Abstract
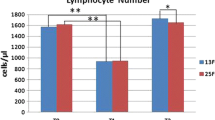
We tested apoptosis levels in in vitro irradiated T-lymphocytes from breast cancer (BC) patients with radiotherapy-induced late effects. Previous results reported in the literature were revised. We also examined the effect of TP53 Arg72Pro polymorphism on irradiation-induced apoptosis (IA). Twenty BC patients, ten with fibrosis and/or telangiectasias and ten matched controls with no late reactions, were selected from those receiving radiotherapy between 1993 and 2007. All patients were followed-up at least 6 years after radiotherapy. Using the combination of both CD3 and CD8 antibodies the in vitro IA was measured in CD3, CD8 and CD4 T-lymphocytes, and CD8 natural killer lymphocytes (CD8 NK) by flow cytometry. The TP53 Arg72Pro genotype was determined by sequencing. Patients with late radiotherapy toxicity showed less IA for all T-lymphocytes except for the CD8 NK. CD8 NK showed the highest spontaneous apoptosis and the lowest IA. IA in patients with toxicity appears to be lower than the control patients only in TP53 Arg/Arg patients (P = 0.077). This difference was not present in patients carrying at least one Pro allele (P = 0.8266). Our data indicate that late side effects induced by radiotherapy of BC are associated to low levels of IA. CD8 NK cells have a different response to in vitro irradiation compared to CD8 T-lymphocytes. It would be advisable to distinguish the CD8 NK lymphocytes from the pool of CD8+ lymphocytes in IA assays using CD8+ cells. Our data suggest that the 72Pro TP53 allele may influence the IA of patients with radiotherapy toxicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett GC, West CM, Dunning AM, Elliott RM, Coles CE, Pharoah PD, Burnet NG (2009) Normal tissue reactions to radiotherapy: towards tailoring treatment dose by genotype. Nat Rev Cancer 9:134–142
Popanda O, Marquardt JU, Chang-Claude J, Schmezer P (2009) Genetic variation in normal tissue toxicity induced by ionizing radiation. Mutat Res 667:58–69
Bentzen SM (2006) Preventing or reducing late side effects of radiation therapy: radiobiology meets molecular pathology. Nat Rev Cancer 6:702–713
Barker CL, Routledge JA, Farnell DJ, Swindell R, Davidson SE (2009) The impact of radiotherapy late effects on quality of life in gynaecological cancer patients. Br J Cancer 100:1558–1565
West CM, Barnett GC (2011) Genetics and genomics of radiotherapy toxicity: towards prediction. Genome Med 3:52
Fernet M, Hall J (2008) Predictive markers for normal tissue reactions: fantasy or reality? Cancer Radiother 12:614–618
Crompton NE, Miralbell R, Rutz HP, Ersoy F, Sanal O, Wellmann D, Bieri S, Coucke PA, Emery GC, Shi YQ, Blattmann H, Ozsahin M (1999) Altered apoptotic profiles in irradiated patients with increased toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45:707–714
Ozsahin M, Crompton NE, Gourgou S, Kramar A, Li L, Shi Y, Sozzi WJ, Zouhair A, Mirimanoff RO, Azria D (2005) CD4 and CD8 T-lymphocyte apoptosis can predict radiation-induced late toxicity: a prospective study in 399 patients. Clin Cancer Res 11:7426–7433
Bordon E, Henriquez Hernandez LA, Lara PC, Pinar B, Fontes F, Rodriguez Gallego C, Lloret M (2009) Prediction of clinical toxicity in localized cervical carcinoma by radio-induced apoptosis study in peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs). Radiat Oncol 4:58
Bordon E, Henriquez-Hernandez LA, Lara PC, Ruiz A, Pinar B, Rodriguez-Gallego C, Lloret M (2010) Prediction of clinical toxicity in locally advanced head and neck cancer patients by radio-induced apoptosis in peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs). Radiat Oncol 5:4
