Abstract
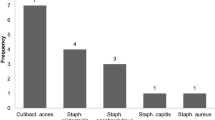
In spine surgery, allogenic bone grafts are often required to ensure bone fusion, however, the main concern regarding their use is the infection risk: therefore, an intraoperative swab for culture test is performed. The cost-effectiveness of these swabs and their influence on the patients’ postoperative course have often been questioned. This study aims at determining whether positive spine allograft culture results are predictive of an increased risk of surgical site infection and whether they influence the surgeon’s choices in postoperative management. The records of 340 patients who received allogenic bone graft during spinal fusion surgery in our institution were reviewed, for a total of 677 allografts. Each graft was swabbed intraoperatively. All patients were followed clinically for postoperative complications. Infection was diagnosed based on clinical data, blood tests and radiographic images, all assessed by an infectious disease specialist. Only 4 of the 677 allografts used (0.6%) resulted positive at the intraoperative swab culture. Three cultures were positive for Staphylococcus epidermidis and one culture for S. warneri. No clinical infection occurred in any of these patients. Twenty-eight of the 340 patients (8.2%) developed an infection, but none of them had a positive intraoperative swab culture. The most common microbiologic pathogen isolated from this cohort was S. aureus. According to our series, intraoperative swab culture results were not predictive for higher risk of infection and did not affect the clinical behavior of the surgeons in postoperative management.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Andrés-Cano P, Cerván A, Rodríguez-Solera M et al (2018) Surgical infection after posterolateral lumbar spine arthrodesis: CT analysis of spinal Fusion. Orthop Surg 10(2):89–97. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/os.12371
Barriga A, Díaz-de-Rada P, Barroso JL et al (2004) Frozen cancellous bone allografts: positive cultures of implanted grafts in posterior fusions of the spine. Eur Spine J 13(2):152–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-003-0633-9
Bartolomeo C, Guimbard Pérez JH, Ortiz PN et al (2018) Fresh frozen allograft in lumbar spine surgery. Does it increase the rate of infection? Rev Asoc Argent Ortop Traumatol 83(3):188–191. https://doi.org/10.15417/issn.1852-7434.2018.83.3.753
Casper DS, Zmistowski B, Hollern DA et al (2018) The effect of postoperative spinal infections on patient mortality. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 43(3):223–227. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000002277
Centeno JM, Woolf S, Reid JB 3rd, Lubowitz JH (2007) Do anterior cruciate ligament allograft culture results correlate with clinical infections? Arthroscopy 23(10):1100–1103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2007.05.006
Couture J, Cabana F (2013) Irradiated allograft bone in spine surgery: to culture or not? A single center retrospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38(7):558–563. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182761109
Davis N, Curry A, Gambhir K et al (1999) Intraoperative bacterial contamination in operations for joint replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Br 81(5):886–889. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.81b5.9545
Ehrler DM, Vaccaro AR (2000) The use of allograft bone in lumbar spine surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res 371:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200002000-00005
Gibson S, McLeod I, Wardlaw D, Urbaniak S (2002) Allograft versus autograft in instrumented posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion: a randomized control trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27(15):1599–1603. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007632-200208010-00002
Ivory JP, Thomas IH (1993) Audit of a bone bank. J Bone Jt Surg Br 75(3):355–357. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.75B3.8496199
James LA, Ibrahim T, Esler CN (2004) Microbiological culture results for the femoral head. Are they important to the donor? J Bone Jt Surg Ser B 86(6):797–800. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.86B6.14783
Karczewski D, Pumberger M, Müller M et al (2020) Implications for diagnosis and treatment of peri-spinal implant infections from experiences in periprosthetic joint infections-a literature comparison and review. J Spine Surg 6(4):800–813. https://doi.org/10.21037/jss-20-12
Karczewski D, Schnake KJ, Osterhoff G et al (2022) Postoperative spinal implant infections (PSII)-A systematic review: what do we know so far and what is critical about it? Glob Spine J 12(6):1231–1246. https://doi.org/10.1177/21925682211024198]
