Abstract
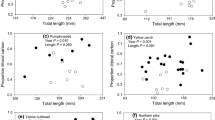
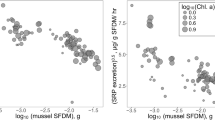
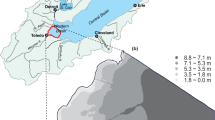
We examined the spatial variation in carbon:nitrogen:phosphorus (C:N:P) stoichiometry and condition index of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha), non-indigenous species, in four Swedish lakes with different productivity. Within-lake variability was observed in tissue C:N molar ratios of Dreissena in all lakes and in tissue C:P ratio only in three lakes. Depth had no effect on tissue C:P and N:P ratios of Dreissena. A positive correlation was found between C:N:P stoichiometry of seston and elemental composition of zebra mussel in one of the lakes. Tissue C:N and N:P ratios were the main factors that related to zebra mussel condition index. Zebra mussel condition was positively related to tissue C:N ratio. Smaller Dreissena had higher C:N ratio than larger Dreissena in two of the four lakes. Zebra mussels in the lake with highest productivity had lower C:P and N:P ratios than zebra mussels in the lake with lowest productivity. Our study suggests that the zebra mussel may modify their phosphorus content in relation to lake trophic state, and therefore cope with stoichiometric constraints which may explain the invasion success of this and other related species.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya K, Jack JD, Smith AS (2006) Stoichiometry of Daphnia lumholtzi and their invasion success: are they linked? Arch Hydrobiol 165:433–453
Alunno-Bruscia M, Petraitis PS, Bourget E, Frechette M (2000) Body size-density relationship for Mytilus edulis in an experimental food-regulated situation. Oikos 90:28–42
Arnott DL, Vanni MJ (1996) Nitrogen and phosphorus recycling by the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in the western basin of Lake Erie. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 53:646–659
Bayne BL, Gee JM, Davey JT, Scullard C (1978) Physiological responses of Mytilus edulis L. to parasitic infestation by Mytilicola intestinalis. J Cons Int Explor Mer 38:12–17
Boersma M, Elser JJ (2006) Too much of good thing: on stoichiometrically balanced diets and maximal growth. Ecology 85:1325–1330
Carlson RE (1977) A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 22:361–369
Claudi R, Mackie GL (1994) Practical manual for zebra mussel monitoring and control. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Côté LM, Reynolds JD (2002) Predictive ecology to the rescue? Science 298:1181–1182
Cross WF, Benstead JP, Rosemand AD, Wallace JB (2003) Consumer-resource stoichiometry in detritusbased streams. Ecol Lett 6:721–732
Eiler A, Bertilson S (2007) Flavobacteria blooms in four eutrophic lakes: linking population dynamics of freshwater bacterioplankton to resource availability. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3511–3518
Elser JJ, Hayakawa K, Urabe J (2001) Nutrient limitation reduces food quality for zooplankton: Daphnia response to seston phosphorus enrichment. Ecology 82:898–903
Elser JJ, Acharya K, Kyle M, Cotner J, Makino W, Markow T, Watts T, Hobbie S, Fagan W, Schade J, Sterner RW (2003) Growth rate–Stoichiometry couplings in diverse biota. Ecol Lett 6:936–943
Eschweiler N, Christensen HT (2011) Trade-off between increased survival and reduced growth for blue mussels living on Pacific oyster reefs. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 403:90–95
Frandsen RP, Dolmer P (2002) Effects of substrate type on growth and mortality of blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) exposed to the predator Carcinus maenas. Mar Biol 141:253–262
Frost PC, Elser JJ (2002) Growth responses of littoral mayflies to the phosphorus content of their food. Ecol Lett 5:232–240
Frost PC, Evans-White MA, Finkel ZV, Jensen TC, Matzek V (2005) Are you what you eat? Physiological constraints on organismal stoichiometry in an elementally imbalanced world. Oikos 109:18–28
Frost PC, Benstead JP, Cross WF, Hillebrand H, Larson JH, Xenopoulos MA, Yoshida T (2006) Threshold elemental ratios of carbon and phosphorus in aquatic consumers. Ecol Lett 9:774–779
Funk JL, Vitousek PM (2007) Resource-use efficiency and plant invasion in low-resource systems. Nature 446:1079–1081
