octylphenol, octyl phenol and hydroquinone were 95.4%, 93.2%, 89.6%, 71.0% and 91.9% at 8 h, 8 h, 12 h, 24 h and 1 h, respectively. Furthermore, the recombinant laccases were used to degrade phenolic compounds in several laccase/mediator systems, which ABTS and vanillin showed most enhancement on degradation rates and reduction of degradation times. In LacB-ABTS and Lcc1-guaiacol/vanillin systems, the degradation rates of five phenolic compounds reached the maximum with totally 100% within 4 h. All of the results open up promising perspectives for the degradation and oxidative biotransformation of typical phenolic pollutants in the environment.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li YX, Yin S, Yang Y et al (2020) J AOAC Int 103(2):348–364
Li ZH, Zhang WQ, Shan BQ (2019) Environ Pollut 250:1010–1018
Serra H, Scholze M, Altenburger R et al (2019) Chemosphere 227:334–344
Huggins C, Pollice L (1958) J Exp Med 107(1):13–32
Müller AK, Markert N, Leser K et al (2019) Environ Pollut 257(4):113636
Fitz-Binder C, Bechtold T (2019) Color Technol 135(1):32–39
Ge XZ, **g LZ, Zhao K et al (2020) Food Chem 335(4):127655
Knapczyk-Stwora K, Nynca A, Ciereszko RE et al (2020) Theriogenology 153(1):102–111
Wu FF, Zhu Y, Zhao XY et al (2020) J Chromatogr A 1635:461765
Zhang KW, Sai YE, Guang-Shui N et al (2008) Chin J Anal Lab 27(8):62–66
Takakura R, Koyama K, Kuwata M et al (2020) Org Biomol Chem 18(34):6594–6597
Huang YQ, Wong CKC, Zheng JS et al (2012) Environ Int 42:91–99
Santos JEP, Villasenor M, Robinson PH et al (2003) J Dairy Sci 86(3):892–905
Joseph L, Zaib Q, Khan IA et al (2011) Water Res 45(13):4056–4068
Loffredo E, Castellana G, Senesi N (2014) Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21(4):2654–2662
Yang HF, He PP, Yin YC et al (2021) Bioproc Biosyst Eng 44:2061–2073
Toyama T, Kainuma Y, Kikuchi S et al (2012) Water Sci Technol 66(10):2202–2208
Farnet AM, Chevremont AC, Gil G et al (2011) Chemosphere 82(2):284–289
Kapich AN, Galkin S, Hatakka A (2009) Biocatal Biotransform 25(2–4):350–358
Morsi R, Bilal M, Iqbal H et al (2020) Sci Total Environ 714:136572
Yang SC, Yang J, Wang T et al (2020) Nanoscale 12(14):7976–7985
Yang XL, Wu YY, Zhang Y et al (2020) Front Microbiol 11:241
Aracri E, Fillat A, Colom JF et al (2010) Bioresour Technol 101(21):8211–8216
Zhou WT, Zhang WX, Cai YP (2021) Chem Eng J 403:126272
Wang H, Deng W, Shen MH et al (2021) J Hazard Mater 408:124775
Li Q, Chai CS, Du YT et al (2021) Catal Lett 151(3):1–14
Nicolucci C, Rossi S, Menale C et al (2011) Biodegradation 22(3):673–683
Wang L, Chen M, Luo XC et al (2020) Front Chem 8:583176
He LY, Wang GB, Cao FL et al (2011) Adv Mat Res 236–238:1039–1044
Li Q, Pei JJ, Zhao LG et al (2014) Appl Biochem Micro 50(2):140–147
Li Q, Ge L, Cai JL et al (2014) J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(4):545–555
Childs RE, Bardsley WG (1975) Biochem J 145(1):93–103
Bradford MM (1976) Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Bailey MJ, Adamitsch B, Rautio J et al (2007) Enzyme Microb Technol 41(4):484–491
Danilo R, Chiara CM, Maurizio R et al (2010) FEMS Yeast Res 6:892–902
Mekmouche Y, Zhou SM, Cusano AM et al (2013) J Biosci Bioeng 117(1):25–27
Martin AIV, Vina-Gonzalez J, Santos-Moriano P et al (2016) J Mol Catal B Enzym 134:323–330
**a J, Wang Q, Luo Q et al (2019) Process Biochem 78:33–41
Zhang WH, Potter KJH, Plantz BA et al (2003) J Ind Microbiol Biot 30(4):210–215
Aza P, Salas F, Molpeceres G et al (2021) Int J Mol Sci 22(3):1157
You LF, Liu ZM, Lin JF et al (2014) J Basic Microb 54(S1):134–141
Savinova OS, Moiseenko KV, Vavilova EA et al (2019) Front Microbiol 10:152
Wang CL, Zhao M, Wei XD et al (2011) Adv Mater Res 113–116:226–230
Zhang H, Hong YZ, **ao YZ et al (2006) Appl Microbiol Biot 73(1):89–94
More SS, Renuka PS, Pruthvi K et al (2011) Jpn J Antibiot 2011(1):248735
Upadhyay P, Shrivastava R, Agrawal PK (2016) 3 Biotech 6(1):15
Navada KK, Kulal A (2020) Biotechnol Lett 43:613–626
Li Q, Zhao DX, Liu SP et al (2014) J Nan**g For Univ 38(3):93–97
Kersten PJ, Kalyanaraman B, Hammel KE et al (1990) Biochem J 268(2):475–480
**e HF, Li Q, Wang MM et al (2013) J Microbiol Biotechnol 23(6):864–871
Jiang YP, Cai JL, Pei JJ et al (2021) ACS Omega 6(14):9741–9749
Kudanga T, Nyanhongo GS, Guebitz GM et al (2011) Enzyme Microb Tech 48(3):195–208
Ren SY, Wu ZH, Guo QX et al (2015) Catal Lett 145(2):712–714
Ana F, Sudipta D, Alina MB et al (2017) Beilstein J Org Chem 13(1):1439–1445
Habimana P, Gao J, Mwizerwa JP et al (2021) ACS Omega 6(4):2777–2789
Mohapatra DP, Brar SK, Tyagi RD et al (2010) Chem Eng J 163:273–283
Gassara F, Brar SK, Verma M et al (2013) Chemosphere 92:1356–1360
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the International Advanced Forestry Science and Technology Project Imported by State Forestry Administration (Grant No. 2011-4-15, 2010-4-19) and Jiangsu “333” Project of Cultivation of High-level Talents (Grant No. BRA2015317).
Funding
Jiangsu “333” Project of Cultivation of High-level Talents,BRA2015317, the International Advanced Forestry Science and Technology Project Imported by State Forestry Administration, 2011-4-15, 2010-4-19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions were as follows: QL and LZ conceived and designed the experiments; QL and CC performed all the experiments and analyzed the data. QL wrote and revised the paper. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Chai, C. & Zhao, L. Biodegradation of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals with Laccase Isozymes from Recombinant Pichia pastori. Catal Lett 152, 2625–2636 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-021-03870-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-021-03870-8