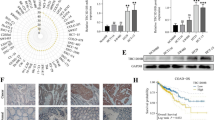
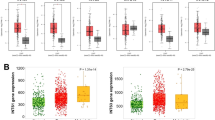
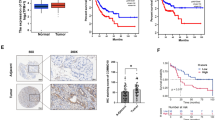
Abstract
With the emergence of combined surgical treatments, complemented by radiotherapy and chemotherapy, survival rates for esophageal cancer patients have improved, but the overall 5-year survival rate remains low. Therefore, there is an urgent need for further research into the pathogenesis of esophageal cancer and the development of effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment methods. We initially utilized the GeneCards and DisGeNET databases to identify the esophageal cancer-associated gene WWOX (WW domain containing oxidoreductase). Subsequently, we employed RT-qPCR (Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR) and WB (western blot) to investigate the differential expression of WWOX in HEEC (human esophageal endotheliocytes) and various ESCC (esophageal squamous cell carcinoma) cell lines. We further evaluated alterations in cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis via CCK8 (cell counting kit-8) and clonal formation, Transwell assays and flow cytometry. Additionally, we investigated changes in protein expressions related to the Hippo signaling pathway (YAP/TEAD) through RT-qPCR and WB. Lastly, to further elucidate the regulatory mechanism of WWOX in ESCC, we performed exogenous YAP rescue experiments in ESCC cells with WWOX overexpression to investigate the alterations in apoptosis and proliferation. Results indicated that the expression of WWOX in ESCC was significantly downregulated. Subsequently, upon overexpression of WWOX, ESCC cell proliferation and migration decreased, while apoptosis increased. Additionally, the expression of YAP and TEAD were reduced. However, the sustained overexpression of YAP attenuated the inhibitory effects of WWOX on ESCC cell malignancy. In conclusion, WWOX exerts inhibitory effects on the proliferation and migration of ESCC and promotes apoptosis by suppressing the Hippo signaling pathway. These findings highlight the potential of WWOX as a novel target for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed in this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abnet CC, Arnold M, Wei WQ (2018) Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology 154:360–373. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.023
Bouteille N, Driouch K, Hage PE et al (2009) Inhibition of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway by the WWOX tumor suppressor protein. Oncogene 28:2569–2580. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.120
Chen YA, Lu CY, Cheng TY et al (2019) WW domain-containing proteins YAP and TAZ in the Hippo pathway as key regulators in stemness maintenance, tissue homeostasis, and tumorigenesis. Front Oncol 9:60. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00060
Cigliano A, Zhang S, Ribback S et al (2022) The Hippo pathway effector TAZ induces intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in mice and is ubiquitously activated in the human disease. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 41(1):192. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-022-02394-2
Del Mare S, Salah Z, Aqeilan RI (2009) WWOX: its genomics, partners, and functions. J Cell Biochem 108:737–745. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.22298
DiSiena M, Perelman A, Birk J, Rezaizadeh H (2021) Esophageal cancer: an updated review. South Med J 114:161–168. https://doi.org/10.14423/smj.0000000000001226
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I et al (2019) Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer 144:1941–1953. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31937
Guo W, Wang G, Dong Y, Guo Y, Kuang G, Dong Z (2013) Decreased expression of WWOX in the development of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Carcinog 52:265–274. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.21853
Huang SS, Chang NS (2018) Phosphorylation/de-phosphorylation in specific sites of tumor suppressor WWOX and control of distinct biological events. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 243:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370217752350
Husanie H, Abu-Remaileh M, Maroun K et al (2022) Loss of tumor suppressor WWOX accelerates pancreatic cancer development through promotion of TGFbeta/BMP2 signaling. Cell Death Dis 13(12):1074. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-05519-9
Hussain T, Liu B, Shrock MS, Williams T, Aldaz CM (2019) WWOX, the FRA16D gene: a target of and a contributor to genomic instability. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 58:324–338. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22693
Jamous A, Salah Z (2018) WW-domain containing protein roles in breast tumorigenesis. Front Oncol 8:580. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00580