Garton DW, Johnson LE (2000) Variation in growth rates of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, within Lake Wawasee. Freshw Biol 45:443–451
Goedkoop W, Naddafi R, Grandin U (2011) Retention of N and P by zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha Pallas) and its quantitative role in the nutrient budget of eutrophic Lake Ekoln, Sweden. Biol Invasions 13:1077–1086
González AL, Kominoski JS, Danger M, Ishida S, Iwai N, Rubach A (2010) Can ecological stoichiometry help explain patterns of biological invasions? Oikos 119:779–790
Grandin U, Larson D (2007) Dykinventering av vandrarmussla i Mälaren och Hjälmaren. Department of Environmental Assessment, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, report 27, Uppsala 17 pp (in Swedish)
Grasshoff K, Ehrhardt M, Kremling K (1983) Methods of seawater analysis, 2nd edn. Verlag Chemie
Hessen DO (2006) Determinants of seston C:P-ratio in lakes. Freshw Biol 51:1560–1569
Hessen DO, Van Donk E, Gulati R (2005) Seasonal seston stoichiometry: effects on zooplankton in cyanobacteria dominated lakes. J Plankton Res 27:449–460
Hillebrand H, Kahlert M (2001) Effect of grazing and nutrient supply on periphyton biomass and nutrient stoichiometry in habitats of different productivity. Limnol Oceanogr 46:1881–1898
Kahlert M, Hasselrot AT, Hillebrand H, Pettersson K (2002) Spatial and temporal variation in the biomass and nutrient status of epilithic algae in Lake Erken, Sweden. Freshw Biol 47:1191–1215
Kvarnäs H (2001) Morphometry and hydrology of the four large lakes of Sweden. Ambio 30:467–474
Liess A, Hillebrand H (2005) Stoichiometric variation in C:N, C:P and N:P ratios of littoral benthic invertebrates. J N Am Benthol Soc 24:256–269
Mackie GL, Schloesser DW (1996) Comparative biology of zebra mussels in Europe and North America: an overview. Am Zool 36:244–258
Malmaeus JM, Blenckner T, Markensten H, Persson I (2006) Lake phosphorus dynamics and climate warming: a mechanistic model approach. Ecol Model 190:1–14
Mersch J, Wagner P, Pihan JC (1996) Copper in indigenous and transplanted zebra mussels in relation to changing water concentrations and body weight. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:886–893
Mills EL, Chrisman JR, Baldwin B, Owens RW, O’Gorman R, Howell T, Roseman E, Raths MK (1999) Changes in the dreissenid community in the lower Great Lakes with emphasis on southern Lake Ontario. J Great Lakes Res 25:187–197
Moe SJ, Stelzer RS, Forman MR, Harpole WS, Daufresne T, Yoshida T (2005) Recent advances in ecological stoichiometry: insights for population and community ecology. Oikos 109:29–39
Morehouse RL (2010) Stoichiometry in a benthic invasive: exploring how stoichiometric imbalances with algal resources affect zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) growth and condition. Oklahoma State University, M.Sc. thesis. pp 44
Naddafi R, Eklöv P, Pettersson K (2007a) Non-lethal predator effects on the feeding rate and prey selection of the exotic zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Oikos 116:1289–1298
Naddafi R, Pettersson K, Eklöv P (2007b) The effect of seasonal variation in selective feeding by zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) on phytoplankton community composition. Freshw Biol 52:823–842
Naddafi R, Pettersson K, Eklöv P (2008) Effects of the zebra mussel, an exotic freshwater species, on seston stoichiometry. Limnol Oceanogr 53:1973–1987
Naddafi R, Eklöv P, Pettersson K (2009) Stoichiometric constraints do not limit successful invaders: zebra mussels in Swedish lakes. PLoS ONE 4:e5345
Naddafi R, Pettersson K, Eklöv P (2010) Predation and water depth as structuring forces of the zebra mussel—effects on density and population size structure. J N Am Benthol Soc 29:444–453
Naddafi R, Blenckner T, Eklöv P, Pettersson K (2011) Physicochemical properties determine zebra mussel invasion success in lakes. Hydrobiologia 669:227–236
Persson J, Brett MT, Vrede T, Ravvet JK (2007) Food quantity and quality regulation of trophic transfer between primary producers and a keystone grazer (Daphnia) in pelagic freshwater food webs. Oikos 116:1152–1163
