Abstract
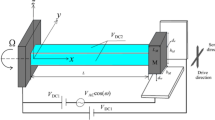
In this paper, a novel vibrating beam gyroscope with exponential variable cross-section is designed. Relationship between the width and length of the variable cross-section exponential beam is in the form of an exponential function change. The exponential shape factor (ESF) of beam is less than or equal to zero, and the thickness of the beam remains constant with the beam length. The effects of curvature nonlinearity and inertia nonlinearity on the system are considered. The vibration control equations, boundary conditions, and nonlinear discretization model of the exponential beam micro-gyroscope (EBMG) are developed by using the extended Hamiltonian principle, the single-mode approximation method, and the Lagrange differential equations. The effects of direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) voltages on the system response in both the drive and sense directions of the gyroscope are analyzed. The static response of the gyroscope system under the different ESF is solved by the Adomian decomposition method (ADM). The nonlinear discretization model is solved by the multi-scale method to analyze the influence of each parameter on the dynamic response of the gyroscope. The results show that with the increase of the ESF, the pull-in voltage and the first-order natural frequency of the EBMG increase gradually, and have a linear change pattern approximately. By adjusting the ESF, the difference between the peak frequency of Coriolis force response and the sense peak frequency can be controlled. Utilizing the nonlinear harden characteristics of the EBMG system, when the AC voltage is applied in the thickness direction of exponential beam, the EBMG system can obtain better bandwidth performance and linear measurable range by choosing the appropriate ESF, dam** ratio, and AC voltage; when the AC voltage is applied in the width direction of the exponential beam, the EBMG can not only obtain the higher sensitivity performance, but also increase the linear detectable range by choosing an appropriate ESF.

摘要
本文设计一类新型的指数型变截面梁式微陀螺, 变截面指数梁的宽度与长度的关系为指数函数变化的形式, 且指数梁的截面变化因子小于等于零, 梁的厚度随梁长仍保持不变. 考虑了曲率非线性和惯性非线性对系统的影响, 利用扩展哈密顿原理、单模**似法和拉格朗日微分方程, 建立了指数型变截面梁式非线性陀螺仪的振动控制方程、边界条件和非线性离散化模型, 且考虑了陀螺仪驱动和检测两个方向上直流电压和交流电压对系统响应的影响, 采用ADM法求解陀螺仪系统在不同截面变化因子下的静态响应, 利用多尺度法对系统的非线性离散化模型进行摄动求解, 分析各个参数对陀螺仪动态响应的影响规律. 结果表明, 随着截面变化因子的增大, 指数梁陀螺仪的吸合电压和一阶固有频率逐渐增加, 并呈现**似线性的变化规律. 通过调节指数梁截面变化因子, 可以控制科氏力响应峰值频率和检测峰值频率的差值. 利用指数梁陀螺仪系统的硬化非线性特征, 当交流电压施加在指数梁厚度方向时, 选择合适的指数截面变化因子、阻尼比和交流电压, 可以使指数梁式陀螺仪系统获得更好的带宽性能及线性可测范围; 当交流电压施加在指数梁宽度方向, 选取合适的截面变化因子, 不仅可以获得较高的系统灵敏度性能, 同时增加陀螺仪对外部输入角速度的线性可测范围.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. M. N. Passaro, A. Cuccovillo, L. Vaiani, M. De Carlo, and C. E. Campanella, Gyroscope technology and applications: A review in the industrial perspective, Sensors 17, 2284 (2017).
N. C. Tsai, and C. Y. Sue, Stability and resonance of micro-machined gyroscope under nonlinearity effects, Nonlinear Dyn. 56, 369 (2009).
D. Giannini, F. Braghin, and N. Aage, Topology optimization of 2D in-plane single mass MEMS gyroscopes, Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 62, 2069 (2020).
M. Ghommem, and A. Abdelkefi, Novel design of microgyroscopes employing electrostatic actuation and resistance-change based sensing, J. Sound Vib. 411, 278 (2017).
K. Larkin, M. Ghommem, M. Serrano, and A. Abdelkefi, A review on vibrating beam-based micro/nano-gyroscopes, Microsyst. Technol. 27, 4157 (2021).
C. G. Cooley, and R. G. Parker, Vibration of spinning cantilever beams with an attached rigid body undergoing bending-bending-torsional-axial motions, J. Appl. Mech. 81, 051002 (2014).
S. A. M. Lajimi, G. R. Heppler, and E. M. Abdel-Rahman, A parametric study of the nonlinear dynamics and sensitivity of a beam-rigid body microgyroscope, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 50, 180 (2017).
S. A. M. Lajimi, G. Heppler, and E. Abdel-Rahman, in A parametric study of the response of a beam-rigid-body microgyroscope: Proceedings of the ASME 2014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Montreal, 2014.
