Abstract
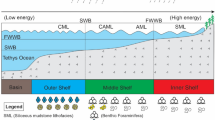
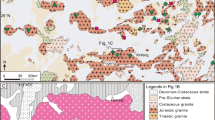
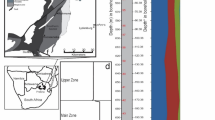
Bromine (Br) is a vital chemical raw material primarily obtained from marine brine. The bromine/chlorine (Br/Cl) ratio serves as a crucial indicator for predicting marine potash mineralization in evaporites. As salinity increases, bromine gradually accumulates through evaporation in residual brine. During the process of brine evaporation to the potassium salt stage, the bromine content in the brine can exceed 1000 ppm. The marine brine sourced from the weathering crust reservoir at the top of the Ordovician Majiagou Formation in the **gbian gas field, Ordos Basin, in northwestern China, displays an exceptionally high bromine content (averaging 1590 ppm), surpassing levels found in contemporary seawater. Based on analysis of major compositions, only brine evaporates to the gypsum stage. Despite extensive exploration in the region, large-scale potassium salt deposits have not been identified. This heightened concentration of bromine in low salinity brine suggests supplementation from additional organic bromine sources. The strata adjacent to the high-bromine oil field water in the **gbian gas field, Ordos Basin, consist of the Ordovician marine evaporite strata of the Majiagou Formation and the overlying Carboniferous and Permian marine and continental deposits rich in fossil algae. Interactions between hydrocarbons and oilfield water contribute to the notable bromine anomaly observed in the **gbian gas field in the Ordos Basin. Elevated bromine levels have also been noted in brine from various oil fields worldwide. Through an analysis of the major compositions of brines and bromine, this study will elucidate the reasons behind the presence of high bromine brines.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao HP, Yang CY, Huang JS (2004) “Evaporation drying” and “reinfluxing and redissolving”—a new hypothesis concerning formation of the Ordovician evaporites in eastern Ordos Basin. J Palaeogeog 6(3):279–288 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cartwright I, Weaver TR, Fifield LK (2006) Cl/Br ratios and environmental isotopes as indicators of recharge variability and groundwater flow: an example from the southeast Murray Basin, Australia. Chem Geol 231:38–56
Chen YH (1983) Sequence of salt separation and regularity of some trace elements distribution during isothermal evaporation (25℃) of the Huanghai Sea water. Acta Geol Sin 4:379–390 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dean WE (1978) Trace and minor elements in evaporates. In: Dean W, Schreiber BC (eds) Marine evaporites, Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Short course notes, vol 4, pp 86–104
Fan F, Zheng MP, Zhang YS (2012) Discovery of oil field water with high content of Br−, I−, Li+, K+ as the indication of finding potash in **gbian Gas Field. J Jilin Univ (earth Sci Edn) 42(2):141–147 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fan F, Meng FW, Zhang YS, Zheng MP, Su K, **ng EY (2020) Differences in evaporate geochemistry of the greater Ordos Ordovician salt basin, China: Evidence from the M56 submember of the Majiagou Formation. Carbonates Evaporites 35:107
Fontes JC, Matray JM (1993) Geochemistry and origin of formation brines from the Paris Basin, France: 1. Brines associated with Triassic salts. Chem Geol 109:149–175
Herczeg AL, Dogramaci SS, Leaney FWJ (2001) Origin of dissolved salts in a large, semi-arid groundwater system: Murray Basin, Australia. Mar Freshw Res 52:41–52
Holser WT (1979) Mineralogy of evaporates. In: Burns RG (ed) Marine Minerals, 6, Mineralogical Society America, Reviews in Mineralogy, pp 211–294
Korenevsky SM, Zakharova VM, Shamakhov VA (1977) Miocene halogen formations in the foothills of the Carpathians. Nedra, L 1–248 (in Russian)
Kovalevich VM (1990) Halogenesis and chemical evolution Ocean in the Phanerozoic. Naukova Dumka, Kiev: 1–154 (in Russian)
Li HX, Cai CF (2017) Origin and evolution of formation water from the Ordovician carbonate reservoir in the Tazhong area, Tarim Basin, NW China. J Petrol Sci Eng 148:103–114
Li JQ, Li AQ, Zhang ZW, Yang ZL, Zhang ZL, Zhao ZJ (2005) Genesis and Exploitation of relative rich aquifer regions in Ma Wu1+2 Gas reservoir of **gbian gas field. Nat Gas Ind 24(9):89–91 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li YT, Liu H, **ao G (2015) Comprehensive utilization of brine resources in Bohai Bay development prospects. J Salt Chem Ind 44(9):51–52 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lin YT, Pan ZR (2001) Give full play to brine resources superiority in Sichuan basin, carry out a great plan for the development of west China. Acta Geol Sichuan 21(1):26–31
Lowenstein TK, Hardie LA, Timofeeff MN, Demicco RV (2003) Secular variation in seawater chemistry and the origin of calcium chloride basinal brines. Geology 31(10):857–860
Lowenstein TK, Timofeeff MN, Brennan ST, Demicco RV (2001) Oscillations in Phanerozoic seawater chemistry: evidence from fluid inclusions. Science 294:1086–1088
