Abstract
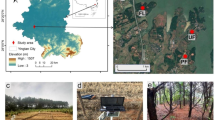
In order to simultaneously describe the spatial and temporal variations of soil moisture and the influence of land cover conditions in the semiarid Loess Plateau in Northwestern China, a field test was performed. In this study, four cover conditions were considered, including bare soil without any cover, non-vegetated soil with plastic mulch (PM), potato field with PM and maize field with PM. The actively heated fiber optics (AHFO) method was used to capture spatial soil moisture distribution, and the frequency domain reflectometry (FDR) sensor with a temporal spatial resolution of 3 min was used to record temporal moisture variation. The experimental results indicate that if the soil moisture remains constant and the cumulative precipitation slowly increases, the in-situ apparent effective soil hydraulic conductivity can be inferred from the precipitation rate. The in-situ measured apparent effective soil hydraulic conductivity has been found to be 7.09 × 10–7 m/s in this study. The estimated evapotranspiration rate was 5.68 mm/d as inferred from linear reduction rate of soil moisture after a rainfall, which agreed well with the reported average value in semiarid regions. The PM can effectively prevent water loss due to field evapotranspiration and result in aggravation of spatially uneven distribution of subsurface soil moisture under the same cover condition and depth. The growth of plant roots facilitates water holding capacity and evapotranspiration rate of soil and reduces its temporal stability.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S, Jan A, Zhang P, Khan MN, Cai T, Wei T, Ren X, Jia Q, Han Q, Jia Z (2016) Effects of ridge-covering mulches on soil water storage and maize production under simulated rainfall in semiarid regions of China. Agric Water Manag 178:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.09.003
Apperl B, Bernhardt M, Schulz K (2019) Towards improved field application of using distributed temperature sensing for soil moisture estimation: a laboratory experiment. Sensors 20(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010029
Benítez-Buelga J, Rodríguez-Sinobas L, Sánchez Calvo R, Gil-Rodríguez M, Sayde C, Selker JS (2016) Calibration of soil moisture sensing with subsurface heated fiber optics using numerical simulation. Water Resour Res 52:2985–2995. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015WR017897
Benítez-Buelga J, Sayde C, Rodríguez-Sinobas L, Selker JS (2014) Heated fiber optic distributed temperature sensing: a dual-probe heat-pulse approach. Vadose Zone J 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2014.02.0014
Cao DF, Shi B, Wei GQ, Chen SE, Zhu HH (2018) An improved distributed sensing method for monitoring soil moisture profile using heated carbon fibers. Measurement 123:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.03.052
Cao DF, Shi B, Zhu H, Wei G, Chen SE, Yan J (2015) A distributed measurement method for in-situ soil moisture content by using carbon-fiber heated cable. J Rock Mec Geotech Eng 7:700–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.08.003
Cao DF, Zhu HH, Guo CC, Wu B, Wang JC (2021) Passive distributed temperature sensing (PDTS)-based moisture estimation in agricultural soils under different vegetative canopies. Paddy Water Environ 72:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-021-00839-6
Chen Z, Sun S, Zhu Z, Jiang H, Zhang X (2019) Assessing the effects of plant density and plastic film mulch on maize evaporation and transpiration using dual crop coefficient approach. Agric Water Manag 225:105765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105765
Cichota R, Hurtado ALB, de Jong van Lier Q (2006) Spatio-temporal variability of soil water tension in a tropical soil in Brazil. Geoderma 133:231–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.07.010
de Souza ER, Montenegro AADA, Montenegro SMG, de Matos JDA (2011) Temporal stability of soil moisture in irrigated carrot crops in Northeast Brazil. Agric Water Manag 99:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2011.08.002
Dehkordi SE, Schincariol RA, Reitsma S (2015) Thermal performance of a tight borehole heat exchanger. Renewable Energy 83:698–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.04.051
Dobriyal P, Qureshi A, Badola R, Hussain SA (2012) A review of the methods available for estimating soil moisture and its implications for water resource management. J Hydrol 458–459:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.06.021
Dong J, Agliata R, Steele-Dunne S, Hoes O, Bogaard T, Greco R, van de Giesen N (2017) The impacts of heating strategy on soil moisture estimation using actively heated fiber optics. Sensors 17:2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17092102
Dong J, Steele-Dunne SC, Ochsner TE, de Giesen N (2016a) Estimating soil moisture and soil thermal and hydraulic properties by assimilating soil temperatures using a particle batch smoother. Adv Water Resour 91:104–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.03.008
Dong J, Steele-Dunne SC, Ochsner TE, van de Giesen N (2016b) Determining soil moisture and soil properties in vegetated areas by assimilating soil temperatures. Water Resour Res 52:4280–4300. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015WR018425
Florides G, Kalogirou S (2008) First in situ determination of the thermal performance of a U-pipe borehole heat exchanger, in Cyprus. Appl Therm Eng 28:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2007.03.026
Gamage DV, Biswas A, Strachan IB (2018a) Actively heated fiber optics method to monitor three-dimensional wetting patterns under drip irrigation. Agric Water Manag 210:243–251
Gil-Rodríguez M, Rodríguez-Sinobas L, Benítez-Buelga J, Sánchez-Calvo R (2013a) Application of active heat pulse method with fiber optic temperature sensing for estimation of wetting bulbs and water distribution in drip emitters. Agric Water Manag 120:72–78
Gamage DNV, Biswas A, Strachan I (2019) Field water balance closure with actively heated fiber-optics and point-based soil water sensors. Water 11:135. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010135
Gamage DNV, Biswas A, Strachan IB (2018b) Actively heated fiber optics method to monitor three-dimensional wetting patterns under drip irrigation. Agric Water Manag 210:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.08.019
