Abstract
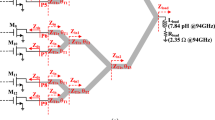
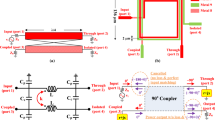
We present the design and analysis of 28 GHz CMOS power amplifiers using miniature coupled-line-based power combiners, which adopt single spiral structure with symmetrical layout to achieve miniature area and small amplitude imbalance (AI) and phase difference (PD). Coupled-line-based two power combiners and one 6-bit phase shifter (covering the 360° tuning range with excellent linearity) are designed and implemented. The first power combiner using two-turn spiral structure (combiner-1) achieves S21 of −3.93 dB and S31 of −3.97 dB at 28 GHz, corresponding to AI of 0.04 dB and PD of 0.11°. The second power combiner using three-turn spiral structure (combiner-2) achieves S21 of −3.9 dB and S31 of −3.86 dB at 28 GHz, corresponding to AI of −0.04 dB and PD of 0.02°. Three 28 GHz power amplifiers using the power combiners are designed and implemented. Excellent results are achieved. For instance, the third power amplifier (PA3) with combiner-2 comprises two ways of cascode input stage with wideband LC input matching network, followed by a common-source output stage with wideband LC inter-stage and output networks. PA3 occupies a chip area of 0.74 mm2 and achieves prominent output power (Pout) of 16.4 dBm, power gain of 22.1 dB, and power-added efficiency (PAE) of 32.6%. The eminent results of the power combiners, phase shifter, and power amplifiers indicate that they are suitable for 5G communication systems.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Kibaroglu, K., Sayginer, M., & Rebeiz, G. M. (2018). A low-cost scalable 32-element 28-GHz phased array transceiver for 5G communication links based on a 2×2 beamformer flip-chip unit cell. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 53(5), 1260–1274.
Kim, H. T., Park, B. S., Song, S. S., Moon, T. S., Kim, S. H., Kim, J. M., Chang, J. Y., & Ho, Y. C. (2018). A 28-GHz CMOS direct conversion transceiver with packaged 2×4 antenna array for 5G cellular system. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 53(5), 1245–1259.
Lin, Y. S., & Nguyen, V. K. (2017). 94 GHz CMOS Power Amplifiers Using Miniature Dual Y-Shaped Combiner with RL Load. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers, 64(6), 1285–1298.
Pozar, D. M. (2012) Microwave Engineering, 4th Edn. Wiley.
Lin, Y. S., & Lan, K. S. (2020). Coupled-line-based Ka-band CMOS power dividers. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 30(3), 253–256.
Zhou, Y., Huang, Y. M., **, H., Ding, S., Xu, D., Silvestri, L., Bozzi, M., & Perregrini, L. (2018). Slow-wave half-mode substrate integrated waveguide 3-dB Wilkinson power divider/combiner incorporating nonperiodic patterning. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 28(9), 765–767.
Kim, K., & Nguyen, C. (May 2015). An ultra-wideband low-loss millimeter-wave slow-wave Wilkinson power divider on 0.18 μm SiGe BiCMOS Process. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 25(5), 331–333.
Hsiao, Y. C., Meng, C. C., & Peng, Y. H. (May 2017). Broadband CMOS Schottky-diode star mixer using coupled-CPW Marchand dual-baluns. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 27(5), 500–502.
Lin, Y. S., & Wang, Y. E. (Aug. 2019). Design and analysis of a 94-GHz CMOS down-conversion mixer with CCPT-RL-based IF load. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers, 66(8), 3148–3161.
**a, J., Fang, X. H., & Boumaiza, S. (2018). 60-GHz power amplifier in 45-nm SOI-CMOS using stacked transformer-based parallel power combiner. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 28(8), 711–713.
Garg, R., & Natarajan, A. S. (2017). A 28-GHz low-power phased-array receiver front-end with 360° RTPS phase shift range. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 65(11), 4703–4714.
Tseng, S. C., Meng, C. C., Chang, C. H., Wu, C. K., & Huang, G. W. (2006). Monolithic broadband Gilbert micromixer with an integrated Marchand balun using standard silicon IC process. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techiques, 54(12), 4362–4371.
International Wireless Industry Consortium (IWPC), "5G millimeter wave frequencies and mobile networks—a technology whitepaper on key features and challenges," Jun. 2019 [Online]. Available: https://www.skyworksinc.com/-/media/SkyWorks/Documents/Articles/IWPC_062019.pdf
Mayeda, J. C., Lopez, J. & Lie, D. Y.C. (2020). Highly-Efficient Broadband Medium Power Amplifier Design in 22nm CMOS FD-SOI for mm-Wave 5G. In IEEE Texas Symposium on Wireless and Microwave Circuits and Systems (WMCS), pp. 1–4.
Ayad, M., Couturier, A. M., Poilvert, P., Marechal, L., & Auxemery, P. (2018) Mixed technologies packaged high power frond-end for broadband 28GHz 5G solutions. European Microwave Conference, pp. 1257–1260, 2018.
Indirayanti, P., & Reynaert, P. (2017) A 32 GHz 20 dBm-PSAT transformer-based Doherty power amplifier for multi-Gb/s 5G applications in 28 nm bulk CMOS. In IEEE Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Jun. 2017, pp. 45–48.
Rostomyan, N., Ozen, M., & Asbeck, P. (2018). 28 GHz Doherty power amplifier in CMOS SOI with 28% back-off PAE. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 28(5), 446–448.
Ozen, M., Rostomyan, N., Aufinger, K., & Fager, C. (2017). Efficient millimeter wave Doherty PA design based on a low-loss combiner synthesis technique. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 27(12), 1143–1145.
Hu, S., Wang, F., & Wang, H. (2017) "A 28 GHz/ 37 GHz/ 39 GHz multiband linear Doherty power amplifier for 5G massive MIMO applications. In IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), Feb. 2017, pp. 32–33.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the MOST of Taiwan under Contracts MOST108-2221-E-260-015- MY3. The authors are grateful for the support from TSRI for chip fabrication and measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YS., Chang, JF., Lan, KS. et al. 28 GHz coupled-line-based CMOS power combiners and phase shifter, and power amplifiers with the power combiners. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 110, 469–487 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-022-01994-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-022-01994-4