Qin P, Mayer CM, Schulz KL, Ji X, Ritchie M (2007) Ecological stoichiometry in benthic food webs: effect of light and nutrients on periphyton food quantity and quality in lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 42:1436–1443
Ricciardi A, Neves RJ, Rasmussen JB (1998) Impending extinctions of North American freshwater mussels (Unionoida) following the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) invasion. J Anim Ecol 67:613–619
Selig U, Hübener T, Heerkloss R, Schubert H (2004) Vertical gradient of nutrients in two dimictic lakes—influence of phototrophic sulfur bacteria on nutrient balance. Aquat Sci 66:247–256
Shea K, Chesson P (2002) Community ecology theory as a framework for biological invasions. Trends Ecol Evol 17:170–176
Smaal AC, Stralen MRV (1990) Average annual growth and condition of mussels as a function of food source. Hydrobiologia 195:179–188
Smolders R, Bervoets L, Blust R (2002) Transplanted zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) as active biomonitors in an effluent dominated river. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:1889–1896
Smolders R, Bervoets L, De Coen W, Blust R (2004) Cellular energy allocation in zebra mussels exposed along a pollution gradient: linking cellular effects to higher levels of biological organization. Environ Poll 129:99–112
Soto M, Ireland MP, Marigomez I (2000) Changes in mussel biometry on exposure to metals: implications in estimation of metal bioavailability in ‘Mussel- Watch’ programmes. Sci Tot Environ 247:175–187
Sterner RW (1997) Modelling interactions of food quality and quantity in homeostatic consumers. Freshw Biol 38:473–481
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry. Princeton University Press, New York
Sterner RW, Andersen T, Elser JJ, Hessen DO, Hood J, Mccauley E, Urabe J (2008) Scale dependent carbon: nitrogen: phosphorus seston stoichiometry in marine and freshwaters. Limnol Oceanogr 53:1169–1180
Strayer DL (2009) Twenty years of zebra mussels: lessons from the mollusk that made headlines. Front Ecol Environ 7:135–141
Tibbets TM, Krist AC, Hall RO Jr, Riley LA (2010) Phosphorus-mediated changes in life history traits of the invasive New Zealand mudsnail (Potamopyrgus antipodarum). Oecologia 163:549–559
Van Diepen JV, Davids C (1976) Zebra mussels and polystyrene. Hydrobiol Bull 19:179–181
Vanderploeg HA, Nalepa TF, Jude DJ, Mills EL, Holeck KT, Liebig JR, Grigorovich IA, Ojaveer H (2002) Dispersal and emerging ecological impacts of Ponto-Caspian species in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 59:1209–1228
Vanderploeg HA, Johengen TH, Liebig JR (2009) Feedback between zebra mussel selective feeding and algal composition affects mussel condition: did the regime changer pay a price for its success? Freshw Biol 54:47–63
Vanni MJ (2002) Nutrient cycling by animals in freshwater ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 33:341–370
Vanni MJ, Bowling AM, Dickman EM, Hale RS, Higgins KA, Horgan MJ, Knoll LB, Renwick WH, Stein RA (2006) Nutrient cycling by fish supports relatively more lake primary production as ecosystem productivity increases. Ecology 87:1696–1709
Voets J, Talloen W, de Tender T, van Dongen S, Covaci A, Blust R, Bervoets L (2006) Microcontaminant accumulation, physiological condition and bilateral asymmetry in zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) from clean and contaminated surface waters. Aquat Toxicol 79:213–225
Wu RSS, Shin PKS (1998) Transplant experiments on growth and mortality of the fan mussel Pinna bicolor. Aquaculture 163:47–62
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support of the Swedish Research Council to R. N. and P. E., Oscar and Lili Lamm Memorial Foundation to R. N., and the Swedish Environmental Protection Agency to U. G. We thank Helena Enderskog, Jan Johansson, and Nazila H. Koupayeh for assistance in laboratory analysis and Dr. Lars Rudstam for discussion. Comments from Dr. Ladd Johnson and two anonymous reviewers greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naddafi, R., Goedkoop, W., Grandin, U. et al. Variation in tissue stoichiometry and condition index of zebra mussels in invaded Swedish lakes. Biol Invasions 14, 2117–2131 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-012-0218-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-012-0218-9