Abstract
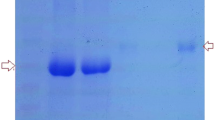
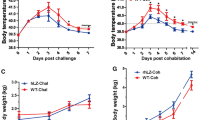
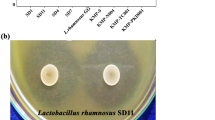
Escherichia coli (E. coli) are the most common aerobic gram-negative bacilli in a normal intestinal tract. They cause most of the intra-abdominal infections, wound infections associated with abdominal surgery, and septicemia. Most of these infections are of endogenous intestinal origin. Lactoferrin (LF) is an iron-binding glycoprotein found in milk and various external secretions. This protein has been found to have a number of biological functions, including antimicrobial, anti-cancer, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory effects. Partial degradation of LF by pepsin can give rise to peptides termed lactoferricin (LFcin) with more potent antimicrobial activity. LF and LFcin have been shown to inhibit the growth of a number of pathogenic bacteria (including E. coli and antibiotic-resistant strains), fungi, and even viruses in both in vitro and in vivo studies. We previously demonstrated that both recombinant porcine LF (pLF) produced from yeast and a synthetic 20-residue porcine LFcin peptide exhibit antimicrobial activity in vitro. In one of our recent studies, we performed pathogen challenges, including pathogenic E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans, of the digestive tract of a transgenic milk-fed animal model. The results showed that LF has broad spectrum antimicrobial activity in the digestive tract and protects the mucosa of the small intestine from injury. Our following study also revealed that pLF as a feedstuff additive enhances avian immunity, including antibody formation and cell-mediated immunity. All of these results suggest that LF could be a novel natural protein in the treatment and prevention of infections with E. coli or antibiotic-resistant bacteria strains.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Actor JK, Hwang SA, Kruzel ML (2009) Lactoferrin as a natural immune modulator. Curr Pharm Des 15:1956–1973
Ando K, Hasegawa K, Shindo K, Furusawa T, Fu**o T, Kikugawa K, Nakano H, Takeuchi O, Akira S, Akiyama T, Gohda J, Inoue J, Hayakawa M (2010) Human lactoferrin activates NF-kappaB through the toll-like receptor 4 pathway while it interferes with the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated TLR4 signaling. FEBS J 277:2051–2066
Appelmelk BJ, An YQ, Geerts M, Thijs BG, de Boer HA, MacLaren DM, de Graaff J, Nuijens JH (1994) Lactoferrin is a lipid A-binding protein. Infect Immun 62:2628–2632
Artym J, Zimecki M, Paprocka M, Kruzel ML (2003) Orally administered lactoferrin restores humoral immune response in immunocompromised mice. Immunol Lett 89:9–15
Baumgartner JD, Glauser MP, McCutchan JA, Ziegler EJ, van Melle G, Klauber MR, Vogt M, Muehlen E, Luethy R, Chiolero R (1985) Prevention of gram-negative shock and death in surgical patients by antibody to endotoxin core glycolipid. Lancet 2:59–63
Bonten MJ, Grundmann H (2003) Selective digestive decontamination and antibiotic resistance: a balancing act. Crit Care Med 31:2239–2240
Bryce J, Boschi-Pinto C, Shibuya K, Black RE (2005) WHO estimates of the causes of death in children. Lancet 365:1147–1152
Campos MA, Vargas MA, Regueiro V, Llompart CM, Alberti S, Bengoechea JA (2004) Capsule polysaccharide mediates bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides. Infect Immun 72:7107–7114
Camus C, Bellissant E, Sebille V, Perrotin D, Garo B, Legras A, Renault A, Le Corre P, Donnio PY, Gacouin A, Gohda J, Inoue J, Hayakawa M (2005) Prevention of acquired infections in intubated patients with the combination of two decontamination regimens. Crit Care Med 33:307–314
Chen HL, Lai YW, Yen CC, Lin YY, Lu CY, Yang SH, Tsai TC, Lin YJ, Lin CW, Chen CM (2004a) Production of recombinant porcine lactoferrin exhibiting antibacterial activity in methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 8:141–149
Chen PW, Ho SP, Shyu CL, Mao FC (2004b) Effects of bovine lactoferrin hydrolysate on the in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli strains isolated from baby pigs. Am J Vet Res 65:131–137
Chen HL, Yen CC, Lu CY, Yu CH, Chen CM (2006) Synthetic porcine lactoferricin with a 20-residue peptide exhibits antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans. J Agric Food Chem 54:3277–3282