Lee CS, Kang KC, Chung SS, Kim KT, Shin SK (2016) Incidence of microbiological contamination of local bone autograft used in posterior lumbar interbody fusion and its association with postoperative spinal infection. J Neurosurg Spine 24(1):20–24. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.3.SPINE14578
Mikhael MM, Huddleston PM, Nassr A (2009a) Postoperative culture positive surgical site infections after the use of irradiated allograft, nonirradiated allograft, or autograft for spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34(22):2466–2468. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181b1fef5
Mikhael MM, Huddleston PM, Nassr A et al (2009b) Risk factors for infection after spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38(2):188. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000166532.58227.4f
Mroz TE, Joyce MJ, Lieberman IH, Steinmetz MP, Benzel EC, Wang JC (2009) The use of allograft bone in spine surgery: is it safe? Spine J 9(4):303–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2008.06.452
National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System (2004) National nosocomial infections surveillance (NNIS) system report, data summary from January 1992 through June 2004, issued October 2004. Am J Infect Control 32(8):470–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0196655304005425
Palmer SH, Gibbons CLMH, Athanasou NA (1999) The pathology of bone allograft. J Bone Jt Surg Ser B 81(2):333–335. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.81B2.9320
Parvizi J, Tan TL, Goswami K et al (2018) The 2018 definition of Periprosthetic hip and knee infection: an evidence-based and validated Criteria. J Arthroplast 33(5):1309-1314e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2018.02.078
Pawar AY, Biswas SK (2016) Postoperative spine infections. Asian Spine J 10(1):176–183. doi:https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2016.10.1.176
Putzier M, Strube P, Funk JF et al (2009) Allogenic versus autologous cancellous bone in lumbar segmental spondylodesis: a randomized prospective study. Eur Spine J 18(5):687–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-008-0875-7
Sims L, Kulyk P, Woo A (2017) Intraoperative culture positive allograft bone and subsequent postoperative infections: a retrospective review. Can J Surg 60(2):94–100. doi:https://doi.org/10.1503/cjs.008016
Stepanovic ZLj, Ristic BM (2014) The effectiveness of bone banking in Central Serbia: audit of the first seven years. Cell Tissue Bank 15(4):567–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-014-9426-0
Tomford WW, Thongphasuk J, Mankin HJ, Ferraro MJ (1990) Frozen musculoskeletal allografts. A study of the clinical incidence and causes of infection associated with their use. J Bone Jt Surg Am 72(8):1137–1143
van de Pol GJ, Sturm PD, van Loon CJ, Verhagen C, Schreurs BW (2007) Microbiological cultures of allografts of the femoral head just before transplantation. J Bone Jt Surg Br 89(9):1225–1228. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.89B9.18864
Veen MR, Bloem RM, Petit PLC (1994) Sensitivity and negative predictive value of swab cultures in musculoskeletal allograft procurement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 300:259–263. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199403000-00036
Villas C, Beguiristain JL, Mora G et al (1996) Aloinjertos en artrodesis vertebrales extensas. Rev Med Univ Navarre 40:15–19
Funding
The research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, o not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors whose names appear on the submission: (1) made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data; or the creation of new software used in the work; (2) drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content; (3) approved the version to be published; and (4) agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
The Ethics Committee of Area Vasta Emilia Centro—Regione Emilia-Romagna (CE-AVEC) approved this retrospective study on 17th February 2022 (protocol n.: 131/2022/Oss/IOR).
Consent to participate
All patients signed an informed consent on the use of their hospitalisation data for scientific purposes.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ruffilli, A., Barile, F., Fiore, M. et al. Allogenic bone grafts and postoperative surgical site infection: are positive intraoperative swab cultures predictive for a higher infectious risk?. Cell Tissue Bank 24, 627–637 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-022-10061-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-022-10061-1