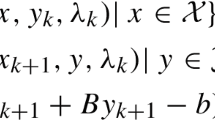Abstract
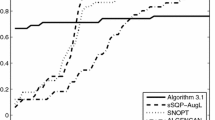
This paper discusses the two-block large-scale nonconvex optimization problem with general linear constraints. Based on the ideas of splitting and sequential quadratic optimization (SQO), a new feasible descent method for the discussed problem is proposed. First, we consider the problem of quadratic optimal (QO) approximation associated with the current feasible iteration point, and we split the QO into two small-scale QOs which can be solved in parallel. Second, a feasible descent direction for the problem is obtained and a new SQO-type method is proposed, namely, splitting feasible SQO (SF-SQO) method. Moreover, under suitable conditions, we analyse the global convergence, strong convergence and rate of superlinear convergence of the SF-SQO method. Finally, preliminary numerical experiments regarding the economic dispatch of a power system are carried out, and these show that the SF-SQO method is promising.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Börgens E, Kanzow C. Regularized Jacobi-type ADMM-methods for a class of separable convex optimization problems in Hilbert spaces. Comput Optim Appl, 2019, 73(3): 755–790
Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E, Peleato B, Eckstein J. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found Trends Mach Learn, 2011, 3(1): 1–122
Douglas J, Rachford H H. On the numerical solution of heat conduction problems in two and three space variables. Trans Amer Math Soc, 1956, 82(2): 421–439
Eckstein J. Splitting Methods for Monotone Operators with Applications to Parallel Optimization[D]. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1989
Fukushima M. A successive quadratic programming algorithm with global and superlinear convergence properties. Math Program, 1986, 35(3): 253–264
Gertz E M, Wright S J. Object orientated software for quadratic programming. ACM Trans Math Software, 2003, 29, 58–81
Glowinski R, Le Tallec P. Augmented Lagrangian and Operator-Splitting Methods in Nonlinear Mechanics. SIAM Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1989
Goldfarb D, Ma S Q, Scheinberg K. Fast alternating linearization methods for minimizing the sum of two convex functions. Math Program, 2013, 141(1–2): 349–382
Goldstein T, O’Donoghue B, Setzer S, Baraniuk R. Fast alternating direction optimization methods. SIAM J Imaging Sci, 2014, 7(3): 1588–1623
Han D R, Sun D F, Zhang L W. Linear rate convergence of the alternating direction method of multipliers for convex composite programming. Math Oper Res, 2018, 43(2): 622–637
He B S, Liu H, Wang Z R, Yuan X M. A strictly contractive Peaceman-Rachford splitting method for convex programming. SIAM J Optim, 2014, 24(3): 1011–1040
He B S, Ma F, Yuan X M. Convergence study on the symmetric version of admm with larger step sizes. SIAM J Imaging Sci, 2016, 9(3): 1467–1501
He B S, Yuan X M. On the O(1/n) convergence rate of the Douglas-Rachford alternating direction method. SIAM J Numer Anal, 2012, 50(2): 700–709
He B S, Yuan X M. On non-ergodic convergence rate of Douglas-Rachford alternating direction method of multipliers. Numer Math, 2015, 130(3): 567–577
Hong M Y, Luo Z Q, Razaviyayn M. Convergence analysis of alternating direction method of multipliers for a family of nonconvex problems. SIAM J Optim, 2016, 26(1): 337–364
Jian J B. A superlinearly convergent implicit smooth SQP algorithm for mathematical programs with nonlinear complementarity constraints. Comput Optim Appl, 2005, 31(3): 335–361
Jian J B. Fast Algorithms for Smooth Constrained Optimization—Theoretical Analysis and Numerical Experiments. Bei**g: Science Press, 2010
Jian J B, Chao M T, Jiang X Z, Han D L. On the convexity and existence of solutions to quadratic programming problems with convex constraint. Pac J Optim, 2019, 15(1): 145–155
Jian J B, Lao Y X, Chao M T, Ma G D. ADMM-SQP algorithm for two blocks linear constrained nonconvex optimization. Oper Res Trans, 2018, 22(2): 79–92
Jian J B, Ma G D. A globally convergent QP-free algorithm for inequality constrained minimax optimization. Acta Math Sci, 2020, 40B: 1723–1738
