Abstract
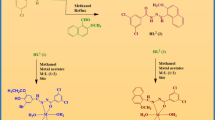
Malaria, a relentless and ancient adversary, continues to cast its shadow over vast swathes of the globe, afflicting millions of people and have a heavy toll on human health and well-being. Despite substantial progress in the fight against this parasitic disease in recent decades, malaria still persists as a substantial global health concern, especially in some specific region which have limited resources and vulnerable populations. Thus, to ascertain an combating agent for malaria and its associated dysfunction, 4-(4-ethylphenyl)-3-thiosemicarbazide and benzaldehydes based two new thiosemicarbazone ligands (1–2) and their cobalt(II), nickel(II), copper(II), zinc(II) metal complexes (3–10) were synthesized in the present research work. The synthesized compounds were comprehensive characterized through spectral and physical investigations, demonstrating octahedral stereochemistry of the complexes. Further, the antimalarial and antioxidant potential of the compounds (1–10) were analyzed by micro assay and DPPH assay protocols, respectively, to examine the therapeutic aspect of the compounds. The performed biological evaluations revealed that the complexes are more efficient in controlling infectious ailment in comparison of ligands. The complexes (5), (6), (10) shows significant efficiency for malarial and oxidant dysfunctions whereas Zn(II) complex (6) exhibit highest potency with 1.02 ± 0.07 and 2.28 ± 0.05 µM IC50 value. Furthermore, to support the highest antimalarial potency of the (3–6) complexes and their associated ligand (1), the computational studies like molecular docking, DFT, MESP and ADMET analysis were executed which were supported the biological efficacy of the complex (6) by providing numerous parameters like binding interaction electronegativity, electrophilicity, HOMO value and electron density.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article and supplementary material. The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the Worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB) repository. In addition, the other information can be made available by the corresponding author upon reasonable request as long as the request does not compromise intellectual property interests.
References
Abd El-Halim HF, Mohamed GG, Anwar MN (2018) Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of Schiff base ligand and its transition metal mixed ligand complexes with heterocyclic base. Appl Organomet Chem 32:e3899. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3899
Abd El Salam HA, Mohamed GG, Zayed EM (2023) Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, biological application and molecular docking studies of some transition metal complexes of isophthalamide ligand. J Mol Struct 1273:134231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134231
Adeleke AA, Zamisa SJ, Islam MS, Olofinsan K, Salau VF, Mocktar C, Omondi B (2022) A study of structure–activity relationship and anion-controlled quinolinyl ag (I) complexes as antimicrobial and antioxidant agents as well as their interaction with macromolecules. Biometals 35:363–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00377-6
Aly AA, Abdallah EM, Ahmed SA, Rabee MM, Abdelhafez ESM (2022) Metal complexes of thiosemicarbazones derived by 2-quinolones with Cu (I), Cu (II) and ni (II); identification by NMR, IR, ESI mass spectra and in silico approach as potential tools against SARS-CoV-2. J Mol Struct 1265:133480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133480
Arora T, Devi J, Dubey A, Tufail A, Kumar B (2023) Spectroscopic studies, antimicrobial activity, and computational investigations of hydrazone ligands endowed metal chelates. Appl Organomet Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.7209
Bharadwaj S, Dubey A, Kamboj NK, Sahoo AK, Kang SG, Yadava U (2021a) Drug repurposing for ligand-induced rearrangement of Sirt2 active site-based inhibitors via molecular modeling and quantum mechanics calculations. Sci Rep 11:10169. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07031-z
Bharadwaj S, Dubey A, Yadava U, Mishra SK, Kang SG, Dwivedi VD (2021) Exploration of natural compounds with anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity via inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. Brief Bioinform 22:1361–1377. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa382
Boora A, Devi J, Rom T, Paul AK (2023) Synthesis, characterization, single crystal structure, biological evaluation of ONO donor hydrazones and their diorganotin (IV) complexes. J Mol Struct 1284:135386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.135386
