Abstract
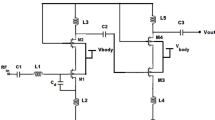
A low-noise amplifier (LNA) topology with tunable input matching and noise cancellation is introduced and described in this paper, which was designed and optimized to interface with a magnetoelectric (ME) antenna in a 0.35 µm MEMS-compatible CMOS process. Compared to conventional antennas, acoustically actuated ME antennas have significantly smaller area for ease of integration. The LNA was simulated with an ME antenna model that was constructed based on antenna measurements. Input matching at the LNA-antenna interface is controlled with a circuit that varies the effective impedance of the gate inductor using a control voltage. Tunability of 455 MHz around 2.4 GHz is achieved for the optimum S11 frequency with a control voltage range of 0.3–1.2 V. The proposed LNA has a noise cancelling feedback loop that improves the noise figure by 4.1 dB. The post-layout simulation results of the LNA show a 1-dB compression point of – 7.4 dBm with an S21 of 17.8 dB.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramakrishnan, R. V. K., & Rao, T. R. (2017). Design of penta-band antenna with integrated LNA circuit for vehicular communications. IET Circuits, Devices & Systems, 12(3), 221–225.
Nan, T., Lin, H., Gao, Y., Matyushov, A., Yu, G., Chen, H., et al. (2017). Acoustically actuated ultra-compact NEMS magnetoelectric antennas. Nature Communications, 8(1), 296. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00343-8
Lin, H., Page, M. R., McConney, M., Jones, J., Howe, B., & Sun, N. X. (2018). Integrated magnetoelectric devices: Filters, pico-Tesla magnetometers, and ultracompact acoustic antennas. MRS Bulletin, 43(11), 841–847. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2018.257
Lin, H., Page, M. R., McConney, M., Jones, J., Howe, B., & Sun, N. X. (2018). Future antenna miniaturization mechanism: Magnetoelectric antennas. In 2018 IEEE/MTT-S international microwave symposium-IMS (pp. 220–223). IEEE.
Zaeimbashi, M., Lin, H., Dong, C., Liang, X., Nasrollahpour, M., Chen, H., et al. (2019). NanoNeuroRFID: A wireless implantable device based on magnetoelectric antennas. IEEE Journal of Electromagnetics, RF and Microwaves in Medicine and Biology, 3(3), 206–215. https://doi.org/10.1109/jerm.2019.2903930
Chu, K.-D., Katanbaf, M., Su, C., Zhang, T., & Rudell, J. C. (2018). Integrated CMOS transceivers design towards flexible full duplex (FD) and frequency division duplex (FDD) systems. In 2018 IEEE custom integrated circuits conference (CICC).
Nasrollahpour, M., Sreekumar, R., Hajilou, F., Aldacher, M., & Hamedi-Hagh, S. (2018). Low-power bluetooth receiver front end design with oscillator leakage reduction technique. Journal of Low Power Electronics, 14(1), 179–184.
Yu, W.-H., Yi, H., Mak, P.-I., Yin, J., Martins, R. P. (2017). A 0.18 V 382 µW bluetooth low-energy (BLE) receiver with 1.33 nW sleep power for energy-harvesting applications in 28 nm CMOS. In 2017 IEEE international solid-state circuits conference (ISSCC).
Razavi, B. (2011). RF microelectronics (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Roobert, A. A., Nirmala Rani, D. G., & Rajaram, S. (9 2019). Design and optimisation of feedforward noise cancelling complementary metal oxide semiconductor LNA for 2.4 GHz WLAN applications. IET Circuits, Devices & Systems, 13(6), 908–919.
Jhon, H.-S., Song, I., Kang, I. M., & Shin, H. (2007). 2.4 GHz ISM-band receiver design in a 0.18 µm mixed signal CMOS process. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 17(10), 736–738.
Xu, L., Chang, C.-H., & Onabajo, M. (May 2016). A 0.77 mW 2.4 GHz RF front-end with – 4.5dBm in-band IIP3 through inherent filtering. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters (MWCL), 26(5), 352–354.
Lin, Z., Mak, P.-I., & Martins, R. P. (2014). A 0.14-mm2 1.4-mW 59.4-dB-SFDR 2.4 GHz ZigBee/WPAN receiver exploiting a split-LNTA + 50% LO topology in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 62(7), 1525–1534.