Chen HL, Lai YW, Chen CS, Chu TW, Lin W, Yen CC, Lin MF, Tu MY, Chen CM (2010) Probiotic Lactobacillus casei expressing human lactoferrin elevates antibacterial activity in the gastrointestinal tract. Biometals 23:543–554
Cimolai N, Carter JE, Morrison BJ, Anderson JD (1990) Risk factors for the progression of Escherichia coli O157:H7 enteritis to hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J Pediatr 116:589–592
Croxen MA, Finlay BB (2010) Molecular mechanisms of Escherichia coli pathogenicity. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:26–38
de Araujo AN, Giugliano LG (2001) Lactoferrin and free secretory component of human milk inhibit the adhesion of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. BMC Microbiol 1:25
de Jonge E, Schultz MJ, Spanjaard L, Bossuyt PM, Vroom MB, Dankert J, Kesecioglu J (2003) Effects of selective decontamination of digestive tract on mortality and acquisition of resistant bacteria in intensive care: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 362:1011–1016
de Oliveira IR, de Araujo AN, Bao SN, Giugliano LG (2001) Binding of lactoferrin and free secretory component to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 203:29–33
Edde L, Hipolito RB, Hwang FF, Headon DR, Shalwitz RA, Sherman MP (2001) Lactoferrin protects neonatal rats from gut-related systemic infection. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G1140–G1150
Fisher CJ Jr, Agosti JM, Opal SM, Lowry SF, Balk RA, Sadoff JC, Abraham E, Schein RM, Benjamin E (1996) Treatment of septic shock with the tumor necrosis factor receptor: Fc fusion protein. The soluble TNF receptor sepsis study group. N Engl J Med 334:1697–1702
Flores-Villasenor H, Canizalez-Roman A, Reyes-Lopez M, Nazmi K, de la Garza M, Zazueta-Beltran J, Leon-Sicairos N, Bolscher JG (2010) Bactericidal effect of bovine lactoferrin, lfcin, lfampin and lfchimera on antibiotic-resistant staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Biometals 23:569–578
Giugliano LG, Ribeiro ST, Vainstein MH, Ulhoa CJ (1995) Free secretory component and lactoferrin of human milk inhibit the adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Med Microbiol 42:3–9
Gonzalez-Chavez SA, Arevalo-Gallegos S, Rascon-Cruz Q (2009) Lactoferrin: structure, function and applications. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33:e301–e308
Haversen LA, Engberg I, Baltzer L, Dolphin G, Hanson LA, Mattsby-Baltzer I (2000) Human lactoferrin and peptides derived from a surface-exposed helical region reduce experimental Escherichia coli urinary tract infection in mice. Infect Immun 68:5816–5823
Hung CM, Wu SC, Yen CC, Lin MF, Lai YW, Tung YT, Chen HL, Chen CM (2010a) Porcine lactoferrin as feedstuff additive elevates avian immunity and potentiates vaccination. Biometals 23:579–587
Hung CM, Yeh CC, Chen HL, Lai CW, Kuo MF, Yeh MH, Lin W, Tu MY, Cheng HC, Chen CM (2010b) Porcine lactoferrin administration enhances peripheral lymphocyte proliferation and assists infectious bursal disease vaccination in native chickens. Vaccine 28:2895–2902
Hutchens TW, Henry JF, Yip TT (1991) Structurally intact (78-kDa) forms of maternal lactoferrin purified from urine of preterm infants fed human milk: identification of a trypsin-like proteolytic cleavage event in vivo that does not result in fragment dissociation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2994–2998
Jones RN (2001) Resistance patterns among nosocomial pathogens: trends over the past few years. Chest 119:397S–404S
Kaito M, Iwasa M, Fujita N, Kobayashi Y, Kojima Y, Ikoma J, Imoto I, Adachi Y, Hamano H, Yamauchi K (2007) Effect of lactoferrin in patients with chronic hepatitis C: combination therapy with interferon and ribavirin. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22:1894–1897
Kawai T, Akira S (2007) Signaling to nf-kappab by toll-like receptors. Trends Mol Med 13:460–469
Kawasaki Y, Tazume S, Shimizu K, Matsuzawa H, Dosako S, Isoda H, Tsukiji M, Fujimura R, Muranaka Y, Isihida H (2000) Inhibitory effects of bovine lactoferrin on the adherence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to host cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:348–354
Kim WS, Tanaka T, Kumura H, Shimazaki K (2002) Lactoferrin-binding proteins in bifidobacterium bifidum. Biochem Cell Biol 80:91–94