Bourouai MA, Si Larbi K, Bouchoucha A, Terrachet-Bouaziz S, Djebbar S (2023) New Ni (II) and pd (II) complexes bearing derived sulfa drug ligands: synthesis, characterization, DFT calculations, and in silico and in vitro biological activity studies. Biometals 36:153–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00469-3
Bursal E, Turkan F, Buldurun K, Turan N, Aras A, Çolak N, Yergeri MC (2021) Transition metal complexes of a multidentate Schiff base ligand containing pyridine: synthesis, characterization, enzyme inhibitions, antioxidant properties, and molecular docking studies. Biometals 34:393–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00287-z
Dalal M, Dubey A, Tufail A, Antil N, Sehrawat N, Garg S (2023) Organyltellurium (IV) complexes incorporating Schiff base ligand derived from 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde: Preparation, spectroscopic investigations, antimicrobial, antioxidant activities, DFT, MESP, NBO, molecular docking and ADMET evaluation. J Mol Struct 1287:135590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.135590
Dawar N, Devi J, Kumar B, Dubey A (2023) Synthesis, characterization, pharmacological screening, molecular docking, DFT, MESP, ADMET studies of transition metal (II) chelates of bidentate schiff base ligand. Inorg Chem Commun 151:110567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110567
Devi J, Devi S, Yadav J, Kumar A (2019) Synthesis, biological activity and QSAR studies of organotin (IV) and organosilicon (IV) complexes. ChemistrySelect 4:4512–4520. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201900317
Devi J, Yadav J, Lal K, Kumar N, Paul AK, Kumar D, **dal DK (2021) Design, synthesis, crystal structure, molecular docking studies of some diorganotin (IV) complexes derived from the piperonylic hydrazide Schiff base ligands as cytotoxic agents. J Mol Struct 1232:129992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129992
Devi J, Kumar B, Taxak B (2022) Recent advancements of organotin (IV) complexes derived from hydrazone and thiosemicarbazone ligands as potential anticancer agents. Inorg Chem Commun 139:109208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109208
Devi J, Kumar S, Kumar B, Asija S, Kumar A (2022) Synthesis, structural analysis, in vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial activity and molecular docking studies of transition metal complexes derived from Schiff base ligands of 4-(benzyloxy)-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde. Res Chem Intermed 48:1541–1576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-021-04644-y
Devi J, Sharma S, Kumar S, Kumar B, Kumar D, **dal DK, Das S (2022) Synthesis, characterization, in vitro antimicrobial and cytotoxic studies of Co (II), ni (II), Cu (II), and zn (II) complexes obtained from Schiff base ligands of 1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydro‐naphthalen‐1‐ylamine. Appl Organomet Chem 36:e6760. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.6760
Dubey A, Marabotti A, Ramteke PW, Facchiano A (2016) In silico approach to find chymase inhibitors among biogenic compounds. Future Med Chem 8:841–851. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc-2016-0030
Dubey A, Marabotti A, Ramteke PW, Facchiano A (2016) Interaction of human chymase with ginkgolides, terpene trilactones of Ginkgo biloba investigated by molecular docking simulations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 473:449–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.028
Dubey A, Dotolo S, Ramteke PW, Facchiano A, Marabotti A (2018) Searching for chymase inhibitors among chamomile compounds using a computational-based approach. Biomolecules 9:5. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9010005
Dubey A, Alawi MM, Alandijany TA, Alsaady IM, Altwaim SA, Sahoo AK, Dwivedi VD, Azhar EI (2023) Exploration of microbially derived natural compounds against Monkeypox virus as viral core cysteine proteinase inhibitors. Viruses 15:251. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010251
Dunn CR, Banfield MJ, Barker JJ, Higham CW, Moreton KM, Turgut-Balik D, Brady RL, Holbrook JJ (1996) The structure of lactate dehydrogenase from Plasmodium falciparum reveals a new target for anti-malarial design. Nat Struct Biol 3:912–915. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1196-912
