Abstract
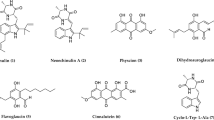
Marine-derived microbial secondary metabolites are promising potential sources of nontoxic antifouling agents. The search for environmentally friendly and low-toxic antifouling components guided us to investigate the antifouling potentials of eight novel fungal isolates from deep-sea sediments of the South China Sea. Sixteen crude ethyl acetate extracts of the eight fungal isolates showed distinct antibacterial activity against three marine bacteria (Loktanella hongkongensis UST950701–009, Micrococcus luteus UST950701–006 and Pseudoalteromonas piscida UST010620–005), or significant antilarval activity against larval settlement of bryozoan Bugula neritina. Furthermore, the extract of Aspergillus westerdijkiae DFFSCS013 displayed strong antifouling activity in a field trial lasting 4 months. By further bioassay-guided isolation, five antifouling alkaloids including brevianamide F, circumdatin F and L, notoamide C, and 5-chlorosclerotiamide were isolated from the extract of A. westerdijkiae DFFSCS013. This is the first report about the antifouling potentials of metabolites of the deep-sea-derived fungi from the South China Sea, and the first stage towards the development of non- or low-toxic antifouling agents from deep-sea-derived fungi.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar JF (1980) The disc susceptibility test. In: Lorian V (ed) Antibiotics in laboratory medicine. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 24–54
Bao J, Sun YL, Zhang XY, Han Z, Gao HC, He F, Qian PY, Qi SH (2013) Antifouling and antibacterial polyketides from marine gorgonian coral-associated fungus Penicillus sp. SCSGAF 0023. J Antibiot 66:219–223. doi:10.1038/ja.2012.110
Bao J, Zhang XY, Xu XY, He F, Nong XH, Qi SH (2013) New cyclic tetrapeptides and asteltoxins from gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSGAF 0076. Tetrahedron 69:2113–2117. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2013.01.021
Birch AJ, Russell RA (1972) Studies in relation to biosynthesis-XLIV: structural elucidations of brevianamides-B, -C, -D and -F. Tetrahedron 28:2999–3008. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(72)80014-0
Bode HB, Bethe B, Hofs R, Zeeck A (2002) Big effects from small changes: possible ways to explore nature’s chemical diversity. Chem Bio Chem 3:619–627. doi:10.1002/1439-7633
Bryan PJ, Kreider JL, Qian PY (1998) Settlement of the serpulid polychaete Hydroides elegans (Haswell) on arborescent bryozoans Bugula neritina (L): evidence of a chemically mediated relationship. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 220:171–190
Cao S, Wang JD, Chen HS, Chen DR (2011) Progress of marine biofouling and antifouling technologies. Chin Sci Bull 56:598–612. doi:10.1007/s11434-010-4158-4
Cardwell RD, Brancato MS, Toll J, Deforest D, Tear L (1999) Aquatic ecological risks posed by tributyltin in United States surface water: pre-1989 to 1996 data. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:211–229. doi:10.1002/etc.5620180327
Damare S, Raghukumar C, Muraleedharan UD, Raghukumar S (2006) Deep-sea fungi as a source of alkaline and cold-tolerant proteases. Enzyme Microb Tech 39:172–181. doi:10.1016/j.emzmictec.2006.03.032
Dash S, ** CL, Lee OO, Xu Y, Qian PY (2009) Antibacterial and antilarval-settlement potential and metabolite profiles of novel sponge-associated marine bacteria. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1047–1056. doi:10.1007/s10295-009-0588-x
Gao CH, Tian XP, Qi SH, Luo XM, Wang P, Zhang S (2010) Antibacterial and antilarval compounds from marine gorgonian-associated bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SCSIO 00856. J Antibiot 63:191–193. doi:10.1038/ja.2010.7
Grubbs AW, Artman III GD, Tsukamoto S, Williams RM (2007) A concise total synthesis of the notoamides C and D. Angew Chem Int Edit 119:2307–2311. doi:10.1002/ange.200604377
He F, Han Z, Peng J, Qian PY, Qi SH (2013) Antifouling indole alkaloids from two marine-derived fungi. Nat Prod Commun 8:329–332
He F, Liu Z, Yang J, Fu P, Peng J, Zhu WM, Qi SH (2012) A novel antifouling alkaloid from halotolerant fungus Penicillium sp. OUCMDZ-776. Tetrahedron Lett 53:2280–2283. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.201202.063
Kato H, Yoshida T, Tokue T, Nojiri Y, Hirota H, Ohta T, Williams RM, Tsukamoto S (2007) Notoamides A-D: prenylated indole alkaloids isolated from a marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sp. Angew Chem Int Edit 46:2254–2256. doi:10.1002/anie.200123456
Kharchenko U, Beleneva I, Dmitrieva E (2012) Antifouling potential of a marine strain, Pseudomonas aeruginosa 1242, isolated from brass microfouling in Vietnam. Int Biodeter Biodegr 75:68–75. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.05.029
Kwong TFN, Miao L, Li XC, Qian PY (2006) Novel antifouling and antimicrobial compound from a marine-derived fungus Ampelomyces sp. Mar Biotech 8:634–640. doi:10.1007/s10126-005-6146-2
