Abstract
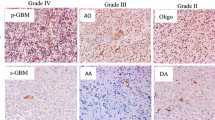
Objective: To study p27/Kip1 expression in gliomas and its application value. Methods: Immunohistochemical technique was used to detect the exprssion of p27/Kip1 gene in 48 different malignant grade human brain glioma tissues categorized according to WHO classification and 12 normal human brain tissues, which were analyzed quantitatively by using the image system and compared retrospectively with the patients' clinical characteristics. Results: In this series, the immunohistochemical reaction for p27/Kip1 was confined to the nuclei. The abnormal positive expression rate of p27/Kip1 in gliomas was found to be higher than that in normal tissues (P<0.05). The positive nuclei expression of p27/Kip1 decreased in number and staining intensity with the increasing degree of histological malignancy (P<0.05). Lower expression of p27/Kip1 was associated with poor prognosis (P<0.05). P27/Kip1 expression could be regarded as an independent prognostic factor. Conclusion: The abnormal expression of p27/Kip1 may be closely related to the occurrence and development of gliomas, and also can be used to evaluate the prognosis independently.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SHI, W., BAI, B., WANG, F. et al. P27/Kip1 Expression in Gliomas and Its Clinical Significance. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol 4, 381–383 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-004-0285-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-004-0285-1