Gamage DNV, Biswas A, Strachan IB, Adamchuk VI (2018c) Soil water measurement using actively heated fiber optics at field scale. Sensors 18:1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041116
Genuchten MTV (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:892–898. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
Gil-Rodríguez M, Rodríguez-Sinobas L, Benítez-Buelga J, Sánchez-Calvo R (2013b) Application of active heat pulse method with fiber optic temperature sensing for estimation of wetting bulbs and water distribution in drip emitters. Agric Water Manag 120:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2012.10.012
Lhendup T, Aye L, Fuller RJ (2014) In-situ measurement of borehole thermal properties in Melbourne. Appl Therm Eng 73:287–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.07.058
Liu XE, Li XG, Hai L, Wang YP, Li FM (2014) How efficient is film fully-mulched ridge–furrow crop** to conserve rainfall in soil at a rainfed site? Field Crops Res 169:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.09.014
Mao Z, Dong B, Pereira LS (2004) Assessment and water saving issues for Ningxia paddies, upper Yellow River Basin. Paddy Water Environ 2:99–110
Sakaki T, Firat Lüthi B, Vogt T, Uyama M, Niunoya S (2019) Heated fiber-optic cables for distributed dry density measurements of granulated bentonite mixtures: feasibility experiments. Geomech Energy Environ 17:57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gete.2018.09.006
Sayde C, Buelga JB, Rodriguez-Sinobas L, Khoury L, English M, van de Giesen N, Selker JS (2014) Map** variability of soil water content and flux across 1–1000 m scales using the actively heated fiber optic method. Water Resour Res 50:7302–7317. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR014983
Selker JS, Thévenaz L, Huwald H, Mallet A, Luxemburg W, van de Giesen N, Stejskal M, Zeman J, Westhoff M, Parlange MB (2006) Distributed fiber-optic temperature sensing for hydrologic systems. Water Resour Res 42:W12202. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006WR005326
Sourbeer JJ, Loheide SP (2016) Obstacles to long-term soil moisture monitoring with heated distributed temperature sensing. Hydrol Processes 30:1017–1035. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10615
Steele-Dunne SC, Rutten MM, Krzeminska DM, Hausner M, Tyler SW, Selker J, Bogaard TA, van de Giesen NC (2010) Feasibility of soil moisture estimation using passive distributed temperature sensing. Water Resour Res 46:W03534. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009WR008272
Striegl AM, Loheide SPII (2012) Heated distributed temperature sensing for field scale soil moisture monitoring. Ground Water 50:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2012.00928.x
Susha LSU, Singh DN, Maryam SB (2014) A critical review of soil moisture measurement. Measurement 54:92–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2014.04.007
Tyler SW, Selker JS, Hausner MB, Hatch CE, Torgersen T, Thodal CE, Schladow SG (2009) Environmental temperature sensing using Raman spectra DTS fiber-optic methods. Water Resour Res 45:23. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007052
Vachaud G, De Silans AP, Vauclin M (1985) Temporal stability of spatially measured soil water probability density function. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:822–828. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1985.03615995004900040006x
Van den Putte A, Govers G, Leys A, Langhans C, Clymans W, Diels J (2013) Estimating the parameters of the Green-Ampt infiltration equation from rainfall simulation data: why simpler is better. J Hydro 476:332–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.10.051
Wu R, Vincent M, Jeffrey M, Stefan B, Bruno B, Michel A, Barret LK (2020) Laboratory-scale assessment of a capillary barrier using fibre optic distributed temperature sensing (FO-DTS). Can Geo J 57:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2018-0283
Xu X, Huang G, Sun C, Pereira LS, Ramos TB, Huang Q, Hao Y (2013) Assessing the effects of water table depth on water use, soil salinity and wheat yield: Searching for a target depth for irrigated areas in the upper Yellow River basin. Agric Water Manag 125:46–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2013.04.004
Zhang X, Kamran M, Xue X, Zhao J, Cai T, Jia Z, Zhang P, Han Q (2019a) Ridge-furrow mulching system drives the efficient utilization of key production resources and the improvement of maize productivity in the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res 190:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.02.015
Zhang X, Yang L, Xue X, Kamran M, Ahmad I, Dong Z, Liu T, Jia Z, Zhang P, Han Q (2019b) Plastic film mulching stimulates soil wet-dry alternation and stomatal behavior to improve maize yield and resource use efficiency in a semi-arid region. Field Crops Res 233:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2019.01.002
Zubelzu S, Rodriguez-Sinobas L, Saa-Requejo A, Benitez J, Tarquis AM (2019) Assessing soil water content variability through active heat distributed fiber optic temperature sensing. Agric Water Manag 212:193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.08.008
Sayde C, Gregory C, Gil-Rodriguez M, Tufillaro N, Tyler S, van de Giesen N, English M, Cuenca R, Selker JS (2010) Feasibility of moisture monitoring with heated fiber optics. Water Resour Res 46: W06201. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009WR007846
Acknowledgements
The financial supports provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 42077235 and 41907244), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2019M653180) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central University (Grant No. 19lgpy254) are gratefully acknowledged. Special thanks are given to Mohammad Azarafza of University of Tabriz, Iran, for his help in polishing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, ZJ., Cao, DF., Zhu, HH. et al. A field test to investigate spatiotemporal distribution of soil moisture under different cropland covers in the semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Paddy Water Environ 20, 339–353 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-022-00896-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-022-00896-5