Kim WS, Ohashi M, Tanaka T, Kumura H, Kim GY, Kwon IK, Goh JS, Shimazaki K (2004) Growth-promoting effects of lactoferrin on L. acidophilus and Bifidobacterium spp. Biometals 17:279–283
King JC Jr, Cummings GE, Guo N, Trivedi L, Readmond BX, Keane V, Feigelman S, de Waard R (2007) A double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot study of bovine lactoferrin supplementation in bottle-fed infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 44:245–251
Kruzel ML, Harari Y, Mailman D, Actor JK, Zimecki M (2002) Differential effects of prophylactic, concurrent and therapeutic lactoferrin treatment on LPS-induced inflammatory responses in mice. Clin Exp Immunol 130:25–31
Kuipers ME, de Vries HG, Eikelboom MC, Meijer DK, Swart PJ (1999) Synergistic fungistatic effects of lactoferrin in combination with antifungal drugs against clinical Candida isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:2635–2641
Lee WJ, Farmer JL, Hilty M, Kim YB (1998) The protective effects of lactoferrin feeding against endotoxin lethal shock in germfree piglets. Infect Immun 66:1421–1426
Legrand D, Vigie K, Said EA, Elass E, Masson M, Slomianny MC, Carpentier M, Briand JP, Mazurier J, Hovanessian AG (2004) Surface nucleolin participates in both the binding and endocytosis of lactoferrin in target cells. Eur J Biochem 271:303–317
Ling JM, Schryvers AB (2006) Perspectives on interactions between lactoferrin and bacteria. Biochem Cell Biol 84:275–281
Llobet E, Tomas JM, Bengoechea JA (2008) Capsule polysaccharide is a bacterial decoy for antimicrobial peptides. Microbiology 154:3877–3886
Longhi C, Marazzato M, Conte MP, Iebba V, Schippa S, Seganti L, Comanducci A (2009) Effect of lactoferricin on fluoroquinolone susceptibility of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 62:109–111
Manzoni P, Rinaldi M, Cattani S, Pugni L, Romeo MG, Messner H, Stolfi I, Decembrino L, Laforgia N, Vagnarelli F et al (2009) Bovine lactoferrin supplementation for prevention of late-onset sepsis in very low-birth-weight neonates: a randomized trial. JAMA 302:1421–1428
Moreno E, Prats G, Sabate M, Perez T, Johnson JR, Andreu A (2006) Quinolone, fluoroquinolone and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole resistance in relation to virulence determinants and phylogenetic background among uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother 57:204–211
Murray PR, Rosenthal KS, Pfaller MA (2009) Medical microbiology, 6th edn. Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 301–315
Nappi C, Tommaselli GA, Morra I, Massaro M, Formisano C, Di Carlo C (2009) Efficacy and tolerability of oral bovine lactoferrin compared to ferrous sulfate in pregnant women with iron deficiency anemia: a prospective controlled randomized study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 88:1031–1035
Nebermann L, Dohler JR, Perlick L (2001) Treatment of enterogenic endotoxinemia with lactoferrin in rats. Langenbecks Arch Surg 386:146–149
Nickel JC (2007) Urinary tract infections and resistant bacteria: highlights of a symposium at the combined meeting of the 25th international congress of chemotherapy (icc) and the 17th European congress of clinical microbiology and infectious diseases (eccmid), March 31–April 3, 2007, Munich, Germany. Rev Urol 9:78–80
Ochoa TJ, Noguera-Obenza M, Ebel F, Guzman CA, Gomez HF, Cleary TG (2003) Lactoferrin impairs type III secretory system function in enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 71:5149–5155
Ochoa TJ, Brown EL, Guion CE, Chen JZ, McMahon RJ, Cleary TG (2006) Effect of lactoferrin on enteroaggregative E. coli (EAEC). Biochem Cell Biol 84:369–376
Ochoa TJ, Chea-Woo E, Campos M, Pecho I, Prada A, McMahon RJ, Cleary TG (2008) Impact of lactoferrin supplementation on growth and prevalence of Giardia colonization in children. Clin Infect Dis 46:1881–1883
Pennington H (2010) Escherichia coli o157. Lancet 376:1428–1435
Pittet D, Eggimann P, Rubinovitch B (2001) Prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia by oral decontamination: just another SDD study? Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:338–339
Salyers AA, Whitt DD (2002) Bacterial pathogenesis: a molecular approach, 2nd edn. ASM press, Washington, DC, pp 24–30