Riley T, Sontag E, Chen P, Levine A (2008) Transcriptional control of human p53-regulated genes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:402–412
Whibley C, Pharoah PD, Hollstein M (2009) p53 polymorphisms: cancer implications. Nat Rev Cancer 9:95–107
Dumont P, Leu JI, Della Pietra AC, George DL, Murphy M (2003) The codon 72 polymorphic variants of p53 have markedly different apoptotic potential. Nat Genet 33:357–365
Ozsahin M, Ozsahin H, Shi Y, Larsson B, Wurgler FE, Crompton NE (1997) Rapid assay of intrinsic radiosensitivity based on apoptosis in human CD4 and CD8 T-lymphocytes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 38:429–440
Crompton NE, Shi YQ, Emery GC, Wisser L, Blattmann H, Maier A, Li L, Schindler D, Ozsahin H, Ozsahin M (2001) Sources of variation in patient response to radiation treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 49:547–554
Azria D, Ozsahin M, Kramar A, Peters S, Atencio DP, Crompton NE, Mornex F, Pelegrin A, Dubois JB, Mirimanoff RO, Rosenstein BS (2008) Single nucleotide polymorphisms, apoptosis, and the development of severe late adverse effects after radiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 14:6284–6288
Foro P, Algara M, Lozano J, Rodriguez N, Sanz X, Torres E, Carles J, Reig A, Membrive I, Quera J, Fernandez-Velilla E, Pera O, Lacruz M, Bellosillo B (2014) Relationship between radiation-induced apoptosis of T-lymphocytes and chronic toxicity in patients with prostate cancer treated by radiation therapy: a prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 88:1057–1063
Finnon P, Kabacik S, Mackay A, Raffy C, A’hern R, Owen R, Badie C, Yarnold J, Bouffler S (2012) Correlation of in vitro lymphocyte radiosensitivity and gene expression with late normal tissue reactions following curative radiotherapy for breast cancer. Radiother Oncol 105:329–336
Greve B, Dreffke K, Rickinger A, Konemann S, Fritz E, Eckardt-Schupp F, Amler S, Sauerland C, Braselmann H, Sauter W, Illig T, Schmezer P, Gomolka M, Willich N, Bolling T (2009) Multicentric investigation of ionising radiation-induced cell death as a predictive parameter of individual radiosensitivity. Apoptosis 14:226–235
Greve B, Bolling T, Amler S, Rossler U, Gomolka M, Mayer C, Popanda O, Dreffke K, Rickinger A, Fritz E, Eckardt-Schupp F, Sauerland C, Braselmann H, Sauter W, Illig T, Riesenbeck D, Konemann S, Willich N, Mortl S, Eich HT, Schmezer P (2012) Evaluation of different biomarkers to predict individual radiosensitivity in an inter-laboratory comparison-essons for future studies. PLoS One 7:e47185
Wistop A, Keller U, Sprung CN, Grabenbauer GG, Sauer R, Distel LV (2005) Individual radiosensitivity does not correlate with radiation-induced apoptosis in lymphoblastoid cell lines or CD3+ lymphocytes. Strahlenther Onkol 181:326–335
Barber JB, West CM, Kiltie AE, Roberts SA, Scott D (2000) Detection of individual differences in radiation-induced apoptosis of peripheral blood lymphocytes in normal individuals, ataxia telangiectasia homozygotes and heterozygotes, and breast cancer patients after radiotherapy. Radiat Res 153:570–578
Brzozowska K, Pinkawa M, Eble MJ, Muller WU, Wojcik A, Kriehuber R, Schmitz S (2012) In vivo versus in vitro individual radiosensitivity analysed in healthy donors and in prostate cancer patients with and without severe side effects after radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Biol 88:405–413
Schnarr K, Boreham D, Sathya J, Julian J, Dayes IS (2009) Radiation-induced lymphocyte apoptosis to predict radiation therapy late toxicity in prostate cancer patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:1424–1430
Shi YQ, Li L, Sanal O, Tezcan I, Emery GC, Blattmann H, Crompton NE (2001) High levels of delayed radiation-induced apoptosis observed in lymphoblastoid cell lines from ataxia-telangiectasia patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 49:555–559