Kurek KC, Del Mare S, Salah Z et al (2010) Frequent attenuation of the WWOX tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma is associated with increased tumorigenicity and aberrant RUNX2 expression. Cancer Res 70(13):5577–5586. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-4602
Liu CW, Chen PH, Yu TJ, Lin KJ, Chang LC (2022) WWOX modulates ROS-dependent senescence in bladder cancer. Molecules 27(21):7388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217388
Maroni P, Matteucci E, Drago L et al (2015) Hypoxia induced E-cadherin involving regulators of Hippo pathway due to HIF-1alpha stabilization/nuclear translocation in bone metastasis from breast carcinoma. Exp Cell Res 330(2):287–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.10.004
Paige AJ, Taylor KJ, Taylor C et al (2001) WWOX: a candidate tumor suppressor gene involved in multiple tumor types. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11417–11422. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.191175898
Pang D, Wang W, Zhou X et al (2020) RACO-1 modulates Hippo signalling in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med 24:11912–11921. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15811
Pospiech K, Płuciennik E, Bednarek AK (2018) WWOX tumor suppressor gene in breast cancer, a historical perspective and future directions. Front Oncol 8:345. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00345
Pospiech K, Orzechowska M, Nowakowska M et al (2022) TGFalpha-EGFR pathway in breast carcinogenesis, association with WWOX expression and estrogen activation. J Appl Genet 63(2):339–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-022-00690-3
Qin L, Li X, Lin Z, Li H, Mo Y, Su F, Mo W, Yang Z (2017) EBV-LMP1 regulating AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and WWOX in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 10(8):8619–8625
Reuven N, Shanzer M, Shaul Y (2015) Tyrosine phosphorylation of WW proteins. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 240(3):375–382. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370214565991
Shi WH, Zhou ZY, Ye MJ et al (2023) Sperm morphological abnormalities in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease are associated with the Hippo signaling pathway via PC1. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 14:1130536. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1130536
Wang HY, Juo LI, Lin YT et al (2012) WW domain-containing oxidoreductase promotes neuronal differentiation via negative regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β. Cell Death Differ 19:1049–1059. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.188
Wang XH, Gan CZ, **e JY (2018) Inhibition of miR-24 suppresses malignancy of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting WWOX in vitro and in vivo. Thorac Cancer 9(12):1583–1593. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.12824
Xu Y, Yan YC, Hu YK, Fang LS, Li Q, Xu J, Yan HC (2020) WWOX regulates the Elf5/Snail1 pathway to affect epithelial-mesenchymal transition of ovarian carcinoma cells in vitro. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(3):1041–1053. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202002_20154
Zhou X, Li W, Wang S et al (2019) YAP aggravates inflammatory bowel disease by regulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization and gut microbial homeostasis. Cell Rep 27(4):1176–1189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.028
Zhou T, **e Y, Hou X et al (2023) Irbesartan overcomes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer by suppressing stemness and iron metabolism via inhibition of the Hippo/YAP1/c-Jun axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 42(1):111. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-023-02671-8
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Xuzhou Medical key talent project (No. XWRCHT20220044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiang Wang, Longzhen Zhang, Zihan Chen and **gyu Sun conceived and designed the study. Zihan Chen and **gyu Sun performed the experiment and drafted the manuscript. Lili Zhang and Yanglin Sun performed the literature searching and data analysis. Qingqing Ni, Hongkun Zhu and Miao Hui contributed to the data analysis. Qiang Wang, Longzhen Zhang, Zihan Chen and **gyu Sun discussed the results. Qiang Wang, Longzhen Zhang, Zihan Chen and **gyu Sun revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Sun, J., Zhang, L. et al. Molecular Mechanism of WWOX Inhibiting the Development of Esophageal Cancer by Inhibiting Hippo Signaling Pathway. Biochem Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10856-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-024-10856-9