Sanchez MS, Watts JL (1999) Enhancement of the activity of novobiocin against Escherichia coli by lactoferrin. J Dairy Sci 82:494–499
Shin K, Yamauchi K, Teraguchi S, Hayasawa H, Tomita M, Otsuka Y, Yamazaki S (1998) Antibacterial activity of bovine lactoferrin and its peptides against enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lett Appl Microbiol 26:407–411
Singh PK, Parsek MR, Greenberg EP, Welsh MJ (2002) A component of innate immunity prevents bacterial biofilm development. Nature 417:552–555
Tomita M, Wakabayashi H, Yamauchi K, Teraguchi S, Hayasawa H (2002) Bovine lactoferrin and lactoferricin derived from milk: production and applications. Biochem Cell Biol 80:109–112
Valenti P, Antonini G (2005) Lactoferrin: an important host defence against microbial and viral attack. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2576–2587
van der Kraan MI, Groenink J, Nazmi K, Veerman EC, Bolscher JG, Nieuw Amerongen AV (2004) Lactoferrampin: a novel antimicrobial peptide in the n1-domain of bovine lactoferrin. Peptides 25:177–183
Viejo-Diaz M, Andres MT, Fierro JF (2004) Modulation of in vitro fungicidal activity of human lactoferrin against Candida albicans by extracellular cation concentration and target cell metabolic activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:1242–1248
Vincent JL (2003) Selective digestive decontamination: for everyone, everywhere? Lancet 362:1006–1007
Vorland LH, Osbakk SA, Perstolen T, Ulvatne H, Rekdal O, Svendsen JS, Gutteberg TJ (1999) Interference of the antimicrobial peptide lactoferricin b with the action of various antibiotics against Escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus. Scand J Infect Dis 31:173–177
Wu SC, Chen HL, Yen CC, Kuo MF, Yang TS, Wang SR, Weng CN, Chen CM, Cheng WT (2007) Recombinant porcine lactoferrin expressed in the milk of transgenic mice enhances offspring growth performance. J Agric Food Chem 55:4670–4677
Yekta MA, Verdonck F, Van Den Broeck W, Goddeeris BM, Cox E, Vanrompay D (2010) Lactoferrin inhibits E. coli O157:H7 growth and attachment to intestinal epithelial cells. Vet Med 55:359–368
Yen CC, Lin CY, Chong KY, Tsai TC, Shen CJ, Lin MF, Su CY, Chen HL, Chen CM (2009) Lactoferrin as a natural regimen for selective decontamination of the digestive tract: recombinant porcine lactoferrin expressed in the milk of transgenic mice protects neonates from pathogenic challenge in the gastrointestinal tract. J Infect Dis 199:590–598
Zagulski T, Lipinski P, Zagulska A, Jarzabek Z (1998) Antibacterial system generated by lactoferrin in mice in vivo is primarily a killing system. Int J Exp Pathol 79:117–123
Zavaleta N, Figueroa D, Rivera J, Sanchez J, Alfaro S, Lonnerdal B (2007) Efficacy of rice-based oral rehydration solution containing recombinant human lactoferrin and lysozyme in Peruvian children with acute diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 44:258–264
Ziegler EJ, McCutchan JA, Fierer J, Glauser MP, Sadoff JC, Douglas H, Braude AI (1982) Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and shock with human antiserum to a mutant Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med 307:1225–1230
Zimecki M, Artym J, Chodaczek G, Kocieba M, Kruzel ML (2004) Protective effects of lactoferrin in Escherichia coli-induced bacteremia in mice: relationship to reduced serum TNF alpha level and increased turnover of neutrophils. Inflamm Res 53:292–296
Zullo A, De Francesco V, Scaccianoce G, Manes G, Efrati C, Hassan C, Maconi G, Piglionica D, Cannaviello C, Panella C, Morini S, Ierardi E (2007) Helicobacter pylori eradication with either quadruple regimen with lactoferrin or levofloxacin-based triple therapy: a multicentre study. Dig Liver Dis 39:806–810
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by grant NSC-98-2313-B-005-012 from the National Science Council, grant COA-97-6.2.1-U1(9) from the Council of Agriculture, and the Ministry of Education, Taiwan, Republic of China, under the ATU plan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chih-Ching Yen and Chih-Jie Shen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yen, CC., Shen, CJ., Hsu, WH. et al. Lactoferrin: an iron-binding antimicrobial protein against Escherichia coli infection. Biometals 24, 585–594 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9423-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9423-8