K. Larkin, M. Ghommem, A. Hunter, and A. Abdelkefi, Nonlinear size dependent analysis and effectiveness of nanocrystalline micro/nanogyroscopes, Phys. E-Low-dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. 117, 113808 (2020).
W. Li, X. D. Yang, W. Zhang, and Y. Ren, Modeling and performance investigation of a piezoelectric vibrating gyroscope, IEEE Sens. J. 19, 9832 (2019).
W. Li, X. D. Yang, W. Zhang, Y. Ren, and T. Z. Yang, Free vibration analysis of a spinning piezoelectric beam with geometric nonlinearities, Acta Mech. Sin. 35, 879 (2019).
K. Larkin, M. Ghommem, A. Hunter, and A. Abdelkefi, Nonlinear modeling and performance analysis of cracked beam microgyroscopes, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 188, 105965 (2020).
W. Li, X. D. Yang, W. Zhang, and Y. Ren, Parametric amplification performance analysis of a vibrating beam micro-gyroscope with size-dependent and fringing field effects, Appl. Math. Model. 91, 111 (2021).
C. Y. Wang, and C. M. Wang, Exact vibration solution for exponentially tapered cantilever with tip mass, J. Vib. Acoust. 134, (2012).
M. Yao, P. Liu, L. Ma, H. Wang, and W. Zhang, Experimental study on broadband bistable energy harvester with L-shaped piezoelectric cantilever beam, Acta Mech. Sin. 36, 557 (2020).
A. Meng, C. Yan, M. Li, W. Pan, J. Yang, and S. Wu, Modeling and experiments on Galfenol energy harvester, Acta Mech. Sin. 36, 635 (2020).
T. Tan, Z. Yan, K. Ma, F. Liu, L. Zhao, and W. Zhang, Nonlinear characterization and performance optimization for broadband bistable energy harvester, Acta Mech. Sin. 36, 578 (2020).
J. Wang, L. Geng, S. Zhou, Z. Zhang, Z. Lai, and D. Yurchenko, Design, modeling and experiments of broadband tristable gallo** piezoelectric energy harvester, Acta Mech. Sin. 36, 592 (2020).
M. N. Aghaei, H. Moeenfard, and M. Moavenian, Nonlinear extensional-flexural vibrations in variable cross section beams with eccentric intermediate mass, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 196, 106248 (2021).
J. Sun, J. Wang, K. Gao, X. He, F. Gao, Y. He, N. Li, and J. Wang, Design and performance study on a new biaxial micro-accelerometer with variable cross-section beam, Microsyst. Technol. 27, 4111 (2021).
Y. Zhou, Y. Zhang, and G. Yao, Nonlinear forced vibration analysis of a rotating three-dimensional tapered cantilever beam, J. Vib. Control 27, 1879 (2021).
B. Wang, X. Luo, Y. Liu, and Z. Yang, Thickness-variable composite beams for vibration energy harvesting, Compos. Struct. 244, 112232 (2020).
X. He, D. Li, H. Zhou, X. Hui, and X. Mu, Theoretical and experimental studies on MEMS variable cross-section cantilever beam based piezoelectric vibration energy harvester, Micromachines 12, 772 (2021).
J. Feng, Z. Chen, S. Hao, and K. Zhang, An improved analytical method for vibration analysis of variable section beam, Math. Problems Eng. 2020, 1 (2020).
R. Beigelbeck, M. Stifter, M. Schneider, F. Keplinger, U. Schmid, T. Voglhuber-Brunnmaier, and B. Jakoby, in Rigorous analytical analysis of resonant euler-bernoulli beams with constant thickness and polynomial width: Proceedings of 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Chicago, 2014.
M. Ghommem, and A. Abdelkefi, Nonlinear analysis of rotating nanocrystalline silicon microbeams for microgyroscope applications, Microsyst. Technol. 23, 5931 (2017).
J. Mohammadi, and M. Nikkhah-Bahrami, Stability analyses of articulated rigid pipes conveying fluid with harmonic velocity using the method of multiple time scales, J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 34, 965 (2020).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12072234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Author contributions
Kunpeng Zhang designed the research. Zhaomin Chang and Kunpeng Zhang wrote the first draft of the manuscript, revised and edited the final version. Qichang Zhang and **g**g Feng participated in the investigation and provided support in research methods. Shuying Hao managed the project, provided research resources, and helped organize the manuscript. All authors participated in edit and review of the paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Chang, Z., Hao, S. et al. Nonlinear characteristics and analysis of an exponential variable cross-section beam-based micro-gyroscope with electrostatic driven. Acta Mech. Sin. 39, 522371 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-022-22371-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-022-22371-x