Lau SCK, Mark KKW, Chen F, Qian PY (2002) Bioactivity of bacterial strains isolated from marine biofilms in Hong Kong water for the induction of larval settlement in the marine polychaete Hydroides elegans. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 226:301–310. doi:10.1007/s11274
Li XC, Bobretsov S, Xu Y, **ao X, Hung OS, Qian PY (2006) Antifouling diketopiperazines produced by a deep-sea bacterium, Streptomyces fungicidicus. Biofouling 22:187–194. doi:10.1080/0892701060780771
Ma CF, Yang HJ, Zhou X, Wu B, Zhang GZ (2012) Polymeric material for anti–biofouling. Colloid Surface B 100:31–35. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.04.045
Nong XH, Zheng ZH, Zhang XY, Lu XH, Qi SH (2013) Polyketides from a marine-fungus Xylariaceae sp. Mar Drugs 11:1718–1727. doi:10.3390/md11051718
Peng J, Zhang XY, Tu ZC, Xu XY, Qi SH (2013) Alkaloids from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus westerdijkiae DFFSCS013. J Nat Prod 76:983–987. doi:10.1021/np400132m
Piazza V, Roussis V, Garaventa F, Greco G, Smyrniotopoulos V, Vagias C, Faimali M (2011) Terpenes from the Red alga Sphaerococcus coronopifolius inhibit the settlement of barnacles. Mar Biotechnol 13:764–772. doi:10.1007/s10126-010-9337-4
Qi SH, Miao L, Gao CH, Xu Y, Zhang S, Qian PY (2010) New steroids and a new alkaloid from the gorgonian Isis minorbrachyblasta: structures, cytotoxicity, and antilarval activity. Helv Chim Acta 93:511–516
Qi SH, Xu Y, **ong HR, Qian PY, Zhang S (2009) Antifouling and antibacterial compounds from a marine fungus Cladosporium sp. F14. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:399–406. doi:10.1007/s11274-008-9904-2
Qi SH, Zhang S, Qian PY, **ao ZH, Li MY (2006) Ten new antifouling briarene diterpenoids from the South China Sea gorgonian Junceella juncea. Tetrahedron 62:9123–9130. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2006.07.049
Qi SH, Zhang S, Qian PY, Xu HH (2009) Antifeedant and antifouling briaranes from the South China Sea gorgonian Junceella juncea. Chem Nat Compd+ 45:49–54
Qi SH, Zhang S, Yang LH, Qian PY (2008) Antifouling and antibacterial compounds from the gorgonians Subergorgia suberosa and Scripearia gracillis. Nat Prod Res 22:154–166. doi:10.1080/14786410701642441
Qian PY, Lau SCK, Dahms HU, Dobretsov S, Harder T (2007) Marine biofilms as mediators of colonization by marine macroorganisms: implications for antifouling and aquaculture. Mar Biotechnol 9:399–410. doi:10.1007/s1026-007-9001-9
Qian PY, Xu Y, Fusetani N (2010) Natural products as antifouling compounds: recent progress and future perspectives. Biofouling 26:223–234. doi:10.1080/08927010903470815
Sun YL, He F, Liu KS, Zhang XY, Bao J, Wang YF, Nong XH, Xu XY, Qi SH (2013) Cytotoxic dihydrothiophen condensed chromones from marine-derived fungus Penicillium oxalicum. Planta Med 79:1474–1479. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1350805
Torres-Carcia G, Diaz M, Blasi D, Farras I, Fernandez I, Ariza X, Farras J, Lloyd-Willianms P, Roya M, Nicolas E (2012) Side chain anchoring of tryptophan to solid supports using a dihydropyranyl handle: synthesis of brevianamide F. Int J Pept Res Ther 18:7–19. doi:10.1007/s10989-011-9274-8
Witt A, Bergman J (2001) Total syntheses of the benzodiazepine alkaloids circumdatin F and circumdatin C. J Org Chem 66:2784–2788. doi:10.1021/jo00169h
Xu Y, He HP, Schulz S, Liu X, Fusetani N, **ong HR, **ao X, Qian PY (2010) Potent antifouling compounds produced by marine Streptomyces. Bioresource Technol 101:1331–1336. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.046
Xu Y, Li HL, Li XC, **ao X, Qian PY (2009) Inhibitory effects of a branched–chain fatty acid on larval settlement of the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Mar Biotechnol 11:495–504. doi:10.1007/s10126-008-9161-2
Yebra DM, Kiil S, Dam JK (2004) Antifouling technology—past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog Org Coat 50:75–104
Zhang XY, Zhang Y, Xu XY, Qi SH (2013) Diverse deep-sea fungi from the South China Sea and their antimicrobial activity. Curr Microbiol 67:525–530. doi:10.1007/s00284-013-03946-6
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial support provided by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, 2012AA092104), the regional innovation demonstration project of Guangdong Province marine economic development (GD2012-D01-002), the National Basic Research Program of China (2010CB833803), the National Marine Public Welfare Research Project of China (201305017), the Natural Science Foundation of China (41206139), and the National Key Technologies R&D Program (2011BAE06B04–03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
X.-Y. Zhang and X.-Y. Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, XY., Xu, XY., Peng, J. et al. Antifouling potentials of eight deep-sea-derived fungi from the South China Sea. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 741–748 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1412-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1412-9