Jian J B, Tang C M, Hu Q J, Zheng H Y. A new superlinearly convergent strongly subfeasible sequential quadratic programming algorithm for inequality-constrained optimization. Numer Func Anal Optim, 2008, 29(3/4): 376–409
Jian J B, Zhang C, Yin J H, Yang L F, Ma G D. Monotone splitting sequential quadratic optimization algorithm with applications in electric power systems. J Optim Theory Appl, 2020, 186: 226–247
Jian J B, Liu P J, Yin J H, Zhang C, Chao M T. A QCQP-based splitting SQP algorithm for two-block nonconvex constrained optimization problems with application. J Comput Appl Math, 2021, 390: 113368
Kellogg R B. A nonlinear alternating direction method. Math Comput, 1969, 23(105): 23–27
Li G Y, Pong T K. Global convergence of splitting methods for nonconvex composite optimization. SIAM J Optim, 2015, 25(4): 2434–2460
Lions P L, Mercier B. Splitting algorithms for the sum of two nonlinear operators. SIAM J Numer Anal, 1979, 16(6): 964–979
Marchuk G I. Splitting and alternating direction methods// Lions J L. Handbook of Numerical Analysis. Vol I. Amsterdam: North-Holland, 1990: 197–462
Monteiro R D, Svaiter B F. Iteration-complexity of block-decomposition algorithms and the alternating direction method of multipliers. SIAM J Optim, 2013, 23(1): 475–507
OOQP solver for Quadratic Program. https://www.inverseproblem.co.nz/OPTI/index.php/Solvers/OOQP
Panier E R, Tits A L. A superlinearly convergent feasible method for the solution of inequality constrained optimization problems. SIAM J Control Optim, 1987, 25(4): 934–950
Passty G B. Ergodic convergence to a zero of the sum of monotone operators in hilbert space. J Math Anal Appl, 1979, 72(2): 383–390
Robinson S M. A quadratically-convergent algorithm for general nonlinear programming problems. Math Program, 1972, 3(1): 145–156
Shefi R, Teboulle M. Rate of convergence analysis of decomposition methods based on the proximal method of multipliers for convex minimization. SIAM J Optim, 2014, 24(1): 269–297
Solodov M V. Global convergence of an SQP method without boundedness assumptions on any of the iterative sequences. Math Program, 2009, 118(1): 1–12
Theerthamalai A, Maheswarapu S. An effective non-iterative “λ-logic based” algorithm for economic dispatch of generators with cubic fuel cost function. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst, 2010, 32(5): 539–542
Wang Y, Luo L, Freedman M T, Kung S Y. Probabilistic principal component subspaces: a hierarchical finite mixture model for data visualization. IEEE Trans Neural Net, 2000, 11(3): 625–636
Wilson R B. A Simplicial Method for Concave Programming[D]. Cambridge: Harvard University, 1963
Xu Z B, Chang X Y, Xu F M, Zhang H. L1/2 regularization: a thresholding representation theory and a fast solver. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2012, 23(7): 1013–1027
Yang L F, Luo J Y, Xu Y, Zhang Z R, Dong Z Y. A distributed dual consensus ADMM based on partition for DC-DOPF with carbon emission trading. IEEE Trans Ind Inform, 2020, 16(3): 1858–1872
Zhang C, Yang L F, Jian J B. Two-stage fully distributed approach for unit commitment with consensus ADMM. Electr Pow Syst Res, 2020, 181(106180): 1–12
Zhu Z B, Jian J B. An efficient feasible SQP algorithm for inequality constrained optimization. Nonlinear Anal Real, 2009, 10(2): 1220–1228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (12171106), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2020GXNSFDA238017 and 2018GXNSFFA281007) and the Shanghai Sailing Program (21YF1430300).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jian, J., Zhang, C. & Liu, P. A Superlinearly Convergent Splitting Feasible Sequential Quadratic Optimization Method for Two-Block Large-Scale Smooth Optimization. Acta Math Sci 43, 1–24 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10473-023-0101-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10473-023-0101-z
Key words
- large scale optimization
- two-block smooth optimization
- splitting method
- feasible sequential quadratic optimization method
- superlinear convergence