Ebrahimi H, Hadi JS, Al-Ansari HS (2013) A new series of Schiff bases derived from sulfa drugs and indole-3-carboxaldehyde: synthesis, characterization, spectral and DFT computational studies. J Mol Struct 1039:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2013.01.063
Ezzat A, Mohamed MBI, Mahmoud AM, Farag RS, El-Tabl AS, Ragab A (2022) Synthesis, spectral characterization, antimicrobial evaluation and molecular docking studies of new Cu (II), zn (II) thiosemicarbazone based on sulfonyl isatin. J Mol Struct 1251:132004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.132004
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA (2016) Gaussian 09, Revision E.01. Gaussian Inc, Wallingford
Goncalves AC, Carneiro ZA, Oliveira CG, Danuello A, Guerra W, Oliveira RJ, Maia PI (2017) PtII, PdII and AuIII complexes with a thiosemicarbazone derived from diacethylmonooxime: structural analysis, trypanocidal activity, cytotoxicity and first insight into the antiparasitic mechanism of action. Eur J Med Chem 141:615–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.10.013
Gonul I, Kose M, Ceyhan G, Serin S (2016) Methoxy group containing bidentate Schiff base ligands and their transition metal complexes: synthesis, structural characterisation, photoluminescence, antioxidant capacity and superoxide dismutase activity studies. Inorg Chim Acta 453:522–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2016.09.004
Jagadeesh M, Lavanya M, Kalangi SK, Sarala Y, Ramachandraiah C, Reddy AV (2015) Spectroscopic characterization, antioxidant and antitumour studies of novel bromo substituted thiosemicarbazone and its copper (II), nickel (II) and palladium (II) complexes. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 135:180–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.06.141
Jain P, Vishvakarma VK, Singh P, Kumar R, Kumar D, Chandra S, Misra N (2023) Bioactive thiosemicarbazone coordination metal complexes: synthesis, characterization, theoretical analysis, biological activity, molecular docking and ADME analysis. Chem Biodivers. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.202300760
Jiang Y, Rakesh KP, Alharbi NS, Vivek HK, Manukumar HM, Mohammed YHE, Qin HL (2019) Radical scavenging and anti-inflammatory activities of (hetero) arylethenesulfonyl fluorides: synthesis and structure-activity relationship (SAR) and QSAR studies. Bioorg Chem 89:103015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103015
Kaushik CP, Pahwa A (2018) Convenient synthesis, antimalarial and antimicrobial potential of thioethereal 1, 4-disubstituted 1, 2, 3-triazoles with ester functionality. Med Chem Res 27:458–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-2072-x
Khatkar P, Asija S, Ahlawat A, Singh V (2019) Synthesis, characterization, in vitro antimicrobial and QSAR studies of diorganotin (IV) complexes of Schiff bases derived from 2-(3-methylbutanoyl)-1 H-indene-1, 3 (2 H)-dione and 4-substituted anilines. Monatsh Chem 150:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-018-2308-6
Konakanchi R, Pamidimalla GS, Prashanth J, Naveen T, Kotha LR (2021) Structural elucidation, theoretical investigation, biological screening and molecular docking studies of metal (II) complexes of NN donor ligand derived from 4-(2-aminopyridin-3-methylene) aminobenzoic acid. Biometals 34:529–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00293-1
Kumar S, Saini V, Maurya IK, Sindhu J, Kumari M, Kataria R, Kumar V (2018) Design, synthesis, DFT, docking studies and ADME prediction of some new coumarinyl linked pyrazolylthiazoles: potential standalone or adjuvant antimicrobial agents. PLoS ONE 13:e0196016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196016
Kumar LV, Sunitha S, Nath GR (2021) Antioxidant, antidiabetic and anticancer studies of nickel complex of Vanillin-4-Methyl-4-Phenyl-3-Thiosemicarbazone. Mater Today 41:669–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.376
Kumar B, Devi J, Manuja A (2023) Synthesis, structure elucidation, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and molecular docking studies of transition metal (II) complexes derived from heterocyclic Schiff base ligands. Res Chem Intermed 49:2455–2493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-023-04991-y
Kumar S, Devi J, Dubey A, Kumar D, **dal DK, Asija S, Sharma A (2023) Co (II), ni (II), Cu (II) and zn (II) complexes of Schiff base ligands: synthesis, characterization, DFT, in vitro antimicrobial activity and molecular docking studies. Res Chem Intermed 49:939–965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-022-04941-0