Henriquez-Hernandez LA, Carmona-Vigo R, Pinar B, Bordon E, Lloret M, Nunez MI, Rodriguez-Gallego C, Lara PC (2011) Combined low initial DNA damage and high radiation-induced apoptosis confers clinical resistance to long-term toxicity in breast cancer patients treated with high-dose radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol 6:60
Pinar B, Henriquez-Hernandez LA, Lara PC, Bordon E, Rodriguez-Gallego C, Lloret M, Nunez MI, De Almodovar MR (2010) Radiation induced apoptosis and initial DNA damage are inversely related in locally advanced breast cancer patients. Radiat Oncol 5:85
Henriquez-Hernandez LA, Pinar B, Carmona-Vigo R, Bordon E, Rodriguez-Gallego C, Flores-Morales A, Lara PC (2013) Common genomic signaling among initial DNA damage and radiation-induced apoptosis in peripheral blood lymphocytes from locally advanced breast cancer patients. Breast 22:28–33
Sharif S, Ferner R, Birch JM, Gillespie JE, Gattamaneni HR, Baser ME, Evans DG (2006) Second primary tumors in neurofibromatosis 1 patients treated for optic glioma: substantial risks after radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 24:2570–2575
Choi G, Huang B, Pinarbasi E, Braunstein SE, Horvai AE, Kogan S, Bhatia S, Faddegon B, Nakamura JL (2012) Genetically mediated nf1 loss in mice promotes diverse radiation-induced tumors modeling second malignant neoplasms. Cancer Res 72:6425–6434
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA (2001) The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol 22:633–640
Vokurkova D, Sinkora J, Vavrova J, Rezacova M, Knizek J, Ostereicher J (2006) CD8+ natural killer cells have a potential of a sensitive and reliable biodosimetric marker in vitro. Physiol Res 55:689–698
Bordon E, Henriquez-Hernandez LA, Lara PC, Pinar B, Rodriguez-Gallego C, Lloret M (2011) Role of CD4 and CD8 T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes and Natural Killer cells in the prediction of radiation-induced late toxicity in cervical cancer patients. Int J Radiat Biol 87:424–431
Louagie H, Van EM, Philippe J, Thierens H, De RL (1999) Changes in peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in patients undergoing radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Biol 75:767–771
Philippe J, Louagie H, Thierens H, Vral A, Cornelissen M, De RL (1997) Quantification of apoptosis in lymphocyte subsets and effect of apoptosis on apparent expression of membrane antigens. Cytometry 29:242–249
Wiggs JL, Hewitt AW, Fan BJ, Wang DY, Figueiredo Sena DR, O’Brien C, Realini A, Craig JE, Dimasi DP, Mackey DA, Haines JL, Pasquale LR (2012) The p53 codon 72 PRO/PRO genotype may be associated with initial central visual field defects in caucasians with primary open angle glaucoma. PLoS One 7:e45613
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the ‘‘Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria’’ [FIS 05/2181] from the Spanish Health Ministry and the ‘‘Fundación de Investigación Médica Mutua Madrileña’’ [FMMA 2008–2012] grants. Dr Sara Gutiérrez-Enríquez is currently funded by a Miguel Servet contract awarded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III of the “Ministerio Español de Economía y Competitividad”. We are grateful to the BC donor patients involved in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuentes-Raspall, M.J., Caragol, I., Alonso, C. et al. Apoptosis for prediction of radiotherapy late toxicity: lymphocyte subset sensitivity and potential effect of TP53 Arg72Pro polymorphism. Apoptosis 20, 371–382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1056-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-014-1056-2