Lunde G (1971) Analysis of arsenic and bromine in marine and terrestrial oils. J Am Oil Chem Soc 49:44–47
Mayer LM, Macko SA, Mook WH, Murray S (1981) The distribution of bromine in coastal sediments and its use as a source indicator for organic matter. Org Geochem 3:37–42
McCaffrey MA, Lazar B, Holland HD (1987) The evaporation path of seawater and the coprecipitation of Br and K with halite. J Sediment Res 57:928–937
Means JL, Hubbard N (1987) Short-chain aliphatic acid anions in deep subsurface brines: a review of their origin, occurrence, properties, and importance and new data on their distribution and geochemical implications in the Palo Duro Basin, Texas. Org Geochem 11:177–191
Meng FW, Zhang YS, Galamay AR, Bukowski K, Ni P, **ng EY, Ji LM (2018) Ordovician seawater composition: evidence from fluid inclusions in halite. Geol Q 62:344–352
Meng FW, Zhang ZL, Yan XQ, Ni P, Liu WH, Fan F, **e GW (2019) Stromatolites in Middle Ordovician carbonate–evaporite sequences and their carbon and sulfur isotopes stratigraphy Ordos Basin, northwestern China. Carbonates Evaporites 34:11–20
Peng BX, Wu DS (2014) Distribution and content of bromine in Chinese coals. J Fuel Chem Technol 42(7):769–773 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Price NB, Calvert SE (1977) The contrasting geochemical behavlours of iodine and bromine in recent sediments from the Namlbian shelf. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 41:1769–1775
Tu JQ, Dong YG, Zhang B, Nan HL, Li CJ, Wang XM, Fei XD, Zhou WB (2016) Discovery of effective scale source rocks of the Ordovician Majiagou Fm inthe Ordos Basin and its geological significance. Natur Gas Ind 36(5):15–24 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Valyashko MG (1956) Geochemistry of bromine in the processes of salt deposition and the use of the bromine content as a genetic and prospecting criterion. Geochemistry 6:570–589
Warren JK (2006) Evaporites: sediments, resources and hydrocarbons. Springer, Berlin
Warren JK (2010) Evaporites through time: tectonic, climatic and eustatic controls in marine and nonmarine deposits. Earth Sci Rev 98:217–268
Wilgus CK, Holser WT (1984) Marine and Nonmarine Salts of Western Interior, United States. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 68:765–767
Winid B (2015) Bromine and water quality-selected aspects and future perspectives. Appl Geochem 63:413–435
Wittrup MB, Kyser TK (1990) The petrogenesis of brine in Devonian potash deposit of western Canada. Chem Geol 82:103–128
**e GW, Meng FW, Ye MF, Han P, Hua H (2024) Stromatolites from the Majiagou Formation in the Ordos Basin, Northwestern China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 633:111879
Yalçin H, Koç T, Pamuk V (1997) Hydrogen and bromine production from concentrated sea-water. Int J Hydrogen Energy 22(10–11):967–970
Zhang XY, Ma HZ, Tan HB, Gao DL, Li BK, Li MX, Tang QL, Yuan XL (2010) Preliminary studies of on geochemistry and post-depositional change of Dong Tai Potash deposit in Laos. Miner Depos 29(4):713–720 (n Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang YS, Bao HP, Zheng MP, Guo Q, Yu CQ, **ng EY, Su K, Fan F, Gong WQ (2013) Tectonic Differentiation of O2m56 Deposition Stage in Salt Basin, Northern Shaanxi, and its control over the formation of potassium Sags. Acta Geol Sin 87(1):101–107 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang YS, **n EY, Zheng MP, Su K, Fan F, Gong WQ, Yuan HR, Liu JH (2014) The discovery of thick-bedded sylvite highly mineralized section from the M56 sub-member of Ordovician Majiagou Formation in Northern Shaanxi Salt Basin and its potash salt-prospecting implications. Acta Geosci Sin 35(6):693–702 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang ZL, Meng FW, Quan FZ, Li HL, Yin LM, Yuan XJ, Yan K, Ahsane N, Rehmane SU (2021) Microfossils from nodular charts in the middle Ordovician Yijianfang Formation carbonates (Well YJ-1X), Tarim Basin, China. Carbonates Evaporites 36:38
Zhou X, Li CJ (1995) Seawater evaporation trajectories and their application. Earth Sci J China Univ Geosci 20(4):410–414 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Basic Frontier Scientific Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. ZDBS-LY-DQC021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A:Dr. Fu Fan; B; Professor Fanwei Meng; C: Professor Yunqi Ma; D: Hong** Bao; E:Zhanrong Ma; F: Saif Ur Rehman A wrote the draft of this paper, and B proposed the idea of this paper and revised the draft. C helped test the brine samples, and senior engineers D and E were responsible for collecting the samples for this study, as well as the geological background information. F participated in the discussion and revision of the paper, as he is an expert in sedimentology. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, F., Meng, F., Ma, Y. et al. Mechanisms Underlying the Bromine Anomaly in the Brine of the **gbian Gas Field, Ordos Basin, Northwestern China. Aquat Geochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-024-09431-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-024-09431-w