Shaeffer, D. K., & Lee, T. H. (1997). A 1.5 V, 1.5 GHz CMOS low-noise amplifier. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 32(5), 745–759.
Chang, C.-H., & Onabajo, M. (2018). Analysis and demonstration of an IIP3 improvement technique for low-power RF low-noise amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 65(3), 859–869.
Roobert, A. A., Rani, D. G. N., & Rajaram, S. (2019). Design and optimisation of feedforward noise cancelling complementary metal oxide semiconductor LNA for 2.4 GHz WLAN applications. IET Circuits, Devices & Systems, 13, 908–919.
Lee, M., & Kwon, I. (2018). 3–10 GHz noise-cancelling CMOS LNA using gm-boosting technique. IET Circuits, Devices & Systems, 12(1), 12–16.
Liang, X., Chen, H., Sun, N., Lin, H., & Sun, N. X. (2018). Novel acoustically actuated magnetoelectric antennas. In 2018 IEEE international symposium on antennas and propagation & USNC/URSI national radio science meeting (pp. 2189–2190). IEEE.
Dong, C., Li, M., Liang, X., Chen, H., Zhou, H., Wang, X., et al. (2018). Characterization of magnetomechanical properties in FeGaB thin films. Applied Physics Letters, 113(26), 262401.
Liang, X., Dong, C., Celestin, S. J., Wang, X., Chen, H., Ziemer, K. S., et al. (2018). Soft magnetism, magnetostriction, and microwave properties of Fe-Ga-C alloy films. IEEE Magnetics Letters, 10, 1–5.
El-Nozahi, M., Sanchez-Sinencio, E., Entesari, K. A. C. M. O. S., & Low-Noise. (2009). Amplifier with reconfigurable input matching network. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 57(5), 1054–1062. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmtt.2009.2017249
Guo, B., Chen, J., Li, L., **, H., & Yang, G. (2017). A wideband noise-canceling CMOS LNA with enhanced linearity by using complementary nMOS and pMOS configurations. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 52(5), 1331–1344.
Rahman, M., & Harjani, R. A. (2018). 2.4-GHz, Sub-1-V, 2.8-dB NF, 475- µ W dual-path noise and nonlinearity cancelling LNA for ultra-low-power radios. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 53(5), 1423–1430.
Pan, Z., Qin, C., Ye, Z., Wang, Y., & Yu, Z. (2018). Wideband inductorless low-power LNAs with Gm enhancement and noise-cancellation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I Regular Papers, 65(1), 26–38.
Bruccoleri, F., Klumperink, A. M., & Nauta, B. (2004). Wide-band CMOS low-noise amplifier exploiting thermal noise canceling. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39(2), 275–282.
Zaeimbashi, M., Nasrollahpour, M., Khalifa, A., et al. (2020). Ultra-compact dual-band smart NEMS magnetoelectric antennas for simultaneous wireless energy harvesting and magnetic field sensing. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.22.165894.
Salama, M. K., & Soliman, A. M. (2009). Low-voltage low-power CMOS RF low noise amplifier. AEU: International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 63(6), 478–482.
Kao, H. L., Chin, A., Chang, K. C., & McAlister, S. P. (2007). A low-power current-reuse LNA for ultra-wideband wireless receivers from 3.1 to 10.6 GHz. In Topical meeting on silicon monolithic integrated circuits in RF systems.
Varga, M., & Radić, J. (2018). Design of two LNA topologies in 0.35 µm CMOS technology for 2 GHz frequency range. In 41st International Spring seminar on electronics technology (ISSE).
Pabon, A. A., Roa, E., & Van Noije, W. (2007). On nonlinearity and noise trade-off in a low power 2.45 GHz CMOS LNA-mixer design. In SBMO/IEEE MTT-S international microwave and optoelectronics conference.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the XFAB foundry for providing access to the 0.35 µm process design kit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasrollahpour, M., Romano, A., Zaeimbashi, M. et al. Integration of a novel CMOS-compatible magnetoelectric antenna with a low-noise amplifier and a tunable input matching. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 105, 407–415 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-020-01721-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-020-01721-x