Laryea MK, Sheringham Borquaye L (2021) Antimalarial, antioxidant, and toxicological evaluation of extracts of Celtis africana, Grosseria vignei, Physalis micrantha, and Stachytarpheta angustifolia. Biochem Res Int 2021:1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9971857
Lee C, Yang W, Parr RG (1988) Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys Rev B 37:785. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.37.785
Li C, Sridhara MB, Rakesh KP, Vivek HK, Manukumar HM, Shantharam CS, Qin HL (2018) Multi-targeted dihydrazones as potent biotherapeutics. Bioorg Chem 81:389–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.08.024
Majumdar D, Dubey A, Tufail A, Sutradhar D, Roy S (2023a) Synthesis, spectroscopic investigation, molecular docking, ADME/T toxicity predictions, and DFT study of two trendy ortho vanillin-based scaffolds. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16057
Majumdar D, Philip JE, Dubey A, Tufail A, Roy S (2023b) Synthesis, spectroscopic findings, SEM/EDX, DFT, and single-crystal structure of Hg/Pb/Cu–SCN complexes: in silico ADME/T profiling and promising antibacterial activities. Heliyon. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16103
Mbaba M, Golding TM, Smith GS (2020) Recent advances in the biological investigation of organometallic platinum-group metal (ir, Ru, Rh, Os, pd, pt) complexes as antimalarial agents. Molecules 25:5276. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225276
Melha KSA (2008) In-vitro antibacterial, antifungal activity of some transition metal complexes of thiosemicarbazone Schiff base (HL) derived from N4-(7′-chloroquinolin-4′-ylamino) thiosemicarbazide. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 23:493–503. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756360701631850
Netalkar PP, Netalkar SP, Revankar VK (2014) Nickel (II) complexes of thiosemicarbazones: synthesis, characterization, X-ray crystallographic studies and in vitro antitubercular and antimicrobial studies. Transit Met Chem 39:519–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-014-9827-8
Netalkar PP, Netalkar SP, Revankar VK (2015) Transition metal complexes of thiosemicarbazone: synthesis, structures and invitro antimicrobial studies. Polyhedron 100:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2015.07.075
Nibila TA, Soufeena PP, Periyat P, Aravindakshan KK (2021) Synthesis, structural characterization and biological activities of transition metal complexes derived from 2, 4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde n (4)-methyl (phenyl) thiosemicarbazone. J Mol Struct 1231:129938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.129938
O’Boyle NM, Banck M, James CA, Morley C, Vandermeersch T, Hutchison GR (2011) Open babel: an open chemical toolbox. J Cheminf 3:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-3-33
Pahontu E, Julea F, Rosu T, Purcarea V, Chumakov Y, Petrenco P, Gulea A (2015) Antibacterial, antifungal and in vitro antileukaemia activity of metal complexes with thiosemicarbazones. J Cell Mol Med 19:865–878. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12508
Pellegatti M, Pagliarusco S (2011) Drug and metabolite concentrations in tissues in relationship to tissue adverse findings: a review. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 7:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425255.2011.545053
Piri Z, Moradi–Shoeili Z, Assoud A (2019) Ultrasonic assisted synthesis, crystallographic, spectroscopic studies and biological activity of three new Zn (II), Co (II) and ni (II) thiosemicarbazone complexes as precursors for nano-metal oxides. Inorganica Chim Acta 484:338–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2018.09.054
Qin HL, Zhang ZW, Lekkala R, Alsulami H, Rakesh KP (2020) Chalcone hybrids as privileged scaffolds in antimalarial drug discovery: a key review. Eur J Med Chem 193:112215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112215
Rakesh KP, Suhas R, Gowda DC (2019) Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant peptide-conjugates: modulation of activity by charged and hydrophobic residues. Int J Pept Res Ther 25:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-017-9668-3
Rani M, Devi J, Kumar B (2023) Thiosemficarbazones-based Co (II), ni (II), Cu (II) and zn (II) complexes: synthesis, structural elucidation, biological activities and molecular docking. Chem Pap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02917-x
Ravindar L, Hasbullah SA, Rakesh KP, Hassan NI (2022) Pyrazole and pyrazoline derivatives as antimalarial agents: a key review. Eur J Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106365
Ravindar L, Hasbullah SA, Rakesh KP, Hassan NI (2023a) Recent developments in antimalarial activities of 4-aminoquinoline derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115458
Ravindar L, Hasbullah SA, Rakesh KP, Hassan NI (2023b) Triazole hybrid compounds: a new frontier in malaria treatment. Eur J Med Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115694
Rieckmann KH, McNamara JV, Frischer H, Stockert TA, Carson PE, Powell RD (1968) Gametocytocidal and sporontocidal effects of primaquine and of sulfadiazine with pyrimethamine in a chloroquine-resistant strain of Plasmodium falciparum. Bull World Health Organ 38:625
Rose PW, Prlic A, Bi C, Bluhm WF, Christie CH, Dutta S, Green RK, Goodsell DS, Westbrook JD, Woo J (2015) The RCSB protein data bank: views of structural biology for basic and applied research and education. Nucl Acids Res 43:D345–D356. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1214
Savir S, Wei ZJ, Liew JWK, Vythilingam I, Lim YAL, Saad HM, Tan KW (2020) Synthesis, cytotoxicity and antimalarial activities of thiosemicarbazones and their nickel (II) complexes. J Mol Struct 1211:128090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128090
Savir S, Liew JWK, Vythilingam I, Lim YAL, Tan CH, Sim KS, Tan KW (2021) Nickel (II) complexes with polyhydroxybenzaldehyde and O, N, S tridentate thiosemicarbazone ligands: synthesis, cytotoxicity, antimalarial activity, and molecular docking studies. J Mol Struct 1242:130815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130815
Stringer T, Melis DR, Smith GS (2019) N, O-Chelating quinoline-based half-sandwich organorhodium and-iridium complexes: synthesis, antiplasmodial activity and preliminary evaluation as transfer hydrogenation catalysts for the reduction of NAD+. Dalton Trans 48:13143–13148. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9DT02030F
Ullas BJ, Rakesh KP, Shivakumar J, Gowda DC, Chandrashekara PG (2020) Multi-targeted quinazolinone-Schiff’s bases as potent bio-therapeutics. Results Chem 2:100067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2020.100067
Verma SK, Verma R, Rakesh KP, Gowda DC (2022) Design, synthesis and structure-activity studies of amino acids conjugated quinazolinone-Schiff’s bases as potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents. Eur J Med Chem Rep 6:100087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmcr.2022.100087
World Health Organization (2022) World malaria report. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240064898
Zacharias AO, Varghese A, Akshaya KB, Savitha MS, George L (2018) DFT, spectroscopic studies, NBO, NLO and fukui functional analysis of 1-(1-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)ethylidene) thiosemicarbazide. J Mol Struct 1158:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.01.002
Zeroka D, Jensen JO, Samuels AC (1999) Infrared spectra of some isotopomers of ethylamine and the ethylammonium ion: a theoretical study. J Mol Struct Theochem 465:119–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-1280(98)00324-8
Acknowledgements
Mr. Binesh Kumar expresses his gratitude to the Department of Chemistry, Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, Hisar, for providing research facilities and he is also highly grateful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi (File no. 09/752(0105)/2020-EMR-I) for financial support as senior research fellowship (SRF).
Funding
This study was funded by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi (09/752(0105)/2020-EMR-I).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JD: Data curation, Supervision, Writing—review & editing, Validation. BK: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing original draft, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Data curation. AD: Software (Molecular Docking, DFT, MESP and ADMET), Visualization, Writing—original draft, Methodology and Validation. AT: Software (Molecular Docking, DFT, MESP and ADMET), Visualization, Writing—original draft, Validation. AB: Formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
No animal/human studies were carried out in the present work.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, J., Kumar, B., Dubey, A. et al. Exploring the antimalarial and antioxidant efficacy of transition metal(II) chelates of thiosemicarbazone ligands: spectral investigations, molecular docking, DFT, MESP and ADMET. Biometals 37, 247–265 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00546-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-023-00546-1